Question: 1. What is the primary difference between a static budget and a flexible budget The static budget contains only fixed costs, while the flexible budget


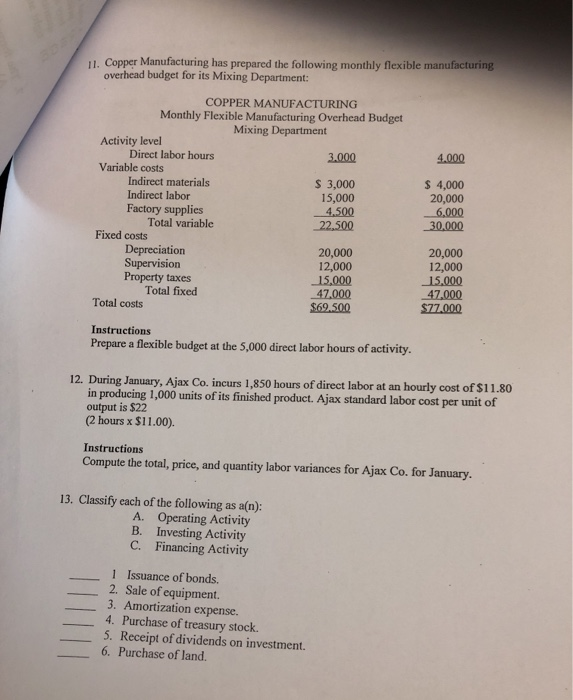

1. What is the primary difference between a static budget and a flexible budget The static budget contains only fixed costs, while the flexible budget contains only variable costs. A) static budget is prepared for a single level of activity, while a flexible budget is adjusted for different activity levels C) The static budget is constructed using input from only upper level management, . while a flexible budget obtains input from all levels of management D) The static budget is prepared only for units produced, while a flexible budget reflects the number of units sold. 2. Another name for the static budget is A) master budget. B) overhead budget. C) permanent budget. D) flexible budget. 3. Management by exception A) causes managers to be buried under voluminous paperwork. B) means that all differences will be investigated C) means that only unfavorable differences will be investigated. D) means that material differences will be investigated. 4. Under management by exception, which differences between planned and actual results should be investigated? A) Material and noncontrollable B) Controllable and noncontrollable C) Material and controllable D) All differences should be investigated 5. If actual costs are greater than standard costs, there is a(n) A) B) C) D) normal variance. unfavorable variance. favorable variance. error in the accounting system. 6. A total materials variance is analyzed in terms of A) price and quantity variances. B) buy and sell variances. C) quantity and quality variances. D) tight and loose variances. 7. The formula for the materials price variance is A) (AQx SP)- (SQx SP). B) (AQx AP)-(AQx SP). C) (AQ x AP)- (SQ SP). D) (AQ SP) (SQx AP). 8. Accounts receivable arising from sales to customers amounted to $85,000 and $75,000 at the beginning and end of the year, respectively. Income reported on the income statement for the year was $285,000. Exclusive of the effect of other adjustments, the cash flows from operating activities to be reported on the statement of cash flows is A) $285,000. B) $295,000 C) $445,000. D) $275,000. 9. The statement of cash flows A) must be prepared on a daily basis. B) summarizes the operating, financing, and investing activities of an entity C) is another name for the income statement. D) is a special section of the income statement. 10. The primary purpose of the statement of cash flows is to A) provide information about the investing and financing activities during a period. B) prove that revenues exceed expenses if there is a net income. C) provide information about the cash receipts and cash payments during a period. D) facilitate banking relationships. 11. Copper Manufacturing has prepared the following monthly flexible manufacturing overhead budget for its Mixing Department COPPER MANUFACTURING Monthly Flexible Manufacturing Overhead Budget Mixing Department Activity level 4.000 Direct labor hours 3.000 Variable costs $ 4,000 20,000 3,000 15,000 Indirect materials Indirect labor Factory supplies 30,000 Total variable 22,500 Fixed costs 20,000 12,000 15,000 47,000 $77.000 20,000 12,000 15,000 47.000 ation Supervision Property taxes Total fixed Total costs Instructions Prepare a flexible budget at the 5,000 direct labor hours of activity. 12. During January, Ajax Co. incurs 1,850 hours of direct labor at an hourly cost of $11.80 in producing 1,000 units of its finished product. Ajax standard labor cost per unit of (2 hours x $11.00). Instructions Compute the total, price, and quantity labor variances for Ajax Co. for January. output is $20 units f 13. Classify each of the following as a(n): A. Operating Activity B. Investing Activity C. Financing Activity 1 Issuance of bonds. 2. Sale of equipment. 3. Amortization expense. 4. Purchase of treasury stock. 5. Receipt of dividends on investment. 6. Purchase of land 14. Barton Company had net income of $193,000 in 20 Depreciation expense for the year is $48,000. During the year, Accounts Receivable increased $9,000 and Prepaid Expenses decreased $1,000. The company also sold equipment at a loss of $3,000. Instructions Calculate net cash flows from operating activities using the indirect method
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


