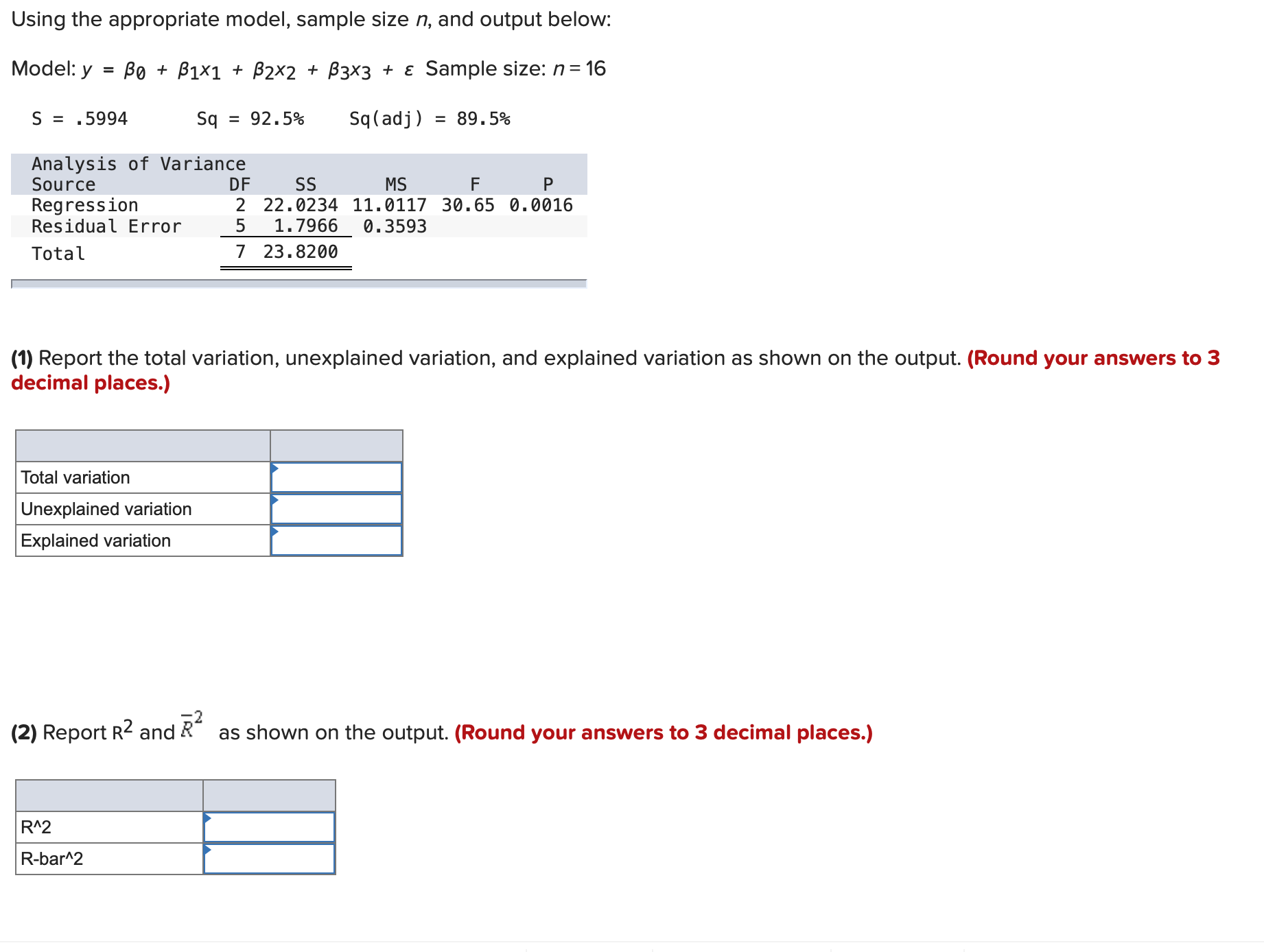
Question: 1)- Using the appropriate model, sample size n, and output below: Model:y = 130 + 01x1 + 32x2 + [33x3 + 5 Sample size: n=16


1)-
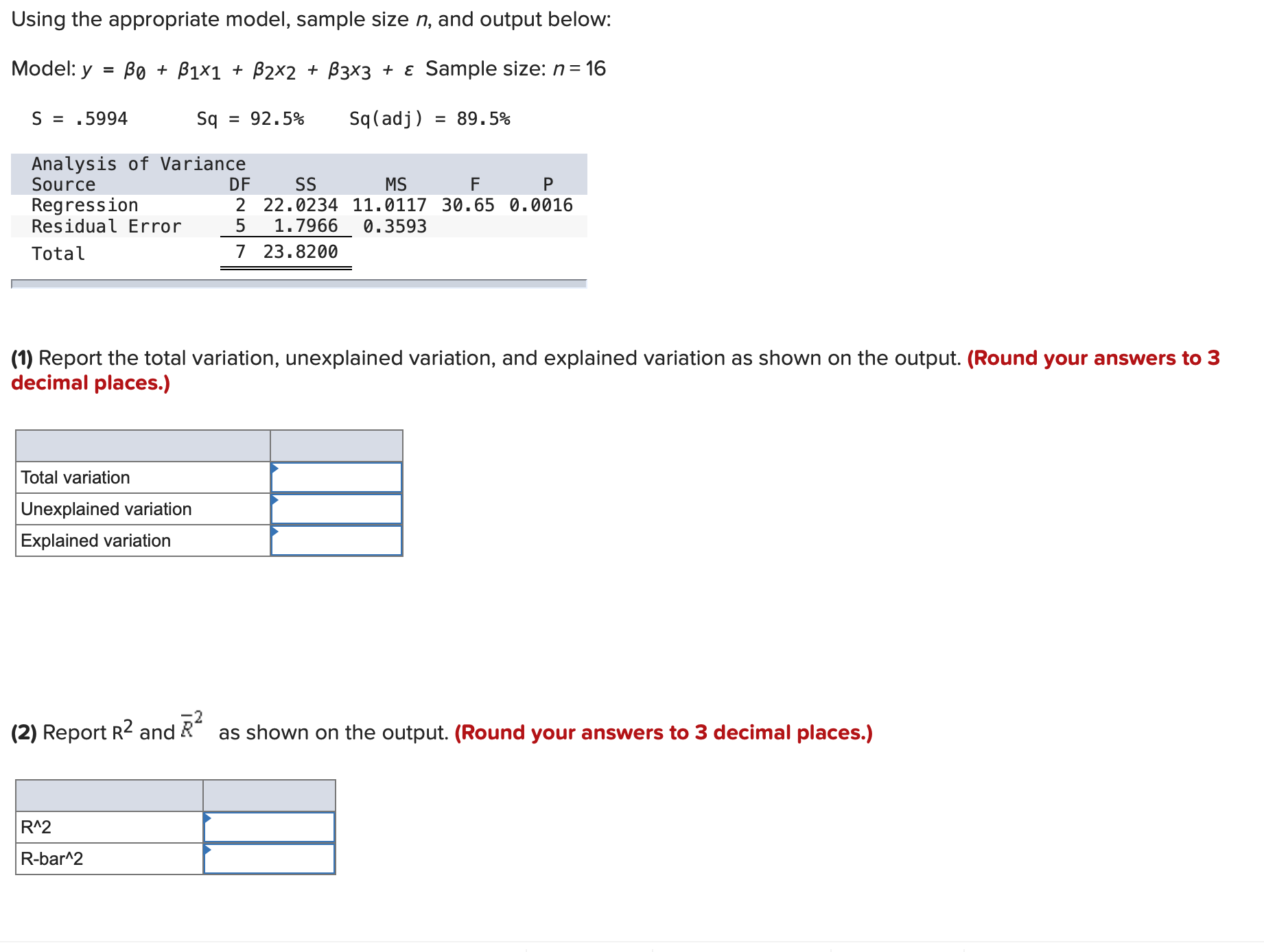
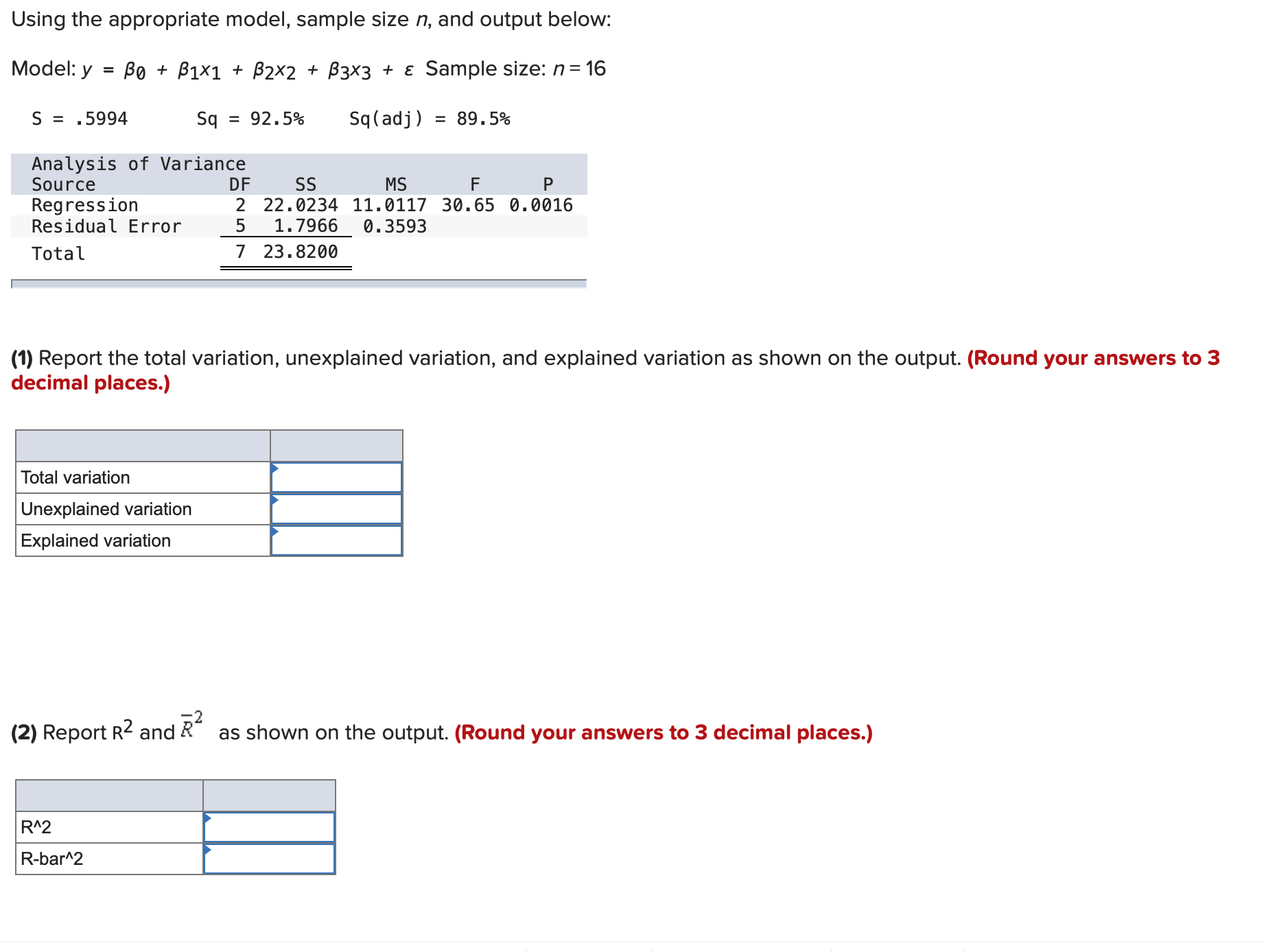
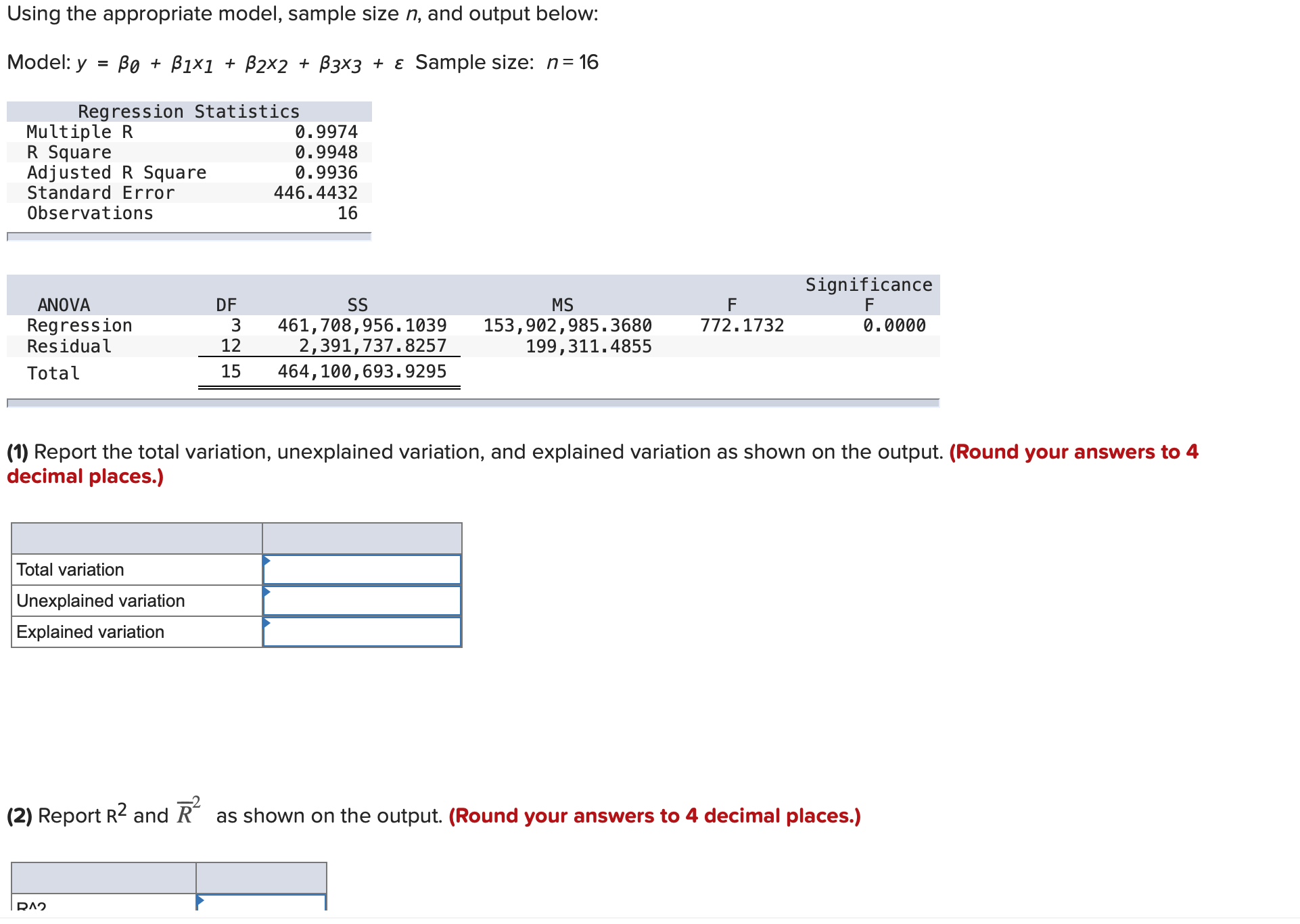
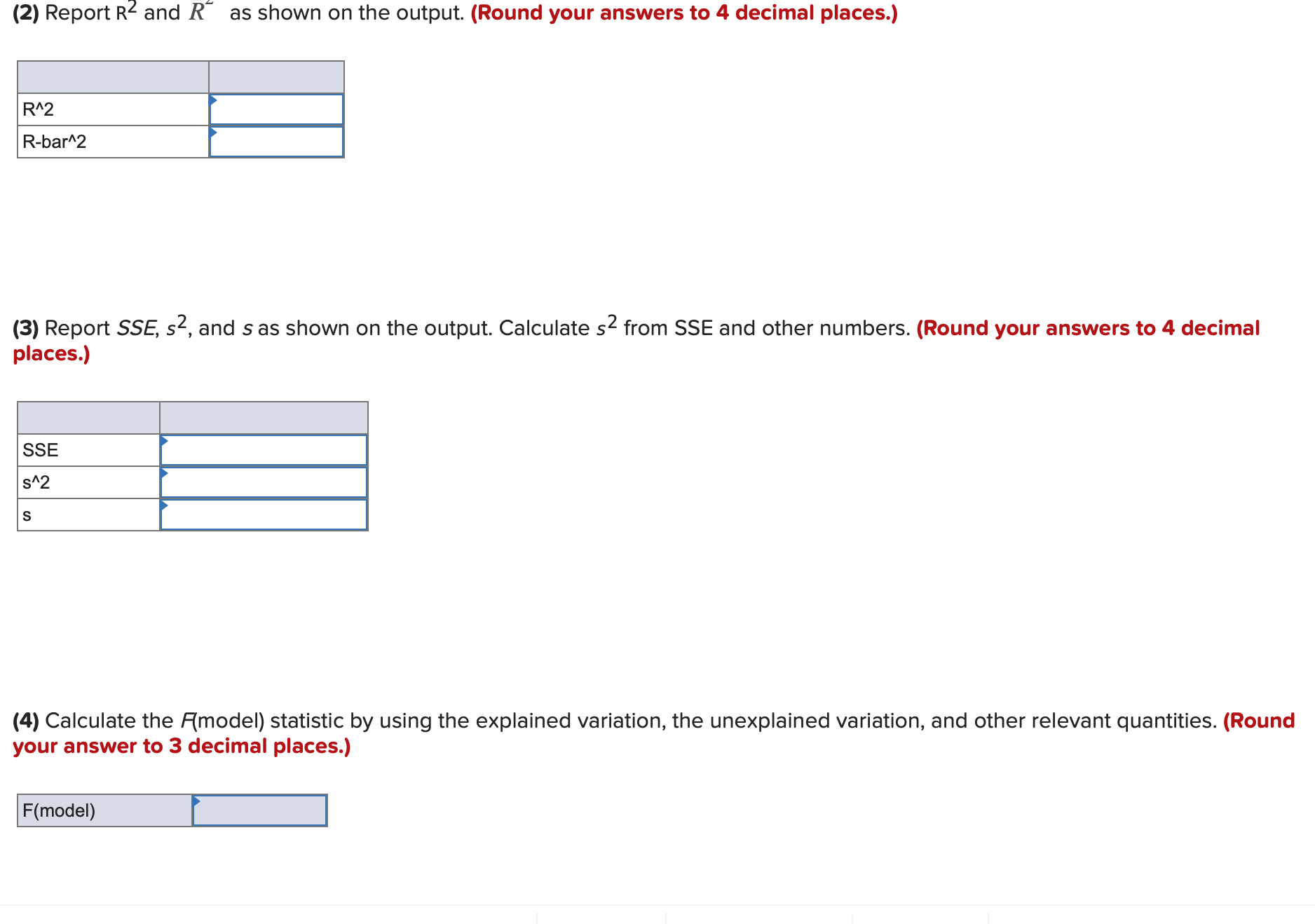


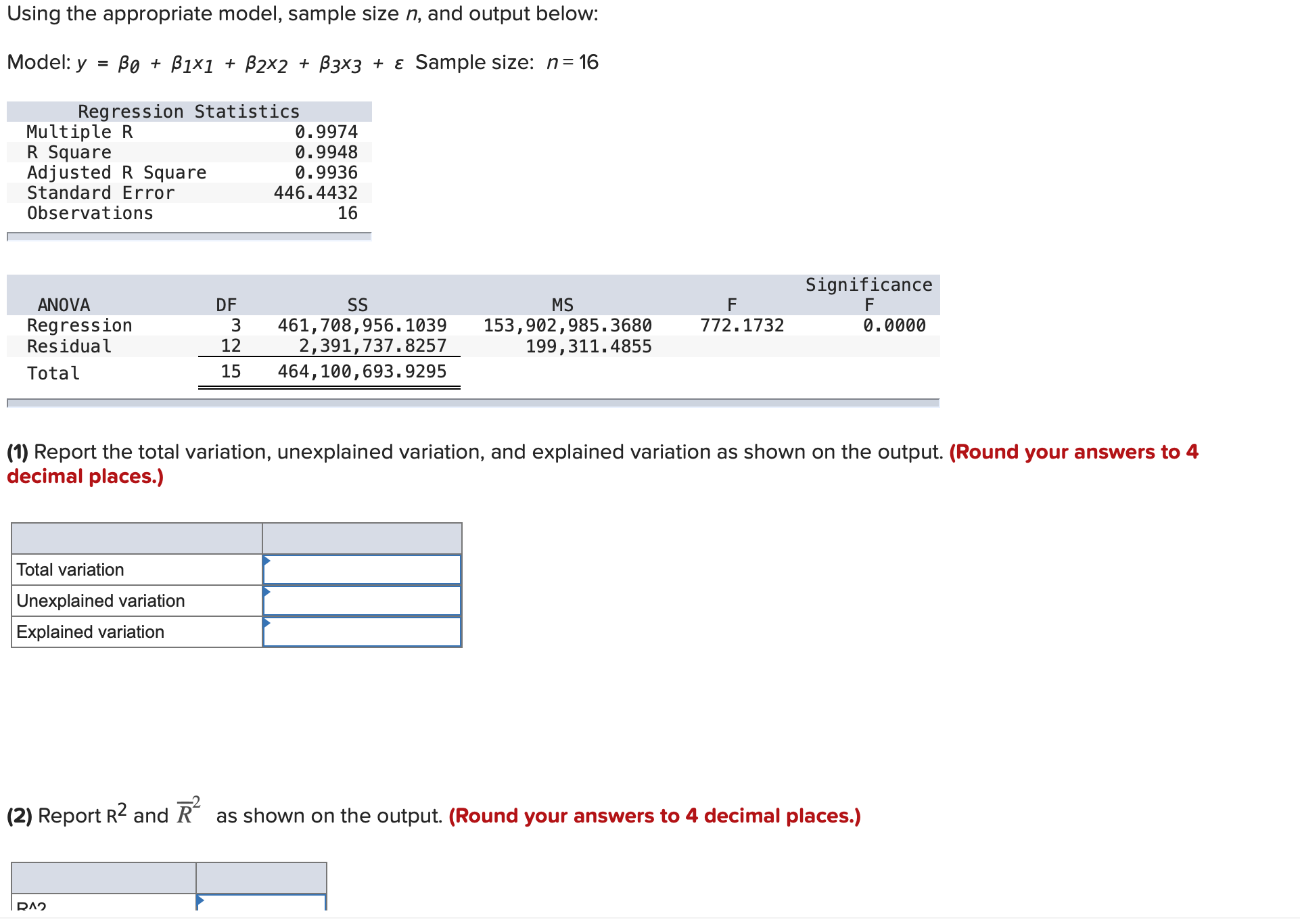
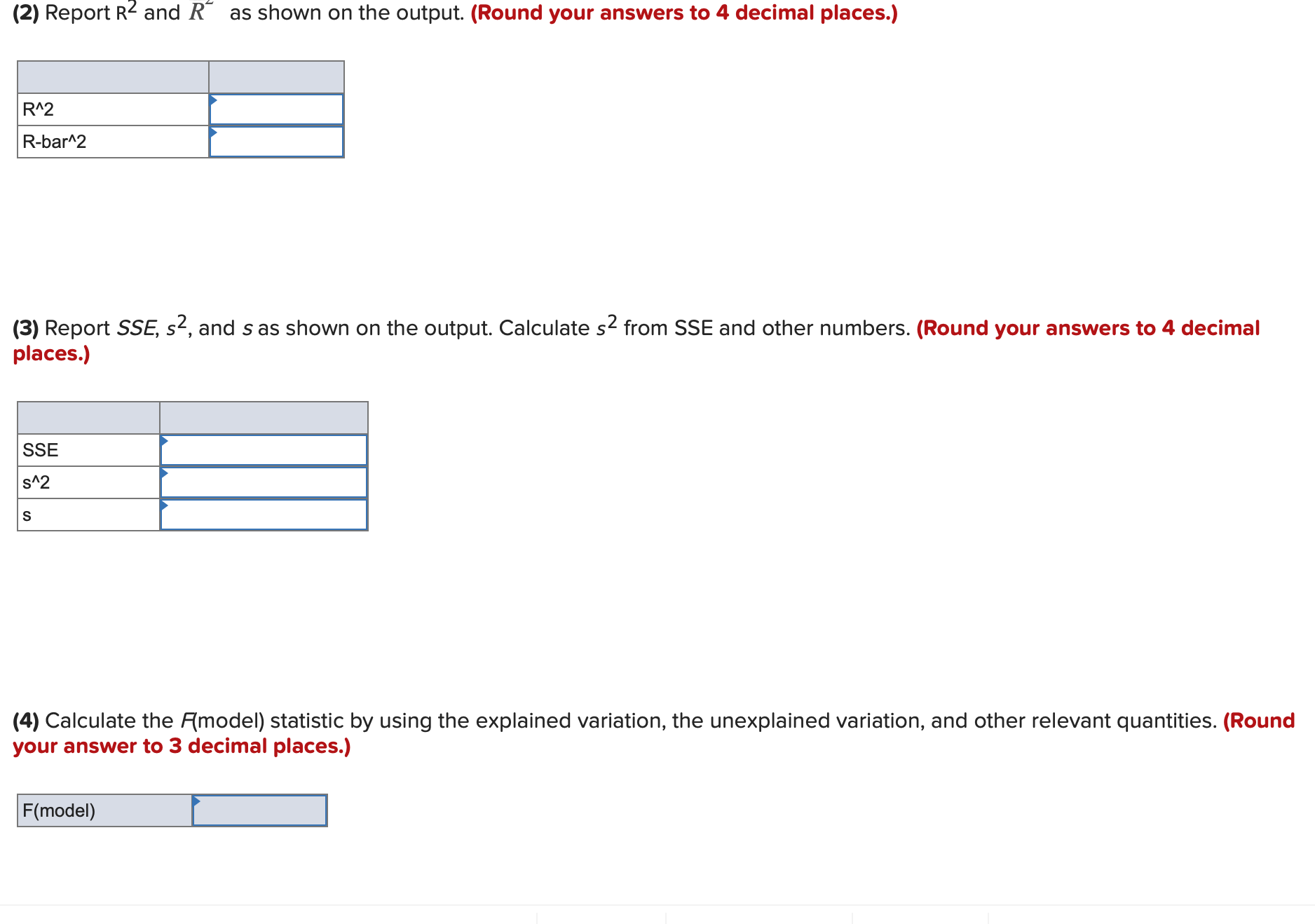
Using the appropriate model, sample size n, and output below: Model:y = 130 + 01x1 + 32x2 + [33x3 + 5 Sample size: n=16 S = .5994 Sq = 