Question: 1. Read the case - What are the issues underlying this case? Fully explain at least 3-4 of them. The key issues refer to the

1. Read the case - What are the issues underlying this case? Fully explain at least 3-4 of them.
The key "issues" refer to the concerns, problems, decisions, challenges, or opportunities faced by the major actor in the case.
2. Read at least 3-4 current articles about the company or industry mentioned in the case. What are the challenges or issues facing the company today (within the last 15-18 months)?
3. For three of the issues you have identified:
a. What key concepts/theories from your major are influencing your assertion that this is an issue? Be sure and define the concept that you are applying. What assumptions underlie these concepts and how do they apply in this case?
b. What evidence (e.g., data, information, etc.) do you have to support that this is indeed an issue [you may use the data you present in your case analysis to complete this part of the paper]? If your evidence is based on a theoretical prediction (using existing theory), identify the theory and the most likely outcome.
c. What can you infer about the issue based on the evidence you have provided? What are the implications and possible consequences?
4. Recommend what will effectively address each challenge/issue and justify your recommendation (please provide as much detail as possible). Why does your recommendation make sense?
Briefly explain how your recommendation addresses the most pertinent issues and why your recommendation makes sense given the issues in the case. What are the potential positive and negative implications of your recommendation?
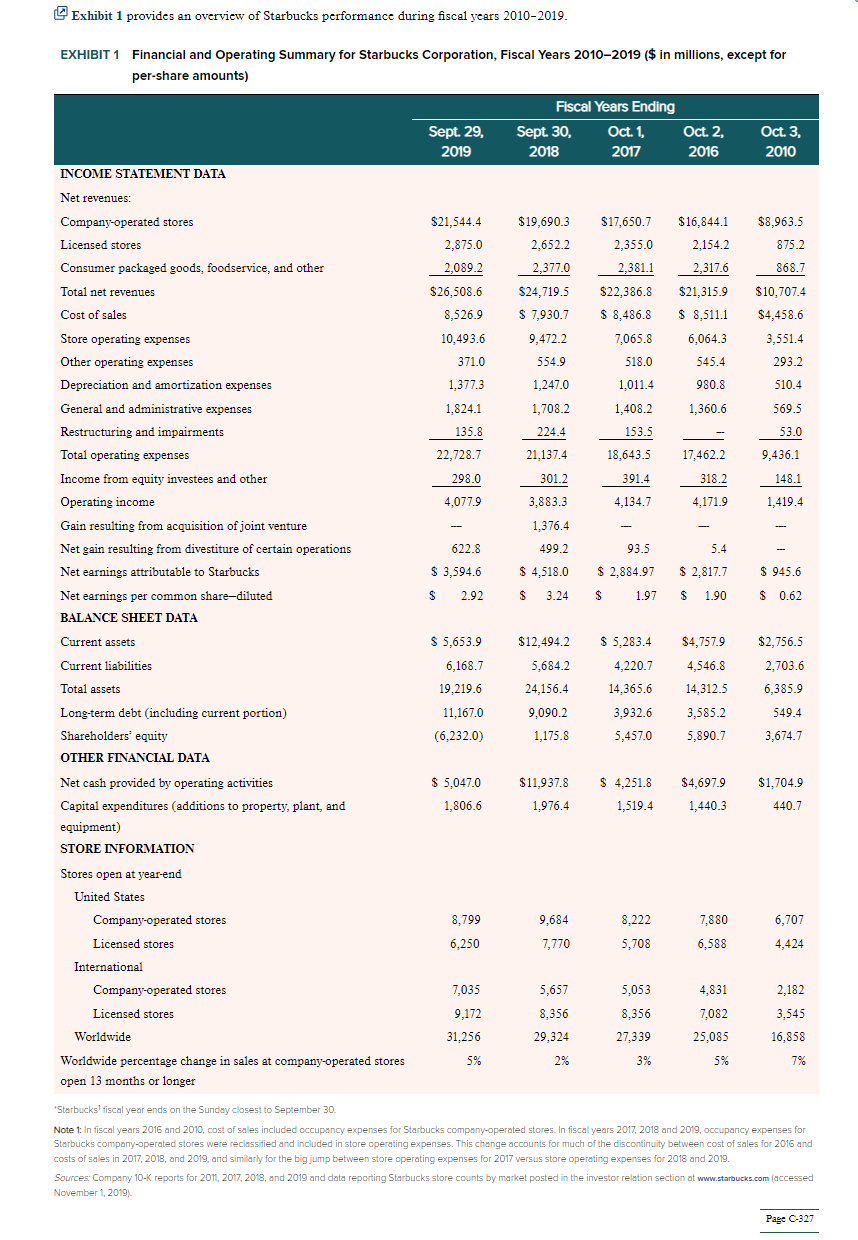
Starbucks in 2020: Is the Company on Track to Achieve Attractive Growth and Operational Excellence? Arthur A. Thompson The Uaiverity of Alabama Since its founding in 1987 as a modest rine-store operation in Seattle, Washington, Starbucks had become the premier roaster, markster, and retailer of specialty coffees in the world, with just over 32,000 store locations in 78 countries as of April 2020 and annual sales of $26.5 billion in fiscal year 2019 , ending September 30 , 2019. In addition to its flagship Starbucks brand coffees and coffee beverages, Starbuchs' other brands and products included Starbucks Reserve blends of coffee, Teavana teas, Seattle's Best Coffee, Evolution Fresh juices and smoothies, Ethos bottled waters, Torrefarione Italia Coffee, and Princi bakery products. Starbucks stores also sold baked pastries, cold and hot sandwiches, salads, salad and grain bow1s, catmeal, yogurt parfaits and fruit cups purchased from a variaty of local, regional, and national suppliers. In January 2017, then CEO and company founder Howard Starbucks launched a somewhat grandiose strategic initiative to inject more innovation and fresh approaches into the company's operations and to spur growth: - Open 20-30 Starbucks Reserve" Roasteries and Tasting Rooms, which would showcase the theater of coffee roasting and brewing in a big, multi-level stores with amazing decorations, seating for upwards of a thousand patrons, multiple types of coffee bars with elaborate menus of innovative coffee beverages and interesting food selections, areas where friends could gather at community tables or in lounge areas with fireplaces, a mixology bar serving traditional ltalian cocktails, multiple dining venues, and an upscale Princi bakery where patrons could watch chefs preparing fresh-baked artisanal Italian breads, sandwiches, and pastries being served to diners. Going into 2020, Roasteries had been opened in Seattle, Shanghai, Milan, New York, Chicago, and Tokyo-all attracted local coffee enthusiasts, partiers, nearby shoppers curious to see what the Brewery offered, and visiting sightseers looking to enjoy a very