Question: 1 Net foreign borrower The United Suites us a persistent balance of trade and current account delict and uses fortign capital to fhance the difference
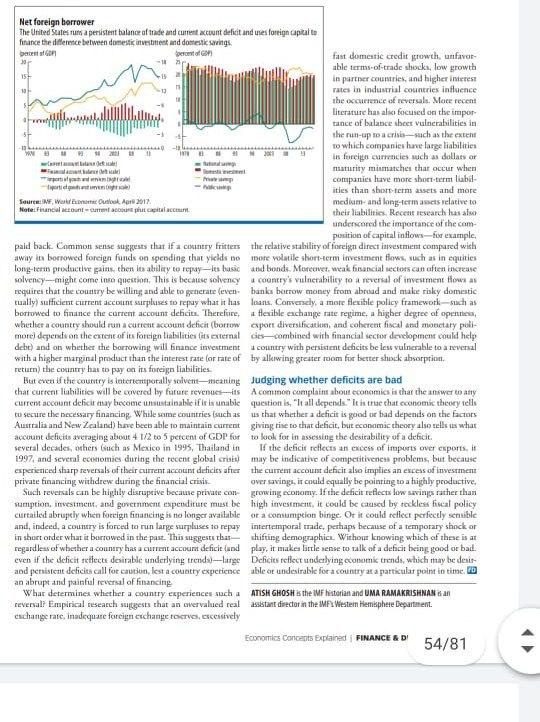
1 Net foreign borrower The United Suites us a persistent balance of trade and current account delict and uses fortign capital to fhance the difference between domestic estent and dontest savings bates on percent of fast domestic credit growth, unfavor 30 -# able terms of trade shocks, low growth 15- 2 in partner countries, and higher interest rates in industrial countries influence the occurrence of reversals. More recent Literature has also focused on the impor tance of balance sheet vulnerabilities in the run-up macro-such as the extent to which companies have large liabilities W! 120 is foreign currencies such as dollars or maturity mimmatches that occur when companies have more short-term lab- - penighet ities than short-term assets and more Source: WF, W Olook. Ars 2017 medium- and long-term asas relative to Notencial contractul their abilities. Recent research has also underscored the importance of the com- position of capital inflows For example, paid back. Common sense suggests that if a country fritters the relative stability of foreign direct investment compared with away in borrowed foreign funds on spending that yields no more wolatile short-term investment flows, such as in equities long-term productive gains then los ablay to repay-lus basic and bonds. Moreover, weak hinancial sectors can often bricease solvency--might come in question. This is because solvency country's vulnerability to a reversal of investment flow as requires that the country be willing and able to generate (even banks borrow money from abroad and make risky domestic tually sufficient current account surpluses to repay what it has loans Conversely, a meste flexible policy framework such as borrowed to finance the current account deficits. Therefore, a Hexible exchange rate regime, a higher degree of openen wherlict a country should run a current account deficit (borrow espor diversificate and coherent fiscal and monctary poll- more depends on the extent of its foreign liabilities its external des combined with financial sector development could help debt) and on whether the borrowing will finance investment country with persistent deficits be less vulnerable to a reversal with a higher marginal product than the Interest rate for rate of by allowing greater room for better shock absorptm. return the country has to pay on its foreign liabilities But even if the country is latertentporally solvent-maning Judging whether deficits are bad char current liabilities will be covered by future revenues A common complain about economics a thar the inswer to any current account deficit may become un talable if it is unable question is, "It all spends." It is true that economic theory tell to secure the necessary financing. While some countries such as us that whether a deficit is good or bad depends on the factors Australia and New Zealand) have been able to maintain current giving tise to that deficit, but economic theory also tells us what account deficits averaging about 4 1/2 to 5 percent of GDP for to look for in assessing the desirability of a deficit. several decades, others Guch as Mexico in 1995, Thailand in If the deficit reflects an excess of imports over exports. It 1997, and several comies during the recent global crue) may be indicative of competitiveness problems, but because experienced sharp reversals of their current account deficies after the currem account deficit also implies an excess of investment private financing withdrew during the financial crisis over saving, it could equally be pointing to a highly productive Such reversals can be highly disruptive because private com growing economy. If the decit reflects low savings rather than mamption, investment, and government expenditure must be high investment, it could be caused by reckles fiscal policy curtailed abruptly when foreign Gancing is to longer available or a consumption binge. Ot it could reflect perfectly scauible and, indeed, a country is forced to run large surpluses to repay intertemporal trade, perhaps because of a temporary shock or in short order what it borrowed in the past. This suggests that shifting demographic. Without knowing which of these is at regardless of whether a counary has a current account deficit und play, it makes little sense to talk of a deficit being good or bad. even if the deficit reiecte desirable underlying trends) ---Surge Deficits reflect underlying economik trends, which may be derit and persistent delicis call for caution, lest a country experience able ce undesirable for a country at a particular point in time.ca an abrupt and painful reversal of financing Whar determine whether a country experiences such a ATISH GHOSH is the MF historian and UMA RAMAKRISHNANG reversal Empirical research suggests that an overvalued real assistant director in the MFX Western Hemisphere Department change