92.595 Sq(adj) = 89.595 Analysis of Variance Source DF 55 Ms F P Regression 2 22.0234 11.0117 30.65 0.0016 Residual Error 5 1.7966 0.3593 Total 7 23.8200 ' (1) Report the total variation, unexplained variation, and explained variation as shown on the output. (Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) Total variation Unexplained variation Explained variation '2 (2) Report R2 and R as shown on the output. (Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) R"2 Rbar'Z Using the appropriate model, sample size n, and output below: Model:y = 130 + 01x1 + 32x2 + [33x3 + 5 Sample size: n=16 S = .5994 Sq = 92.595 Sq(adj) = 89.595 Analysis of Variance Source DF 55 Ms F P Regression 2 22.0234 11.0117 30.65 0.0016 Residual Error 5 1.7966 0.3593 Total 7 23.8200 ' (1) Report the total variation, unexplained variation, and explained variation as shown on the output. (Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) Total variation Unexplained variation Explained variation '2 (2) Report R2 and R as shown on the output. (Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) R"2 Rbar'Z Using the appropriate model, sample size n, and output below: ModeIIy = [30 + lxl + zxz + [33x3 + E Sample size: n=16 Regression Statistics Multiple R 0.9974 R Square 0.9948 Adjusted R Square 0.9936 Standard Error 446.4432 Observations 16 I Significance ANOVA DF SS MS F F Regression 3 461.708.956.1039 153.902.985.3680 772.1732 0.0000 Residual 12 2.391.737.8257 199.311.4855 Total 15 464.100.693.9295 (1) Report the total variation, unexplained variation, and explained variation as shown on the output. (Round your answers to 4 decimal places.) Unexplained variation Explained variation 2 (2) Report R2 and R as shown on the output. (Round your answers to 4 decimal places.) DIV) (2) Report R2 and R\" as shown on the output. (Round your answers to 4 decimal places.) R"2 Rbar\"2 (3) Report 555 52, and s as shown on the output. Calculate 52 from SSE and other numbers. (Round your answers to 4 decimal places.) SSE 5A2 (4) Calculate the F(model) statistic by using the explained variation, the unexplained variation, and other relevant quantities. (Round your answer to 3 decimal places.) (5) Use the F(model) statistic and the appropriate rejection point to test the significance of the linear regression model under consideration by setting a equal to .05. HO: 31 = 32 = $3 = 0 by setting a = .05. (6) Find the p-value related to F(model) on the output. Using the p-value, test the significance of the linear regression model by setting a = .10, .05, .01, and .001. p-value = .000. HO at a = .05, .01, and .001.United Oil Company is attempting to develop a reasonably priced unleaded gasoline that will deliver higher gasoline mileages than can be achieved by its current unleaded gasolines. As part of its development process, United Oil wishes to study the effect oftwo independent variablesx1, amount of gasoline additive RST (O, 1, or 2 units), and X2, amount of gasoline additive XST(0,1, 2, or 3 units), on gasoline mileage, y. Mileage tests are carried out using equipment that simulates driving under prescribed conditions. The combinations of x1 and X2 used in the experiment, along with the corresponding values of y, are given below. RST XST Gas Units Units Mileage (X1) (X2) (y, mpg) 0 0 27.80 0 0 28.48 0 0 28.06 1 0 29.65 1 0 30.06 2 0 28.20 2 0 29.64 0 1 32.53 0 1 33. 11 1 1 33.60 1 1 34.78 0 2 32.89 0 2 33.88 1 2 34.84 1 2 35.59 1 2 35.24 2 2 33.24 2 2 34.53 2 2 34.72 1 3 33.46 2 3 33.75 2 3 33.86 [ Using the model, y = 50 + [31x1 + B2x12 + [33x2 + 54x22 + a, calculate the point estimate. (Moreover, consider the mean mileage obtained by all gallons of the gasoline when it is made with one unit of RST and two units of XST (a combination that the data on the page margin indicates would maximize mean mileage). Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Point estimate
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