different kind of Starbucks experience. - Open 1,000 Starbucks Reserve stores worldwide to bring premium experiences to customers and promote the company's recently-introduced Starbucks Reserve'" coffees; these locations were to offer a more intimate small-lot coffee experience and gave customers a chance to chat with a barista about all things coffee. The menu at Starbucks Reserve stores was to consist of handcrafted hot and cold Starbucks Reserve" coffee beverages, hot and cold teas, ice cream/coffee beverages, and an assortment of small plates, sandwiches and wraps, desserts, wines, and beer. Packages of Starbucks Reserve" whole bean coffees were to be available for purchase. Plans called for four types of brewing methods for the coffees and teas. Starbucks had 43 Starbucks Reserve locations in February 2020. - Transform about 20 percent of the company's existing porffolio of Starbucks stores into upgraded Starbucks Reserve coffee bars. However, shortly after announcing the initiative, Howard Schultz stepped down as Starbucks CEO, turning the role orer to Pugs C-326 Kevin Johnson, Starbucks chief operating ofllcer with whom Schultz had worksd closely for the past two years - they had adjoining offlces connected by a door and usually visited together multiple times a day. Shultz stayed on as chairman of the company's board of directors and focused his time on social initiatives and plans for the upscale Roastery locations and Starbucks Reserve brand. Schultz exuded confidence that Johnson was the right person to lead Starbucks in the future and that he was well prepared to meet the challenges of continuing to build the Starbucks brand, enhance the consumer experience, and manage its global operations. Johnson fairly quickly scaled back the sizes of all three of the somewhat transformational strategic moves announced by Schultz, chiefly due to their cost and questionable profitability, and proceeded to steer Starbucks back to the strategio path the company had steadfastly pursued for most of the past decade; these included the following strategy elements: - Maintain Starbucks standing as one of the most recognized and respected brands in the world and stay strongly focused on providing customers with a pleasing Starbucks experience that prompted them to patronize Starbucks stores frequently. - Continue disciplined expansion of the company's store base, adding stores in both existing, developed markets and in newer, higher growth markets like China, which for several years had been singled out as Starbucks best opportunity for opening hundreds of new stores annually. During fiscal 2018 and fiscal 2019, Starbucks opened new stores in China at the rate of 1 every 15 hours; as of March 31, 2020, the company had 4,351 company-operated stores in China. Shanghai alone had over 600 Starbucks stores, more than any other city in the world. Starbucks goal was to have 5,000 stores in China by 2021. - Optimize the mix of company-operated and licensed stores by determining which type of store was best suited to ongoing changes in business and political circumstances in various countries around the world and by recognizing that to the special situations of stores operating in big hotels, resorts, airports, hospitals, major office buildings, and on university campuses sometimes called for licensed stores and sometimes for stores owned and operated by Starbucks. - Continue to offer consumers new coffee and other products in a variety of forms, across new categories, diverse channels, and alternative store formats. - Continue to enhance the company's social responsibility strategy and increase the company's efforts to be a good corporate citizen, ethically source high-quality coffee, contribute positively to the communities in which it does business, be an employer of choice, and exert ever-stronger efforts to