Question: = 1. Open Bank Machine.java and read over the code in its main() method. 2. The program produces two compilation errors, one when invoking method



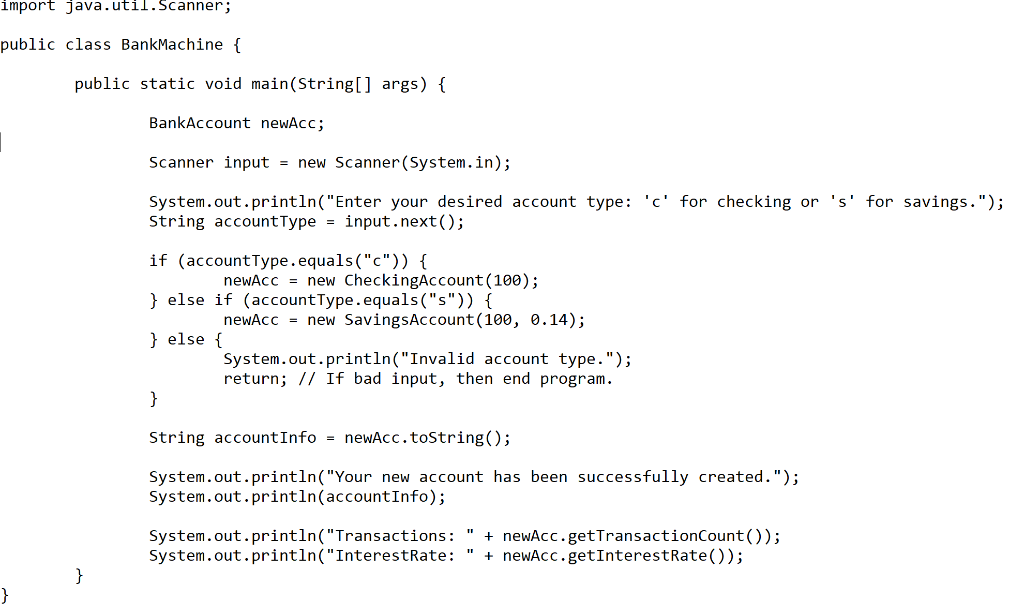
= 1. Open Bank Machine.java and read over the code in its main() method. 2. The program produces two compilation errors, one when invoking method getTransactionCount() and the other when invoking getInterestRate(). Explain why the compiler issues these two errors. Write your answer in AnswersLab3.txt. 3. In the statement String accountInfo newAcc. tostring(); just by looking at the code can you tell whether the method toString() being invoked is from SavingsAccount or from CheckingAccount? Explain your answer and write it in AnswersLab3.txt. 4. Modify the code so that newAcc.getTransactioncount() is invoked only if newAcc references an object of the class CheckingAccount, and newAcc.getInterestRate() is invoked only if newAcc references an object of the class SavingsAccount. 5. Run the program and verify that it works correctly for both account types (run the program and type either 'c' or 's' so the program prints a message indicting that an account has been created and it also prints information about the account including either the interest rate or the number of transactions). * BankAccount.java: This class is a simple model of a general banking account, to be used for understanding inheritance. * @author From the book "Big Java" by Cay Horstmann public class BankAccount { /** Attribute: Keeps track of current balance */ private double balance; /** Creates a new instance of BankAccount * @param initialAmount initial amount deposited into new account */ public BankAccount(double initialAmount) { balance = initialAmount; } /** Accessor method for balance * @return current balance */ public double getBalance() { return balance; } /** Deposit money into account * @param amount amount to be deposited */ public void deposit (double amount) { balance = balance + amount; } /** Withdraw money from account * @param amount amount to be withdrawn */ public void withdraw(double amount) { if (amount FREE_TRANSACTIONS) { double fees = TRANSACTION_FEE * (transactionCount - FREE_TRANSACTIONS); super.withdraw(fees); } transactionCount = 0; } /** Method to represent checking account as a String for display purposes * @return String representation of checking account */ public String toString() { return ("CheckingAccount: balance $" + getBalance() + ", transactions " + transactionCount); } } import java.util.Scanner; public class BankMachine { public static void main(String[] args) { BankAccount newACC; Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter your desired account type: 'c' for checking or 's' for savings."); String accountType = input.next(); if (accountType.equals("")) { newAcc = new CheckingAccount(100); } else if (accountType.equals("s")) { newAcc = new SavingsAccount(100, 0.14); } else { System.out.println("Invalid account type."); return; // If bad input, then end program. } String accountInfo = newAcc.toString(); System.out.println("Your new account has been successfully created."); System.out.println(accountInfo); System.out.println("Transactions : " + newAcc.getTransactionCount()); System.out.println("InterestRate: " + newAcc.getInterestRate()); } }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


