Question: 1 II. PQ problem + Process Analysis + Batching (Max 55 points): This question relates to the HBS Natural Blends (NB) Case C, which follows
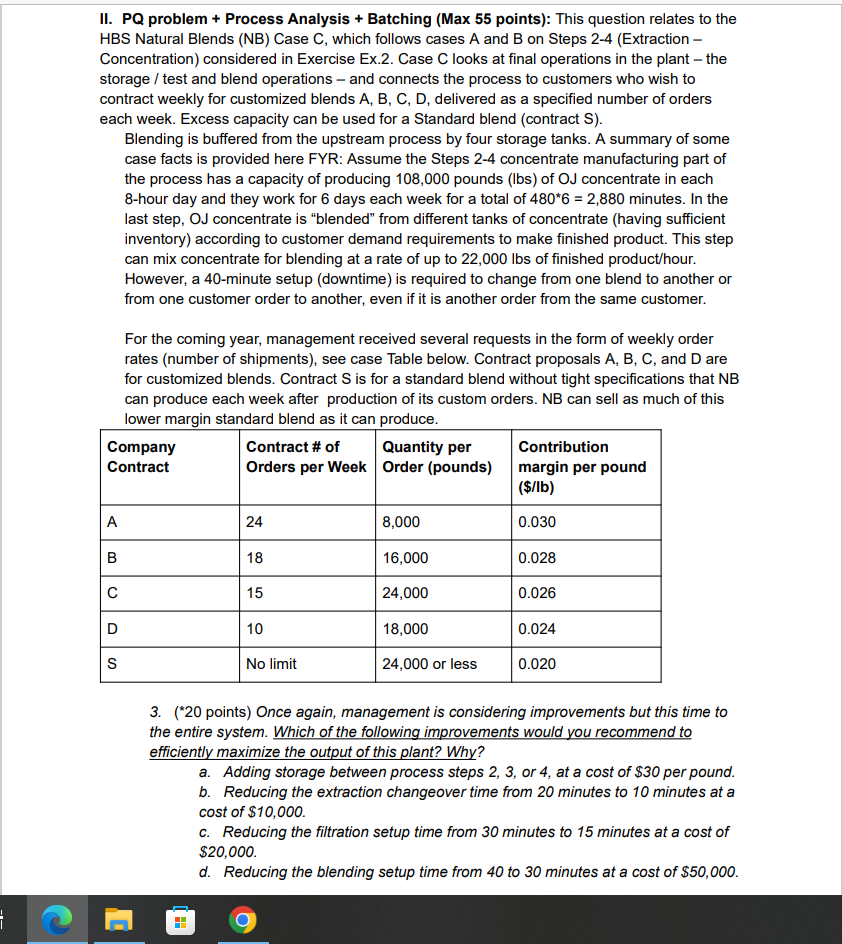
1 II. PQ problem + Process Analysis + Batching (Max 55 points): This question relates to the HBS Natural Blends (NB) Case C, which follows cases A and B on Steps 2-4 (Extraction - Concentration) considered in Exercise Ex.2. Case C looks at final operations in the plant - the storage / test and blend operations and connects the process to customers who wish to contract weekly for customized blends A, B, C, D, delivered as a specified number of orders each week. Excess capacity can be used for a Standard blend (contract S). Blending is buffered from the upstream process by four storage tanks. A summary of some case facts is provided here FYR: Assume the Steps 2-4 concentrate manufacturing part of the process has a capacity of producing 108,000 pounds (lbs) of OJ concentrate in each 8-hour day and they work for 6 days each week for a total of 480*6 = 2,880 minutes. In the last step, OJ concentrate is "blended" from different tanks of concentrate (having sufficient inventory) according to customer demand requirements to make finished product. This step can mix concentrate for blending at a rate of up to 22,000 lbs of finished product/hour. However, a 40-minute setup (downtime) is required to change from one blend to another or from one customer order to another, even if it is another order from the same customer. For the coming year, management received several requests in the form of weekly order rates (number of shipments), see case Table below. Contract proposals A, B, C, and D are for customized blends. Contract S is for a standard blend without tight specifications that NB can produce each week after production of its custom orders. NB can sell as much of this lower margin standard blend as it can produce. Company Contract # of Quantity per Order (pounds) Contract Orders per Week Contribution margin per pound ($/lb) A 24 8,000 0.030 B 18 16,000 0.028 15 24,000 0.026 D 10 18,000 0.024 S No limit 24,000 or less 0.020 3. (*20 points) Once again, management is considering improvements but this time to the entire system. Which of the following improvements would you recommend to efficiently maximize the output of this plant? Why? a. Adding storage between process steps 2, 3, or 4, at a cost of $30 per pound. b. Reducing the extraction changeover time from 20 minutes to 10 minutes at a cost of $10,000. c. Reducing the filtration setup time from 30 minutes to 15 minutes at a cost of $20,000. d. Reducing the blending setup time from 40 to 30 minutes at a cost of $50,000. 1 II. PQ problem + Process Analysis + Batching (Max 55 points): This question relates to the HBS Natural Blends (NB) Case C, which follows cases A and B on Steps 2-4 (Extraction - Concentration) considered in Exercise Ex.2. Case C looks at final operations in the plant - the storage / test and blend operations and connects the process to customers who wish to contract weekly for customized blends A, B, C, D, delivered as a specified number of orders each week. Excess capacity can be used for a Standard blend (contract S). Blending is buffered from the upstream process by four storage tanks. A summary of some case facts is provided here FYR: Assume the Steps 2-4 concentrate manufacturing part of the process has a capacity of producing 108,000 pounds (lbs) of OJ concentrate in each 8-hour day and they work for 6 days each week for a total of 480*6 = 2,880 minutes. In the last step, OJ concentrate is "blended" from different tanks of concentrate (having sufficient inventory) according to customer demand requirements to make finished product. This step can mix concentrate for blending at a rate of up to 22,000 lbs of finished product/hour. However, a 40-minute setup (downtime) is required to change from one blend to another or from one customer order to another, even if it is another order from the same customer. For the coming year, management received several requests in the form of weekly order rates (number of shipments), see case Table below. Contract proposals A, B, C, and D are for customized blends. Contract S is for a standard blend without tight specifications that NB can produce each week after production of its custom orders. NB can sell as much of this lower margin standard blend as it can produce. Company Contract # of Quantity per Order (pounds) Contract Orders per Week Contribution margin per pound ($/lb) A 24 8,000 0.030 B 18 16,000 0.028 15 24,000 0.026 D 10 18,000 0.024 S No limit 24,000 or less 0.020 3. (*20 points) Once again, management is considering improvements but this time to the entire system. Which of the following improvements would you recommend to efficiently maximize the output of this plant? Why? a. Adding storage between process steps 2, 3, or 4, at a cost of $30 per pound. b. Reducing the extraction changeover time from 20 minutes to 10 minutes at a cost of $10,000. c. Reducing the filtration setup time from 30 minutes to 15 minutes at a cost of $20,000. d. Reducing the blending setup time from 40 to 30 minutes at a cost of $50,000