protect the planet. Exhibit 1 provides an overview of Starbucks performance during fiscal years 2010-2019. Note 1: In fiscal years 2016 and 2010, cost of sales included occupancy expenses for Starbucks company-operated stores. In fiscal years 2017 , 2018 and 2019 , occupancy expenses for Starbucks company-operated stores were reclassified and included in store operating expenses. This change accounts for much of the discontinuity between cost of sales for 2016 and costs of sales in 2017, 2018, and 2019, and similarly for the big jump between store operating expenses for 2017 versus store operating expenses for 2018 and 2019. Sources: Company 10-K reports for 2011, 2017, 2018, and 2019 and data reporting Starbucks store counts by market posted in the irvestor relation section at www.starbucks.com (accessed November 1, 2019). Starbucks in 2020: Is the Company on Track to Achieve Attractive Growth and Operational Excellence? Arthur A. Thompson The Uaiverity of Alabama Since its founding in 1987 as a modest rine-store operation in Seattle, Washington, Starbucks had become the premier roaster, markster, and retailer of specialty coffees in the world, with just over 32,000 store locations in 78 countries as of April 2020 and annual sales of $26.5 billion in fiscal year 2019 , ending September 30 , 2019. In addition to its flagship Starbucks brand coffees and coffee beverages, Starbuchs' other brands and products included Starbucks Reserve blends of coffee, Teavana teas, Seattle's Best Coffee, Evolution Fresh juices and smoothies, Ethos bottled waters, Torrefarione Italia Coffee, and Princi bakery products. Starbucks stores also sold baked pastries, cold and hot sandwiches, salads, salad and grain bow1s, catmeal, yogurt parfaits and fruit cups purchased from a variaty of local, regional, and national suppliers. In January 2017, then CEO and company founder Howard Starbucks launched a somewhat grandiose strategic initiative to inject more innovation and fresh approaches into the company's operations and to spur growth: - Open 20-30 Starbucks Reserve" Roasteries and Tasting Rooms, which would showcase the theater of coffee roasting and brewing in a big, multi-level stores with amazing decorations, seating for upwards of a thousand patrons, multiple types of coffee bars with elaborate menus of innovative coffee beverages and interesting food selections, areas where friends could gather at community tables or in lounge areas with fireplaces, a mixology bar serving traditional ltalian cocktails, multiple dining venues, and an upscale Princi bakery where patrons could watch chefs preparing fresh-baked artisanal Italian breads, sandwiches, and pastries being served to diners. Going into 2020, Roasteries had been opened in Seattle, Shanghai, Milan, New York, Chicago, and Tokyo-all attracted local coffee enthusiasts, partiers, nearby shoppers curious to see what the Brewery offered, and visiting sightseers looking to enjoy a very different kind of Starbucks experience. - Open 1,000 Starbucks Reserve stores worldwide to bring premium experiences to customers and promote the company's recently-introduced Starbucks Reserve'" coffees; these locations were to offer a more intimate small-lot coffee experience and gave customers a chance to chat with a barista about all things coffee. The menu at Starbucks Reserve stores was to consist of handcrafted hot and cold Starbucks Reserve" coffee beverages, hot and cold teas, ice cream/coffee beverages, and an assortment of small plates, sandwiches and wraps, desserts, wines, and beer. Packages of Starbucks Reserve" whole bean coffees were to be available for purchase. Plans called for four types of brewing methods for the coffees and teas. Starbucks had 43 Starbucks Reserve locations in February 2020. - Transform about 20 percent of the company's existing porffolio of