Question: 1. Develop a new data structure that can work either as a stack or as a queue. That is, upon instantiation of the object, it
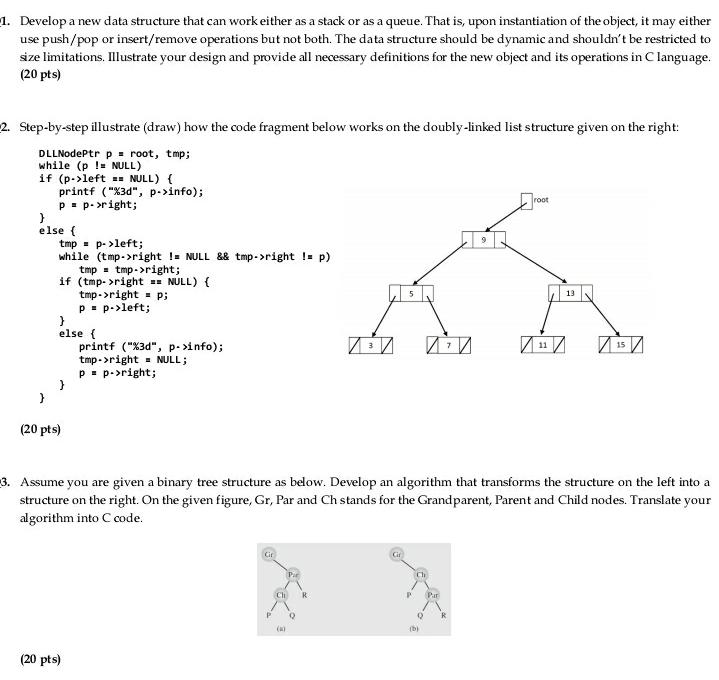
1. Develop a new data structure that can work either as a stack or as a queue. That is, upon instantiation of the object, it may either use push/pop or insert/remove operations but not both. The data structure should be dynamic and shouldn't be restricted to size limitations. Illustrate your design and provide all necessary definitions for the new object and its operations in Clanguage. (20 pts) root 2. Step-by-step illustrate (draw) how the code fragment below works on the doubly-linked list structure given on the right: DLLNodePtr p = root, tmp; while (p != NULL) if (p->left . NULL) { printf ("%3d", p->info); p. p->right; } else { tmp = p >left; while (tmp->right != NULL && tmp->right != p) tmp = tmp->right; if (tmp->right . NULL) { tmp->right = p; p. p->left; } else { printf ("%3d", p->info); tmp->right = NULL; p. p->right; ) 5 13 11 15 (20 pts) 3. Assume you are given a binary tree structure as below. Develop an algorithm that transforms the structure on the left into a structure on the right. On the given figure, Gr, Par and Ch stands for the Grandparent, Parent and Child nodes. Translate your algorithm into C code. Cir ch Ch Par P R (20 pts) 1. Develop a new data structure that can work either as a stack or as a queue. That is, upon instantiation of the object, it may either use push/pop or insert/remove operations but not both. The data structure should be dynamic and shouldn't be restricted to size limitations. Illustrate your design and provide all necessary definitions for the new object and its operations in Clanguage. (20 pts) root 2. Step-by-step illustrate (draw) how the code fragment below works on the doubly-linked list structure given on the right: DLLNodePtr p = root, tmp; while (p != NULL) if (p->left . NULL) { printf ("%3d", p->info); p. p->right; } else { tmp = p >left; while (tmp->right != NULL && tmp->right != p) tmp = tmp->right; if (tmp->right . NULL) { tmp->right = p; p. p->left; } else { printf ("%3d", p->info); tmp->right = NULL; p. p->right; ) 5 13 11 15 (20 pts) 3. Assume you are given a binary tree structure as below. Develop an algorithm that transforms the structure on the left into a structure on the right. On the given figure, Gr, Par and Ch stands for the Grandparent, Parent and Child nodes. Translate your algorithm into C code. Cir ch Ch Par P R (20 pts)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


