Question: A man walks into a pet store just before closing and tells the sales clerk, I want a male cat, neutered, either white or

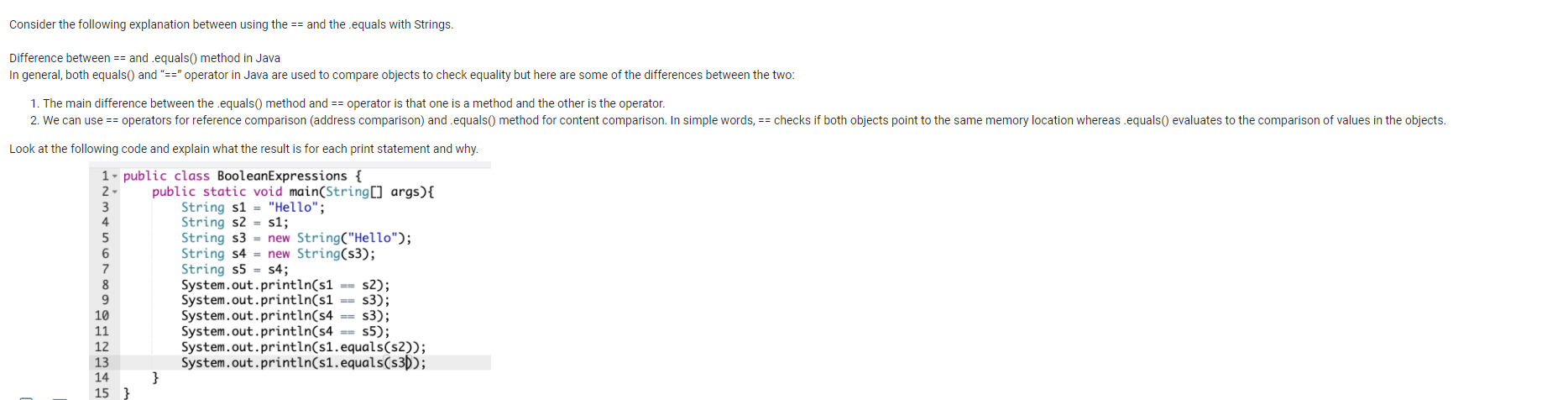
A man walks into a pet store just before closing and tells the sales clerk, "I want a male cat, neutered, either white or tan; or a spayed female cat, any color but white; or I'll take any cat you have as long as it is black." The sales clerk puts down her computer science notes, grabs a piece of paper and a pencil, and responds, "So you want a cat from the class of cats represented by the following expression." (M & & N && (W || T)) || (F & & N && !W)) || B "Yes!" The man replies. "That's exactly what I want. How did you do that?" Boolean algebra can be used to solve so many different problems," she says. "That's amazing," he says. "But do you have a cat to meet my criteria?" The sales clerk replies, "Well, we have three cats available. Why don't you see if one meets your criteria using my Boolean expression? If you get it right I'll knock 10% off the price. Otherwise, you clean one of the hamster cages The man is a little surprised by this offer, but agrees. They look at the first cat: an unneutered tan male. The second cat is a spayed gray female. The third cat is a spayed white female. "I'll take cat number two," the man says rather confidently. "If I have chosen correctly, I will name it Boolie!" Did he choose the right cat and get his discount, or did he have to clean a cage and make another choice? Why? Be sure to explain the logic. Consider the following explanation between using the == and the .equals with Strings. Difference between == and .equals() method in Java In general, both equals() and "==" operator in Java are used to compare objects to check equality but here are some of the differences between the two: 1. The main difference between the .equals() method and == operator is that one is a method and the other is the operator. 2. We can use == operators for reference comparison (address comparison) and .equals() method for content comparison. In simple words, == checks if both objects point to the same memory location whereas .equals() evaluates to the comparison of values in the objects. Look at the following code and explain what the result is for each print statement and why. 1 public class Boolean Expressions { 2- 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 } public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 "Hello"; String s2 s1; String s3= new String("Hello"); String s4= new String(s); String s5 s4; System.out.println(s1 ==S2); System.out.println(s1 s3); System.out.println(s4 = s3); System.out.println(s4 == s5); } System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
In the scenario described with the man choosing a cat from the pet store he did not choose the right cat Lets break down the criteria and compare them ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


