Question: 1. Under 100% sales assumption, using absorption coating, the COGS is calculated by adding Dorect Material (DM), Direct Labor (DL), and Fixed Overhead (FOH)a) Trueb)
1. Under 100% sales assumption, using absorption coating, the COGS is calculated by adding Dorect Material (DM), Direct Labor (DL), and Fixed Overhead (FOH)a) Trueb) False2. Under 100% sales assumption, using absorption costing, the SG&A is calculated by adding Fixed SG&A, variable SG&A, and Fixed Overhead (FOH).a) Trueb) False3. Under 75% sales assumption, using absorption costing, the COGS is calculated by adding Direct Material (DM), Direct Labor (DL), variable Overhead (VOH), and Fixed Overhead (FOH) multiply by 75%.a) Trueb) False4. Under 100% sales assumption using absorption costing, the ending inventory balance is?5. Under 75% sale assumption, using absorption costing, the ending inventory balance is?6. Under 75% sale assumption, using variable costing, the ending inventory balance is?7. Under 75% sale assumption, using variable costing, the ending inventory balance can be calculated by:(150,000 + 75.000+ 25,000) 25%a Trueb) False8. Under 75% sales assumption, using variable costing, the variable product cost balance can be calculated ov:(150,000 + 75.000+ 25,000) 25%a) Trueb) False9. Under 75% sales assumption, using variable costing, the contribution margin balance can be calculated by:Less: (150,000 + 75.000+ 25,000) 75%Less: 450,000 10%a) Trueb False10. Under Variable Costing, if a company produces more and sales less:The Net income is LESS, and the End Inventory IS LESS:a) Trueb False
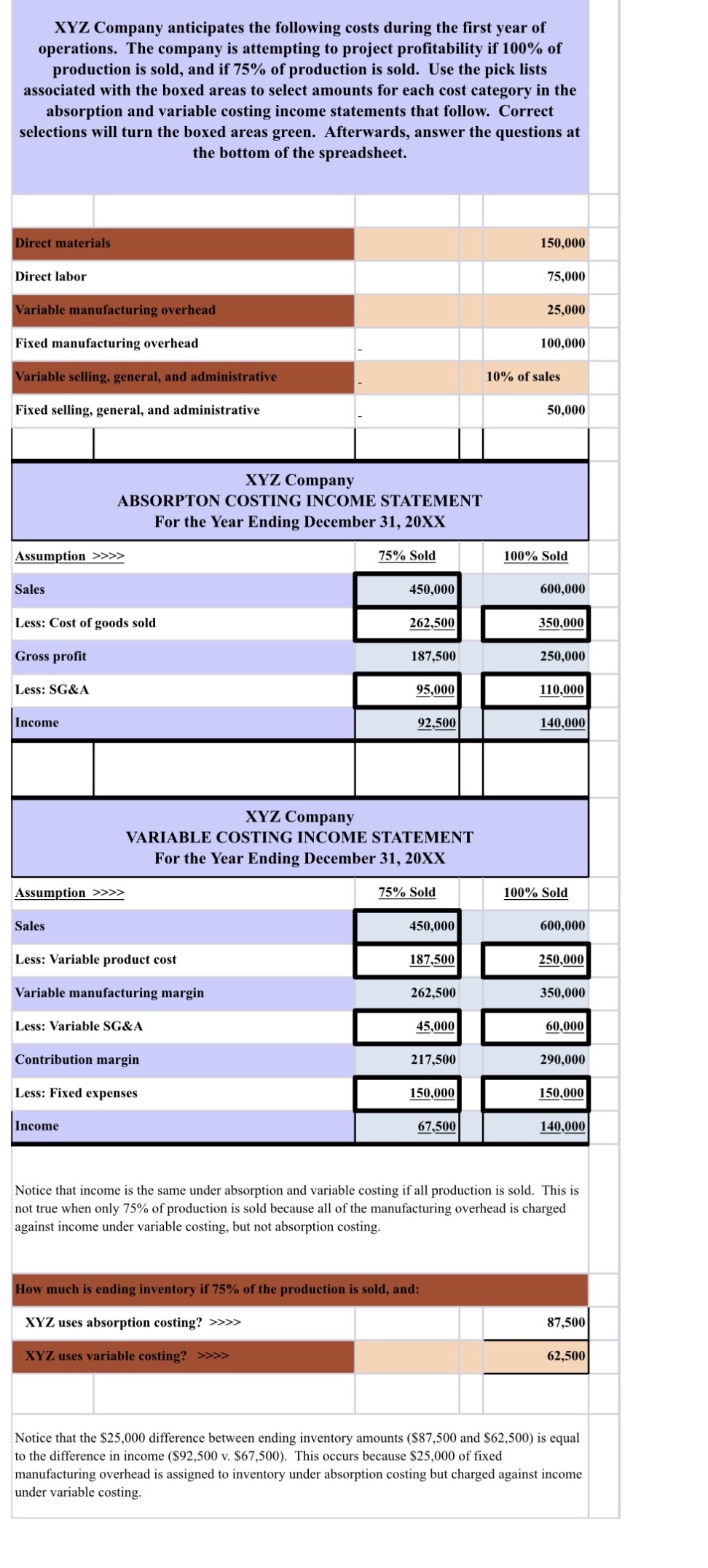
XYZ Company anticipates the following costs during the first year of operations. The company is attempting to project profitability if 100% of production is sold, and if 75% of production is sold. Use the pick lists associated with the boxed areas to select amounts for each cost category in the absorption and variable costing income statements that follow. Correct selections will turn the boxed areas green. Afterwards, answer the questions at the bottom of the spreadsheet. Direct materials 150,000 Direct labor 75,000 Variable manufacturing overhead 25,000 Fixed manufacturing overhead 100,000 Variable selling, general, and administrative 10% of sales Fixed selling, general, and administrative 50,000 XYZ Company ABSORPTON COSTING INCOME STATEMENT For the Year Ending December 31, 20XX Assumption >>>> 75% Sold 100% Sold Sales 450,000 600,000 Less: Cost of goods sold 262,500 350,000 Gross profit 187,500 250,000 Less: SG&A 95,000 110,000 Income 92,500 140,000 XYZ Company VARIABLE COSTING INCOME STATEMENT For the Year Ending December 31, 20XX Assumption >> >> 75% Sold 100% Sold Sales 450,000 600,000 Less: Variable product cost 187,500 250,000 Variable manufacturing margin 262,500 350,000 Less: Variable SG&A 45,000 60,000 Contribution margin 217,500 290,000 Less: Fixed expenses 150,000 150,000 Income 67,500 140,000 Notice that income is the same under absorption and variable costing if all production is sold. This is not true when only 75% of production is sold because all of the manufacturing overhead is charged against income under variable costing, but not absorption costing. How much is ending inventory if 75% of the production is sold, and: XYZ uses absorption costing? >> > > 87,500 XYZ uses variable costing? >>>> 62,500 Notice that the $25,000 difference between ending inventory amounts ($87,500 and $62,500) is equal to the difference in income ($92,500 v. $67,500). This occurs because $25,000 of fixed manufacturing overhead is assigned to inventory under absorption costing but charged against income under variable costing
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


