Question: 1. The adjacency and incidence matrices below use the conventions discussed in class for graphs and the rows and columns of these matrices are arranged
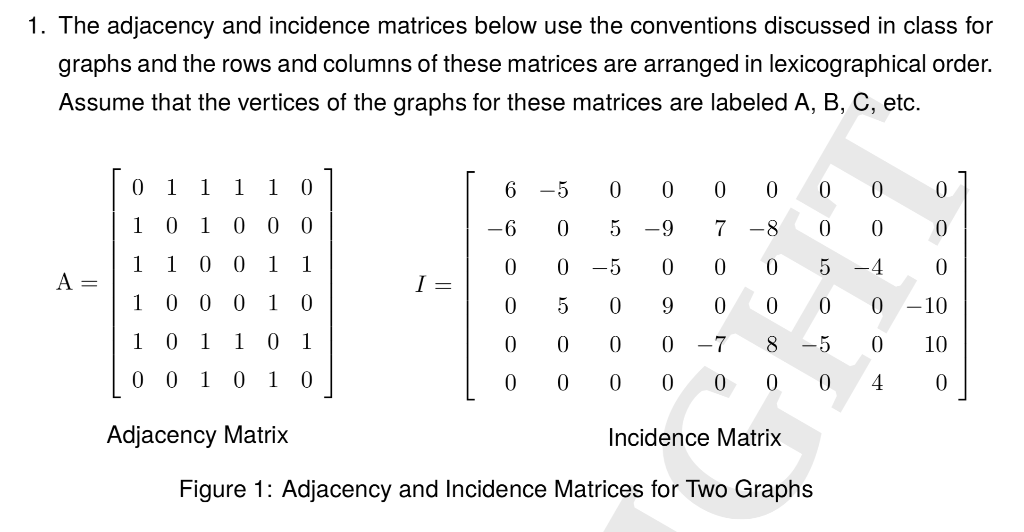
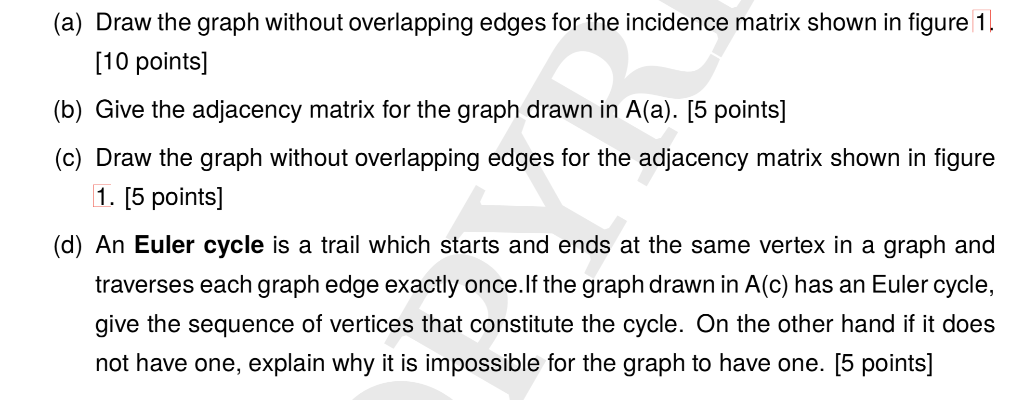
1. The adjacency and incidence matrices below use the conventions discussed in class for graphs and the rows and columns of these matrices are arranged in lexicographical order. Assume that the vertices of the graphs for these matrices are labeled A, B, C, etc. 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 -6 0 5-9 7-8 0 0 0 0 05 0 90 0 010 00 0 0-7 8 5 0 10 0 6-50 0 0000 0 0 -50 0 054 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 00 0 0 0 00 4 Adjacency Matrix Incidence Matrix Figure 1: Adjacency and Incidence Matrices for Two Graphs (a) Draw the graph without overlapping edges for the incidence matrix shown in figure 1 10 points] (b) Give the adjacency matrix for the graph drawn in A(a). [5 points] c) Draw the graph without overlapping edges for the adjacency matrix shown in figure 1. [5 points] (d) An Euler cycle is a trail which starts and ends at the same vertex in a graph and traverses each graph edge exactly once.lf the graph drawn in A(c) has an Euler cycle, give the sequence of vertices that constitute the cycle. On the other hand if it does not have one, explain why it is impossible for the graph to have one. [5 points]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