rate, inadequate foreign exchange to vel, excentively Economics Concerts Explained FINANCE & DI 54/81 1 Net foreign borrower The United Suites us a persistent balance of trade and current account delict and uses fortign capital to fhance the difference between domestic estent and dontest savings bates on percent of fast domestic credit growth, unfavor 30 -# able terms of trade shocks, low growth 15- 2 in partner countries, and higher interest rates in industrial countries influence the occurrence of reversals. More recent Literature has also focused on the impor tance of balance sheet vulnerabilities in the run-up macro-such as the extent to which companies have large liabilities W! 120 is foreign currencies such as dollars or maturity mimmatches that occur when companies have more short-term lab- - penighet ities than short-term assets and more Source: WF, W Olook. Ars 2017 medium- and long-term asas relative to Notencial contractul their abilities. Recent research has also underscored the importance of the com- position of capital inflows For example, paid back. Common sense suggests that if a country fritters the relative stability of foreign direct investment compared with away in borrowed foreign funds on spending that yields no more wolatile short-term investment flows, such as in equities long-term productive gains then los ablay to repay-lus basic and bonds. Moreover, weak hinancial sectors can often bricease solvency--might come in question. This is because solvency country's vulnerability to a reversal of investment flow as requires that the country be willing and able to generate (even banks borrow money from abroad and make risky domestic tually sufficient current account surpluses to repay what it has loans Conversely, a meste flexible policy framework such as borrowed to finance the current account deficits. Therefore, a Hexible exchange rate regime, a higher degree of openen wherlict a country should run a current account deficit (borrow espor diversificate and coherent fiscal and monctary poll- more depends on the extent of its foreign liabilities its external des combined with financial sector development could help debt) and on whether the borrowing will finance investment country with persistent deficits be less vulnerable to a reversal with a higher marginal product than the Interest rate for rate of by allowing greater room for better shock absorptm. return the country has to pay on its foreign liabilities But even if the country is latertentporally solvent-maning Judging whether deficits are bad char current liabilities will be covered by future revenues A common complain about economics a thar the inswer to any current account deficit may become un talable if it is unable question is, "It all spends." It is true that economic theory tell to secure the necessary financing. While some countries such as us that whether a deficit is good or bad depends on the factors Australia and New Zealand) have been able to maintain current giving tise to that deficit, but economic theory also tells us what account deficits averaging about 4 1/2 to 5 percent of GDP for to look for in assessing the desirability of a deficit. several decades, others Guch as Mexico in 1995, Thailand in If the deficit reflects an excess of imports over exports. It 1997, and several comies during the recent global crue) may be indicative of competitiveness problems, but because experienced sharp reversals of their current account deficies after the currem account deficit also implies an excess of investment private financing withdrew during the financial crisis over saving, it could equally be pointing to a highly productive Such reversals can be highly disruptive because private com growing economy. If the decit reflects low savings rather than mamption, investment, and government expenditure must be high investment, it could be caused by reckles fiscal policy curtailed abruptly when foreign Gancing is to longer available or a consumption binge. Ot it could reflect perfectly scauible and, indeed, a country is forced to run large surpluses to repay intertemporal trade, perhaps because of a temporary shock or in short order what it borrowed in the past. This suggests that shifting demographic. Without knowing which of these is at regardless of whether a counary has a current account deficit und play, it makes little sense to talk of a deficit being good or bad. even if the deficit reiecte desirable underlying trends) ---Surge Deficits reflect underlying economik trends, which may be derit and persistent delicis call for caution, lest a country experience able ce undesirable for a country at a particular point in time.ca an abrupt and painful reversal of financing Whar determine whether a country experiences such a ATISH GHOSH is the MF historian and UMA RAMAKRISHNANG reversal Empirical research suggests that an overvalued real assistant director in the MFX Western Hemisphere Department change rate, inadequate foreign exchange to vel, excentively Economics Concerts Explained FINANCE & DI 54/81