Starbucks stores into upgraded Starbucks Reserve coffee bars. However, shortly after announcing the initiative, Howard Schultz stepped down as Starbucks CEO, turning the role orer to Pugs C-326 Kevin Johnson, Starbucks chief operating ofllcer with whom Schultz had worksd closely for the past two years - they had adjoining offlces connected by a door and usually visited together multiple times a day. Shultz stayed on as chairman of the company's board of directors and focused his time on social initiatives and plans for the upscale Roastery locations and Starbucks Reserve brand. Schultz exuded confidence that Johnson was the right person to lead Starbucks in the future and that he was well prepared to meet the challenges of continuing to build the Starbucks brand, enhance the consumer experience, and manage its global operations. Johnson fairly quickly scaled back the sizes of all three of the somewhat transformational strategic moves announced by Schultz, chiefly due to their cost and questionable profitability, and proceeded to steer Starbucks back to the strategio path the company had steadfastly pursued for most of the past decade; these included the following strategy elements: - Maintain Starbucks standing as one of the most recognized and respected brands in the world and stay strongly focused on providing customers with a pleasing Starbucks experience that prompted them to patronize Starbucks stores frequently. - Continue disciplined expansion of the company's store base, adding stores in both existing, developed markets and in newer, higher growth markets like China, which for several years had been singled out as Starbucks best opportunity for opening hundreds of new stores annually. During fiscal 2018 and fiscal 2019, Starbucks opened new stores in China at the rate of 1 every 15 hours; as of March 31, 2020, the company had 4,351 company-operated stores in China. Shanghai alone had over 600 Starbucks stores, more than any other city in the world. Starbucks goal was to have 5,000 stores in China by 2021. - Optimize the mix of company-operated and licensed stores by determining which type of store was best suited to ongoing changes in business and political circumstances in various countries around the world and by recognizing that to the special situations of stores operating in big hotels, resorts, airports, hospitals, major office buildings, and on university campuses sometimes called for licensed stores and sometimes for stores owned and operated by Starbucks. - Continue to offer consumers new coffee and other products in a variety of forms, across new categories, diverse channels, and alternative store formats. - Continue to enhance the company's social responsibility strategy and increase the company's efforts to be a good corporate citizen, ethically source high-quality coffee, contribute positively to the communities in which it does business, be an employer of choice, and exert ever-stronger efforts to protect the planet. Exhibit 1 provides an overview of Starbucks performance during fiscal years 2010-2019. Note 1: In fiscal years 2016 and 2010, cost of sales included occupancy expenses for Starbucks company-operated stores. In fiscal years 2017 , 2018 and 2019 , occupancy expenses for Starbucks company-operated stores were reclassified and included in store operating expenses. This change accounts for much of the discontinuity between cost of sales for 2016 and costs of sales in 2017, 2018, and 2019, and similarly for the big jump between store operating expenses for 2017 versus store operating expenses for 2018 and 2019. Sources: Company 10-K reports for 2011, 2017, 2018, and 2019 and data reporting Starbucks store counts by market posted in the irvestor relation section at www.starbucks.com (accessed November 1, 2019)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


