Question: 1 . This assignment allocates the word table in a region of memory called the heap, which permits a new and larger table to be
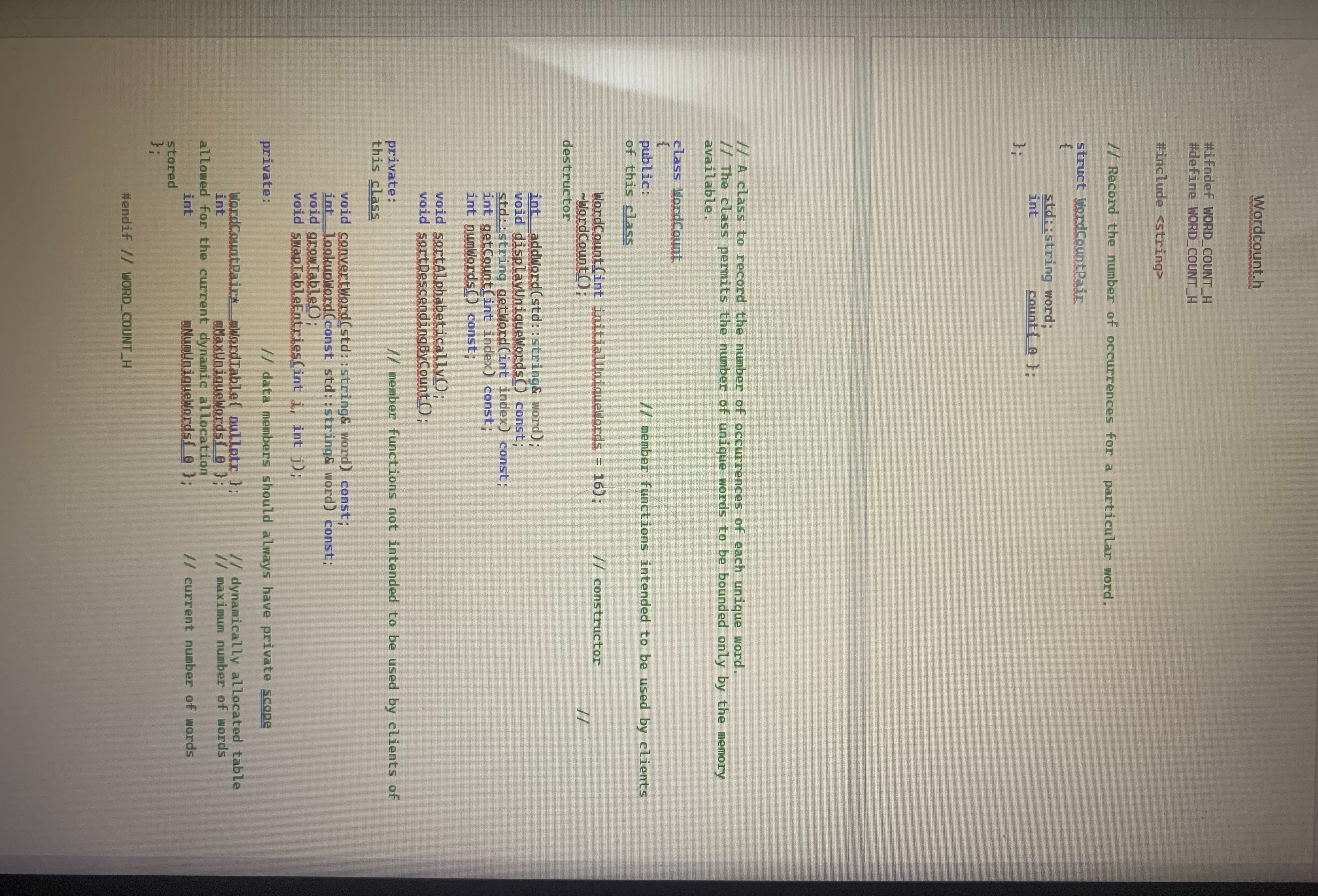
This assignment allocates the word table in a region of memory called the heap, which permits a new and larger table to be allocated elsewhere on the heap when the old table fills up The contents of the old table are copied over to the new table, and the old table's memory is recycled. Because the word table's implementation is hidden from client code main in this case this change does not impact client code. Allowing the word table to grow gives you some insight into how the C std::vector container is implemented. This change permits the number of unique words to be bounded only by the available memory. Read all the provided code before you move on to the next step. Note that the mWordTable data member is now defined as a pointer initialized to nullptr in WordCount.h
Implement the WordCount constructor and destructor in WordCount.cpp The constructor should use the new operator to allocate the mWordTable with initialUniqueWords entries, which is defined by the constructor's parameter and has a default value of The destructor should use the array form of the delete operator to deallocate the mWordTable. The WordCount constructor is called when the mWordCount object is created in main and the WordCount destructor is implicitly called when the mWordCount object goes out of scope in main A memory leak would occur if the WordCount destructor did not free the memory allocated.
A private growTable member function is now defined in the WordCount class. This function has private access because it is not part of the public WordCount API. The growTable function is called in addWord when there is no table entry available for a new word. Implement the growTable member function. The comments preceding growTable provide guidance.
implementthe addWord getWord getCount numWords and lookupWord member functions. The addWord function now calls growTable if the mWordTable is already full prior to adding a word to the table.
Use the selection sortLinks to an external site. algorithm to implement the sortAlphabetically and sortDescendingByCount member functions. The sort member functions should call the private swapTableEntries helper function to exchange two mWordTable entries, which you also need to implement.
As in Assignment implement the main function in the main.cpp according to the comments that precede main Do not override the WordCount object's default initial table size of Display the number of unique words, call sortAlphabetically before calling displayUniqueWords and then call sortDescendingByCount before again calling displayUniqueWords
Test your code with the provided test.txt and usdeclar.txt files.
After you complete this assignment, please make sure to commit and push your solution, followed by confirmation with a browser.
Note you may have to edit convertWord to handle white spaces when adding words.
Wordcount.cpp
#include "WordCount.h
#include
#include
#include
void WordCount::displayUniqueWords const
for int i; i mNumUniqueWords; i
std::cout std::left std::setw mWordTableiword
std::right std::setw mWordTableicount std::endl;
void WordCount::convertWordstd::string& word const
int i;
while i word.length
char c wordi;
if ispunctc
word.erasei;
else
if isupperc
wordi tolowerc;
i;
Return the mWordTable index of the word argument.
If the word is not found in the mWordTable then is returned.
TODO: Implement the lookupWord member function.
Increase the size of the mWordTable by: doubling mMaxUniqueWords
and allocating a new mWordTable with this many entries; copying the
old mWordTable entries to the new mWordTable; and deleting the old
mWordTable and reassigning the mWordTable pointer to the new mWordTable.
TODO: Implement the growTable member function.
Exchange the mWordTable entries at the specified indices.
Used by the sort member functions.
TODO: Implement the swapEntries member function.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


