Question: 1. How would the answer to Problem 2-34 be modified if you were asked for a schedule of cost of goods manufactured and sold instead
1. How would the answer to Problem 2-34 be modified if you were asked for a schedule of cost of goods manufactured and sold instead of a schedule of cost of goods manufactured? Be specific. 2. Would the sales managers salary (included in marketing, distribution, and customer-service costs) be accounted for any differently if the Howell Corporation were a merchandising-sector company instead of a manufacturing-sector company? Using the flow of manufacturing costs outlined in Exhibit 2-9
(page 43), describe how the wages of an assembler in the plant would be accounted for in this manu- facturing company.
3. Plant supervisory salaries are usually regarded as manufacturing overhead costs. When might some of these costs be regarded as direct manufacturing costs? Give an example.
4. Suppose that both the direct materials used and the plant and equipment depreciation are related to the manufacture of 1 million units of product. What is the unit cost for the direct materials assigned to those units? What is the unit cost for plant and equipment depreciation? Assume that yearly plant and equipment depreciation is computed on a straight-line basis. 5. Assume that the implied cost-behavior patterns in requirement 4 persist. That is, direct material costs behave as a variable cost and plant and equipment depreciation behaves as a fixed cost. Repeat the computations in requirement 4, assuming that the costs are being predicted for the manufacture of 1.2 million units of product. How would the total costs be affected? 6. As a management accountant, explain concisely to the president why the unit costs differed in requirements 4 and 5.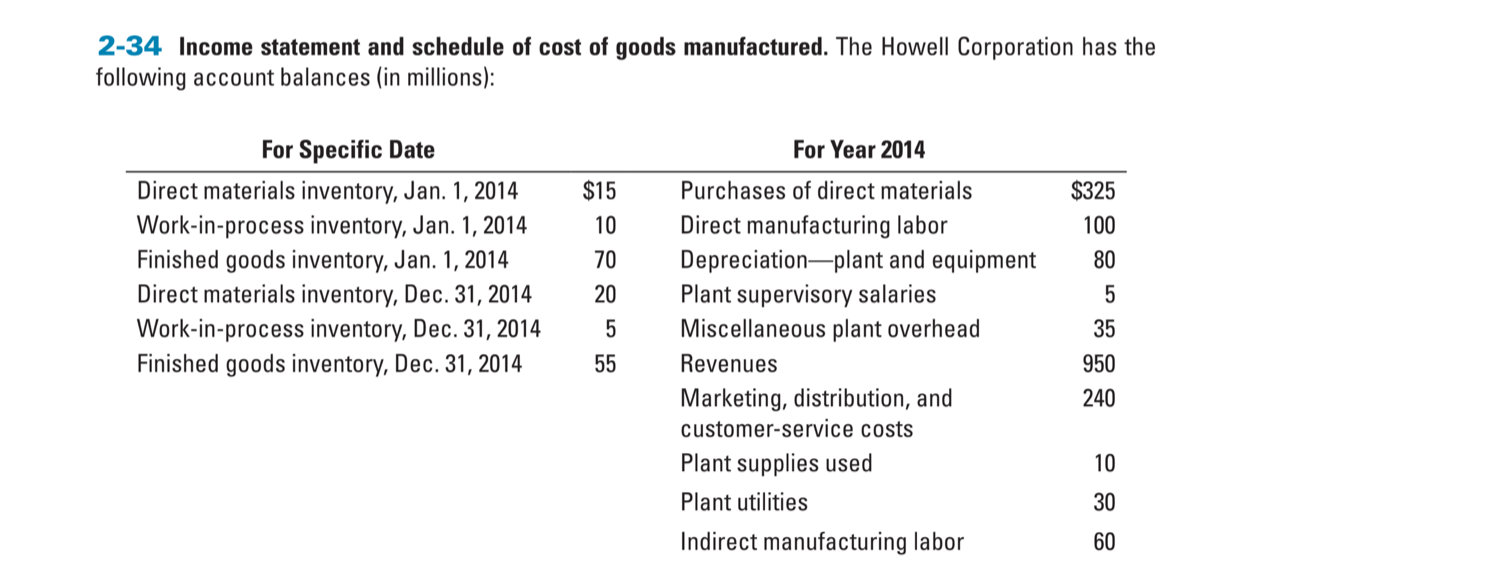
2-34 Income statement and schedule of cost of goods manufactured. The Howell Corporation has the following account balances (in millions): For Year 2014 For Specific Date Direct materials inventory, Jan. 1, 2014 Work-in-process inventory, Jan. 1, 2014 Finished goods inventory, Jan. 1, 2014 Direct materials inventory, Dec. 31, 2014 Work-in-process inventory, Dec. 31, 2014 Finished goods inventory, Dec. 31, 2014 $325 100 80 $15 10 70 20 5 55 Purchases of direct materials Direct manufacturing labor Depreciationplant and equipment Plant supervisory salaries Miscellaneous plant overhead Revenues Marketing, distribution, and customer-service costs Plant supplies used Plant utilities Indirect manufacturing labor 5 35 950 240 10 30 60
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


