Question: 1. Question 1: Review exercise 4.2 and the solution below. Do you agree with solution? Explain why or why not? Exercise 4.2. (P.76) Simplify the
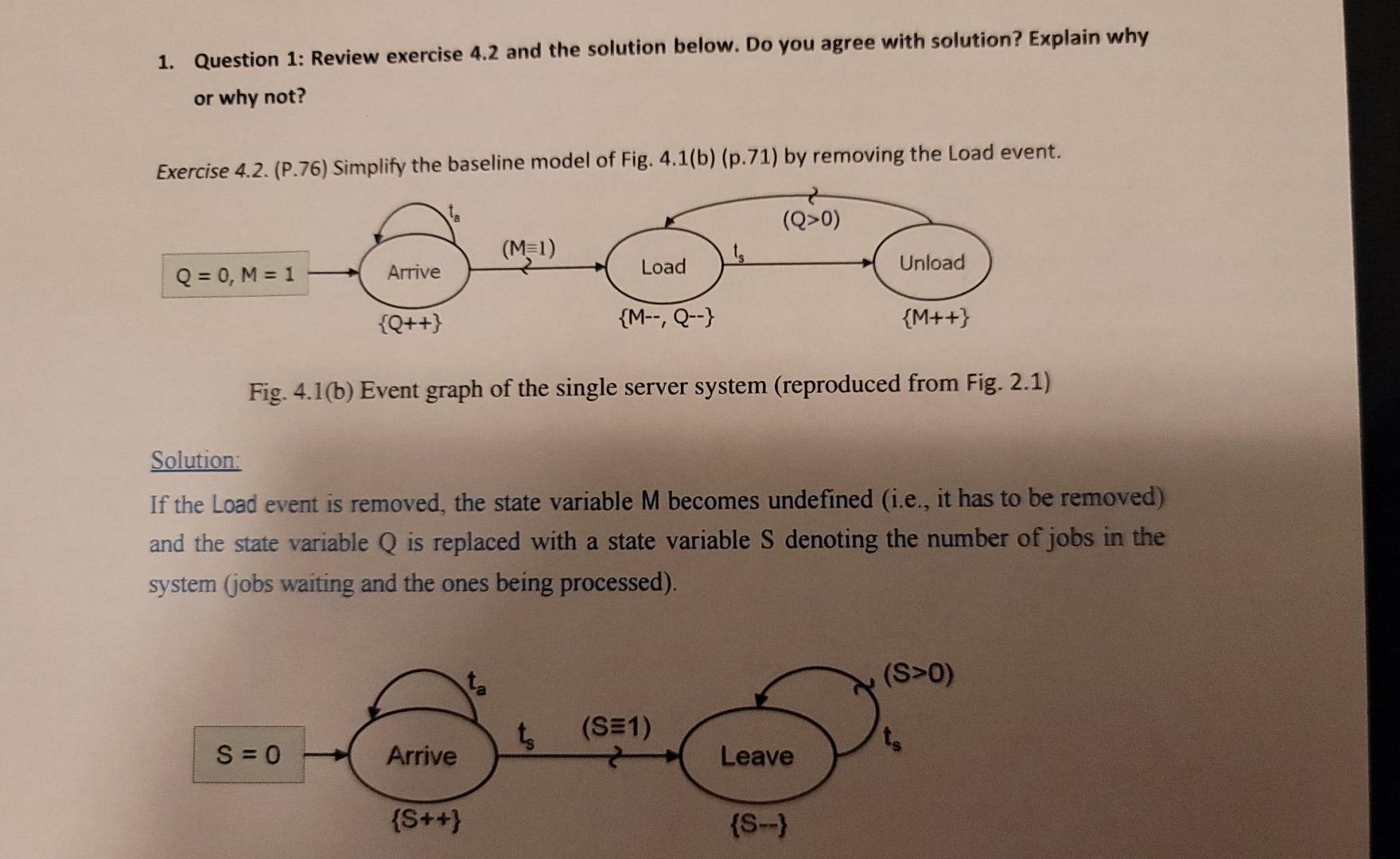
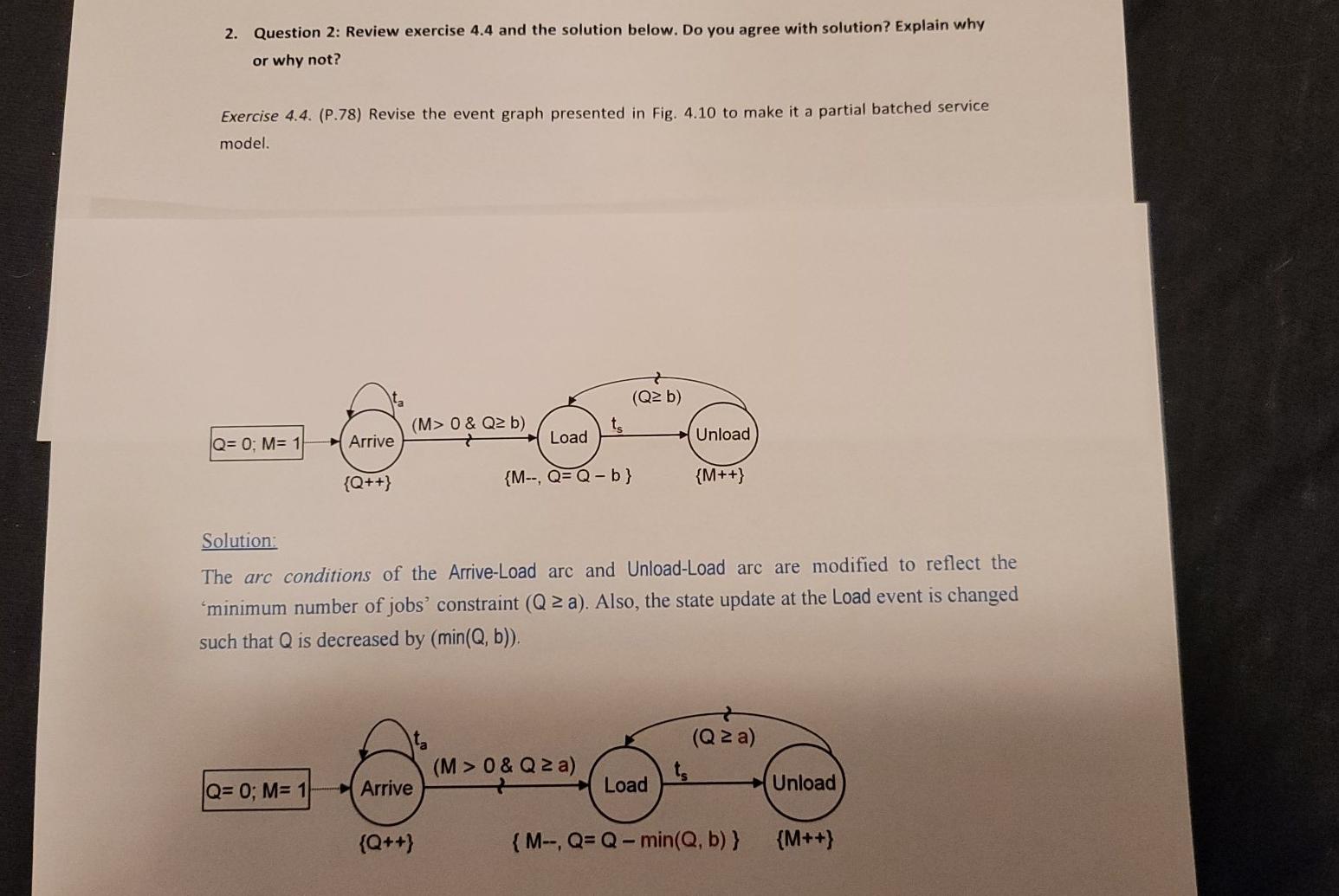
1. Question 1: Review exercise 4.2 and the solution below. Do you agree with solution? Explain why or why not? Exercise 4.2. (P.76) Simplify the baseline model of Fig. 4.1(b) (p.71) by removing the Load event. (Q>0) (M=1) Q = 0, M = 1 Unload Arrive Load {Q++} {M--, Q--} {M++} Fig. 4.1(b) Event graph of the single server system (reproduced from Fig. 2.1) Solution: If the Load event is removed, the state variable M becomes undefined (i.e., it has to be removed) and the state variable Q is replaced with a state variable S denoting the number of jobs in the system (jobs waiting and the ones being processed). (S>0) ts (SE1) S = 0 Arrive Leave {S++) {S--) 2. Question 2: Review exercise 4.4 and the solution below. Do you agree with solution? Explain why or why not? Exercise 4.4. (P.78) Revise the event graph presented in Fig. 4.10 to make it a partial batched service model. (Q2 b) (M>0 & Q2 b) ts Q= 0; M= 1 Arrive Load Unload {Q++} {M--, Q=Q-b} {M++} Solution: The arc conditions of the Arrive-Load arc and Unload-Load arc are modified to reflect the minimum number of jobs' constraint (Q 2 a). Also, the state update at the Load event is changed such that Q is decreased by (min(Q, b)). (M >0 & Q2 a) (Q2a) ts Q= 0; M= 1 Arrive Load Unload Unload {Q++) {M-, Q= Q - min(Q, b) } {M++) 1. Question 1: Review exercise 4.2 and the solution below. Do you agree with solution? Explain why or why not? Exercise 4.2. (P.76) Simplify the baseline model of Fig. 4.1(b) (p.71) by removing the Load event. (Q>0) (M=1) Q = 0, M = 1 Unload Arrive Load {Q++} {M--, Q--} {M++} Fig. 4.1(b) Event graph of the single server system (reproduced from Fig. 2.1) Solution: If the Load event is removed, the state variable M becomes undefined (i.e., it has to be removed) and the state variable Q is replaced with a state variable S denoting the number of jobs in the system (jobs waiting and the ones being processed). (S>0) ts (SE1) S = 0 Arrive Leave {S++) {S--) 2. Question 2: Review exercise 4.4 and the solution below. Do you agree with solution? Explain why or why not? Exercise 4.4. (P.78) Revise the event graph presented in Fig. 4.10 to make it a partial batched service model. (Q2 b) (M>0 & Q2 b) ts Q= 0; M= 1 Arrive Load Unload {Q++} {M--, Q=Q-b} {M++} Solution: The arc conditions of the Arrive-Load arc and Unload-Load arc are modified to reflect the minimum number of jobs' constraint (Q 2 a). Also, the state update at the Load event is changed such that Q is decreased by (min(Q, b)). (M >0 & Q2 a) (Q2a) ts Q= 0; M= 1 Arrive Load Unload Unload {Q++) {M-, Q= Q - min(Q, b) } {M++)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


