Question: 1. Let G = (V, E, w) be a directed graph with weighted edges w : E R; edge weights could be positive, negative, or
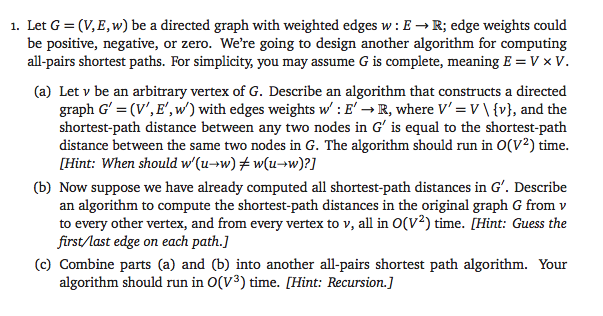
1. Let G = (V, E, w) be a directed graph with weighted edges w : E R; edge weights could be positive, negative, or zero. We're going to design another algorithm for computing all-pairs shortest paths. For simplicity, you may assume G is complete, meaning E = V V (a) Let v be an arbitrary vertex of G. Describe an algorithm that constructs a directed graph G (V,E', w) with edges weights w':E-R,where V'-V\ (v), and the shortest-path distance between any two nodes in G is equal to the shortest-path distance between the same two nodes in G. The algorithm should run in O(V2) time [Hint: When should w'(u-w-w(u-w)?] (b) Now suppose we have already computed all shortest-path distances in G'. Describe an algorithm to compute the shortest-path distances in the original graph G fromv to every other vertex, and from every vertex to v, all in O(V2) time. [Hint: Guess the first/last edge on each path.] (c) Combine parts (a) and (b) into another all-pairs shortest path algorithm. Your algorithm should run in O(V3) time. [Hint: Recursion.] 1. Let G = (V, E, w) be a directed graph with weighted edges w : E R; edge weights could be positive, negative, or zero. We're going to design another algorithm for computing all-pairs shortest paths. For simplicity, you may assume G is complete, meaning E = V V (a) Let v be an arbitrary vertex of G. Describe an algorithm that constructs a directed graph G (V,E', w) with edges weights w':E-R,where V'-V\ (v), and the shortest-path distance between any two nodes in G is equal to the shortest-path distance between the same two nodes in G. The algorithm should run in O(V2) time [Hint: When should w'(u-w-w(u-w)?] (b) Now suppose we have already computed all shortest-path distances in G'. Describe an algorithm to compute the shortest-path distances in the original graph G fromv to every other vertex, and from every vertex to v, all in O(V2) time. [Hint: Guess the first/last edge on each path.] (c) Combine parts (a) and (b) into another all-pairs shortest path algorithm. Your algorithm should run in O(V3) time. [Hint: Recursion.]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


