Question: 1. What data collection design or designs would you consider most appropriate for the evaluation? a.Pre-post or time series design. b.Summative design c.Interactive model design
1. What data collection design or designs would you consider most appropriate for the evaluation?
a.Pre-post or time series design.
b.Summative design
c.Interactive model design
d.User experience design Post-evaluation design
2. What variables could be measured for evaluation of this training program?
a.Learning, motivation or self-efficacy.
b.Self-regulation, intent, ease of use.
c.Rejection, apathy or derision.
d.Learning, behaviour, user experience.
e.None of the above.
3.How would you go about measuring participant reactions?
a.Questionnaires, focus groups and interviews.
b.Formative and summative exams.
c.Standardized questionnaires and organizational records.
d.Self-reports, supervisory reports, direct observations.
e.Indirect observations and informal interviews.
4.What approaches could you take to measure participant learning?
a.Questionnaires, focus groups and interviews.
b.Declarative and procedural testing
c.Self-reports and questionnaires.
d.Organizational records.
e.Indirect observations.

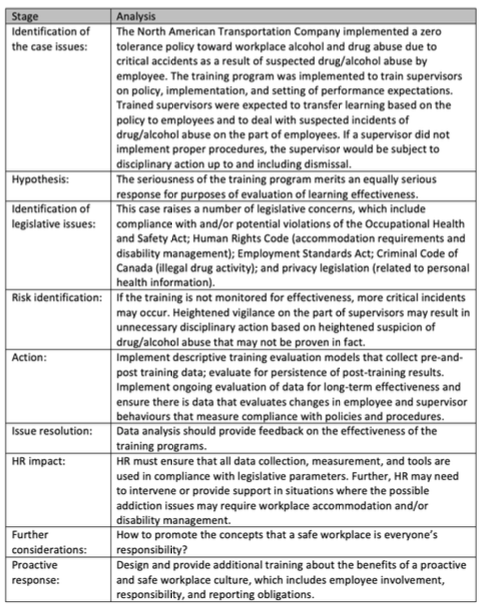
Training Evaluation The North American Transportation Company (NATC) is a very large organization that provides continent-wide facilities for the shipping of goods, from tonnes of wheat and iron ore to individual parcels. Headquartered in Canada, the company uses all forms of heavy equipment to load, transport, and deliver goods and materials for its clients. In recent years, a number of accidents and near-accidents have occurred. In some cases the accidents caused injuries to people (mainly employees, though some injuries were sustained by bystanders). In three cases in the last five years, people were killed. They also caused substantial material damage to property and/or the environment. Investigation of these accidents indicated that drug and/or alcohol abuse by company personnel was relatively common and that these may have been contributing factors to the accidents. This analysis also uncovered that absenteeism and job performance problems were also the result of drug/alcohol use by employees. The CEO of the company asked the HR department to solve the problem. In response, the department formulated a zero-tolerance policy toward workplace alcohol and drug abuse. The policy outlawed alcohol/drug use on the job and made the implementation and enforcement of the policy the direct responsibility of all supervisory personnel in the company. They further developed and implemented a training program to instruct all supervisors on the policy, the means to implement it, and the specific behaviours expected of them. This training program became known as the Alcohol/Drug Abuse Prevention Program (ADAPP). The day-long training program explained that it was the responsibility of supervisors to be vigilant with respect to drug/alcohol use on the job and to act immediately when there was a problem. The training program focused on three main aspects of the ADAPP policy that supervisors were to learn and to transfer to the job: (1) explain the policy to their employees as a group; (2) watch for employees who show signs of being under the influence; and (3) choose the specific supervisory action required correctly. Supervisors were instructed to (a) assess the situation with the employee; (b) immediately relieve the employee from his/her post should the impairment prevent safe and effective job performance; and (c) direct the person to the Employee Aid Program for further investigation and treatment. Supervisors who failed to implement the procedure would face disciplinary actions including, in some cases, immediate dismissal. The training program consisted of lectures and video presentations, followed by various role-playing exercises and discussions designed to help supervisors learn the policy, motivate them to implement it, and enhance their confidence in their ability to do so. Analysis Stage Identification of the case issues: The North American Transportation Company implemented a zero tolerance policy toward workplace alcohol and drug abuse due to critical accidents as a result of suspected drug/alcohol abuse by employee. The training program was implemented to train supervisors on policy, implementation, and setting of performance expectations. Trained supervisors were expected to transfer learning based on the policy to employees and to deal with suspected incidents of drug/alcohol abuse on the part of employees. If a supervisor did not implement proper procedures, the supervisor would be subject to disciplinary action up to and including dismissal. Hypothesis: Identification of legislative issues: The seriousness of the training program merits an equally serious response for purposes of evaluation of learning effectiveness. This case raises a number of legislative concerns, which include compliance with and/or potential violations of the Occupational Health and Safety Act; Human Rights Code (accommodation requirements and disability management); Employment Standards Act; Criminal Code of Canada (illegal drug activity); and privacy legislation (related to personal health information). Risk identification: If the training is not monitored for effectiveness, more critical incidents may occur. Heightened vigilance on the part of supervisors may result in unnecessary disciplinary action based on heightened suspicion of drug/alcohol abuse that may not be proven in fact. Action: Implement descriptive training evaluation models that collect pre-and- post training data; evaluate for persistence of post-training results. Implement ongoing evaluation of data for long-term effectiveness and ensure there is data that evaluates changes in employee and supervisor behaviours that measure compliance with policies and procedures. Data analysis should provide feedback on the effectiveness of the training programs. Issue resolution: HR impact: HR must ensure that all data collection, measurement, and tools are used in compliance with legislative parameters. Further, HR may need to intervene or provide support in situations where the possible addiction issues may require workplace accommodation and/or disability management. Further considerations: How to promote the concepts that a safe workplace is everyone's responsibility? Proactive response: Design and provide additional training about the benefits of a proactive and safe workplace culture, which includes employee involvement, responsibility, and reporting obligations





