Question: 1. The MAD for Method 1 is _______ thousand gallons (round your response to three decimal places). Part 5 Mean squared error (MSE) is the
1. The MAD for Method 1 is
_______
thousand gallons (round your response to three decimal places).
Part 5
Mean squared error (MSE) is the average of
(ActualForecast)2.
For the information given in Method 1, the value of n =
4.
The value of
(ActualForecast)2
will be
______________
(thousand gallons)2
(round your response to three decimal places).
Part 6
3. The mean squared error (MSE) for Method 1 is
____________
(thousand gallons)2
(round your response to three decimal places).
Part 7
4. The absolute deviation based on the forecast developed using Method 2 adds to
__________
thousand gallons (round your response to three decimal places).
Part 8
5. The MAD for Method 2 is
___________
thousand gallons (round your response to three decimal places).
Part 9
6. The relationship for calculating
MSE = (Forecast Error)2n.
For the given information, in this relationship n =
4.
The value of
(ActualForecast)2for
Method 2 will be
______________
(thousand gallons)2
(round your answer to three decimal places).
Part 10
6.  The mean squared error (MSE) for Method 2 is
The mean squared error (MSE) for Method 2 is
___________
(thousand gallons)2
(round your response to three decimal places).
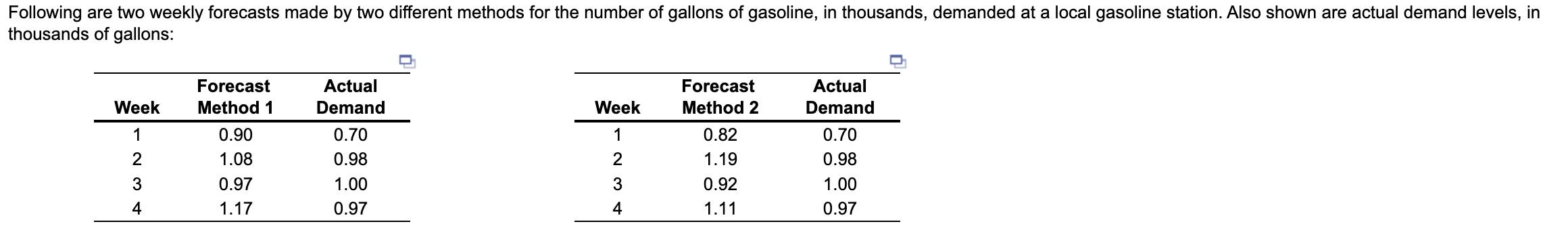
thousands of gallons: \begin{tabular}{ccc} \hline Week & Forecast Method 1 & Actual Demand \\ \hline 1 & 0.90 & 0.70 \\ 2 & 1.08 & 0.98 \\ 3 & 0.97 & 1.00 \\ 4 & 1.17 & 0.97 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{ccc} \hline Week & Forecast Method 2 & Actual Demand \\ \hline 1 & 0.82 & 0.70 \\ 2 & 1.19 & 0.98 \\ 3 & 0.92 & 1.00 \\ 4 & 1.11 & 0.97 \\ \hline \end{tabular}Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


