Question: 1) Using Bayesian Networks- Exact Inference In this task, you should use the idea that the Bayesian Network is an efficient representation of the Joint
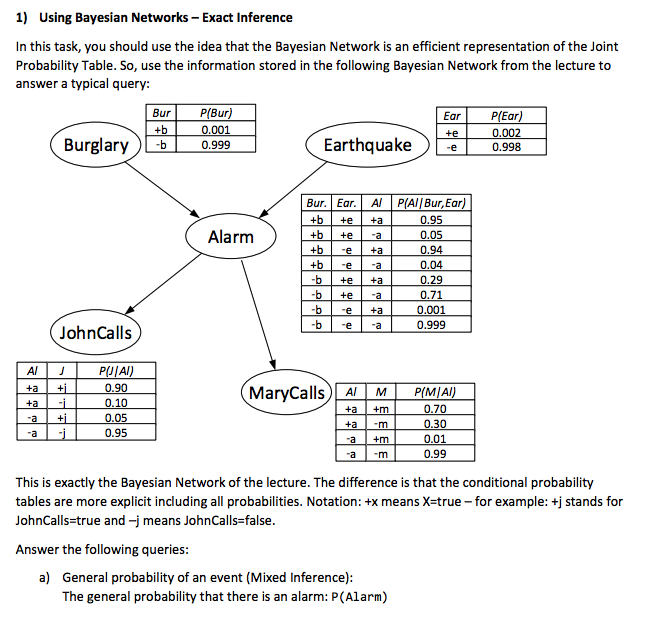
1) Using Bayesian Networks- Exact Inference In this task, you should use the idea that the Bayesian Network is an efficient representation of the Joint Probability Table. So, use the information stored in the following Bayesian Network from the lecture to answer a typical query: ur P(Bur 001 Ear PEar 002 Earthquake0.998 Burglary )0.999 Bur. Ear.AP(AlIBur, Ear) 95 05 94 04 Alarm 71 001 0.999 b ea JohnCalls AJ UJAI) MaryCalls) A MPIMA +a +m 05 0.95 01 0.99 +m am This is exactly the Bayesian Network of the lecture. The difference is that the conditional probability tables are more explicit including all probabilities. Notation: +x means X-true-for example: tj stands for JohnCalls-true and -j means JohnCalls-false Answer the following querie:s a) General probability of an event (Mixed Inference): The general probability that there is an alarm: P(Alarm) 1) Using Bayesian Networks- Exact Inference In this task, you should use the idea that the Bayesian Network is an efficient representation of the Joint Probability Table. So, use the information stored in the following Bayesian Network from the lecture to answer a typical query: ur P(Bur 001 Ear PEar 002 Earthquake0.998 Burglary )0.999 Bur. Ear.AP(AlIBur, Ear) 95 05 94 04 Alarm 71 001 0.999 b ea JohnCalls AJ UJAI) MaryCalls) A MPIMA +a +m 05 0.95 01 0.99 +m am This is exactly the Bayesian Network of the lecture. The difference is that the conditional probability tables are more explicit including all probabilities. Notation: +x means X-true-for example: tj stands for JohnCalls-true and -j means JohnCalls-false Answer the following querie:s a) General probability of an event (Mixed Inference): The general probability that there is an alarm: P(Alarm)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


