Question: 1. Is this statement a possible explanation for why the firm hasnt paid a dividend yet? No Yes 2. What type of bonds are these?
1. 
Is this statement a possible explanation for why the firm hasnt paid a dividend yet?
No
Yes
2.

What type of bonds are these?
a. Municipal bonds
b. Corporate bonds
c. Government bonds
3.  4.
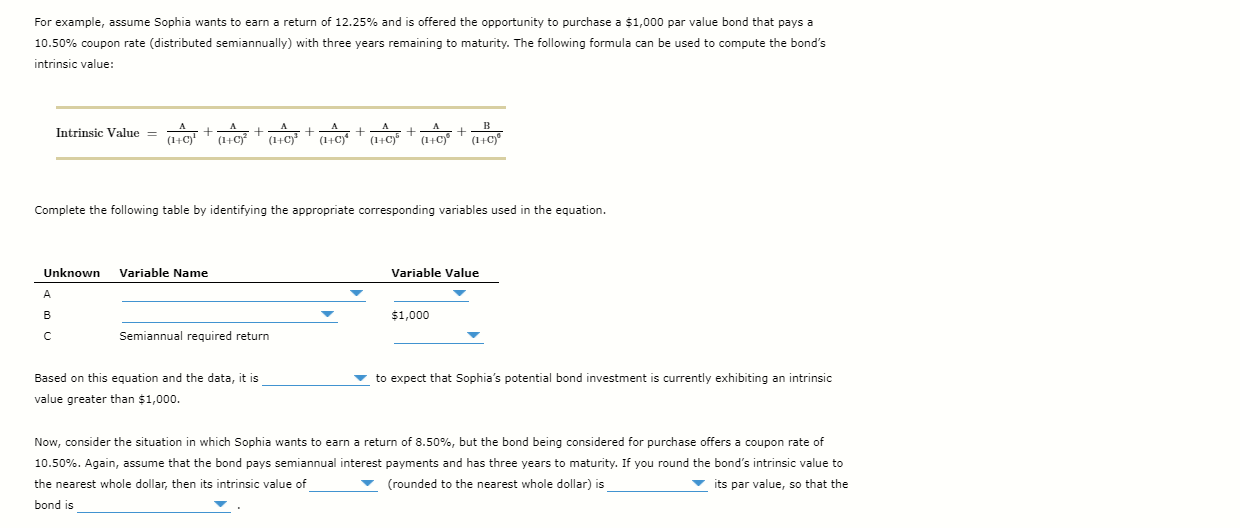
4. 
Given your computation and conclusions, which of the following statements is true?
a. When the coupon rate is greater than Sophias required return, the bonds intrinsic value will be less than its par value.
b. A bond should trade at a par when the coupon rate is greater than Sophias required return.
c. When the coupon rate is greater than Sophias required return, the bond should trade at a premium.
d. When the coupon rate is greater than Sophias required return, the bond should trade at a discount.
Goodwin Technologies, a relatively young company, has been wildly successful but has yet to pay a dividend. An analyst forecasts that Goodwin is likely to pay its first dividend three years from now. She expects Goodwin to pay a $4.00000 dividend at that time (D3 = $4.00000) and believes that the dividend will grow by 20.80000% for the following two years (D4 and Ds). However, after the fifth year, she expects Goodwin's dividend to grow at a constant rate of 4.02000% per year. A-Z Goodwin's required return is 13.40000%. Fill in the following chart to determine Goodwin's horizon value at the horizon date (when constant growth begins) and the current intrinsic value. To increase the accuracy of your calculations, do not round your intermediate calculations, but round all final answers to two decimal places. Term Value Horizon value Current intrinsic value Assuming that the markets are in equilibrium, Goodwin's current expected dividend yield is , and Goodwin's capital gains yield is Goodwin has been very successful, but it hasn't paid a dividend yet. It circulates a report to its key investors containing the following statement: Goodwin's investment opportunities are poor. Fixed-income securities consist of debt instruments and preferred stock. Bonds are debt securities in which a borrower promises to pay a specified interest rate and principal at a future date. A-Z The entity that promises to make the interest and maturity payments for a bond issue is called the Based on the information given in the following statement, answer the questions that follow: In July 2009, Walmart sold 100 billion yen of five-year samurai bonds. Lead managers in the deal were Mizuho Securities, BNP Paribas, and Mitsubishi UFJ Securities. Who is the issuer of the bonds? O Walmart O BNP Paribas O Mitsubishi UF] Securities The process of bond valuation is based on the fundamental concept that the current price of a security can be determined by calculating the present value of the cash flows that the security will generate in the future. There is a consistent and predictable relationship between a bond's coupon rate, its par value, a bondholder's required return, and the bond's resulting intrinsic value. Trading at a discount, trading at a premium, and trading at par refer to particular relationships between a bond's intrinsic value and its par value. This also results from the relationship between a bond's coupon rate and a bondholder's required rate of return. A-Z pay, and a bondholder's required return Remember, a bond's coupon rate partially determines the interest-based return that a bond reflects the return that a bondholder to receive from a given investment. The mathematics of bond valuation imply a predictable relationship between the bond's coupon rate, the bondholder's required return, the bond's par value, and its intrinsic value. These relationships can be summarized as follows: When the bond's coupon rate is equal to the bondholder's required return, the bond's intrinsic value will equal its par value, and the bond will trade at par. When the bond's coupon rate is greater than the bondholder's required return, the bond's intrinsic value will its par value, and the bond will trade at a premium. When the bond's coupon rate is less than the bondholder's required return, the bond's intrinsic value will be less than its par value, and the bond will trade at For example, assume Sophia wants to earn a return of 12.25% and is offered the opportunity to purchase a $1,000 par value bond that pays a 10.50% coupon rate (distributed semiannually) with three years remaining to maturity. The following formula can be used to compute the bond's intrinsic value: Intrinsic Value = 0 +0,1 + 0 + 0 + + (c* + (1+0) (1+0) (1+0) Complete the following table by identifying the appropriate corresponding variables used in the equation. Unknown Variable Name Variable Value A B $1,000 C Semiannual required return to expect that Sophia's potential bond investment is currently exhibiting an intrinsic Based on this equation and the data, it is value greater than $1,000. Now, consider the situation in which Sophia wants to earn a return of 8.50%, but the bond being considered for purchase offers a coupon rate of 10.50%. Again, assume that the bond pays semiannual interest payments and has three years to maturity. If you round bond's intrinsic value to the nearest whole dollar, then its intrinsic value of (rounded to the nearest whole dollar) is its par value, so that the bond is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


