Question: 1) What is wrong with the last formula ($740,000) , provide your explanation. 2) What formula do you suggest? Write your own answer. Logistics Example
1) What is wrong with the last formula ($740,000) , provide your explanation.
2) What formula do you suggest? Write your own answer.
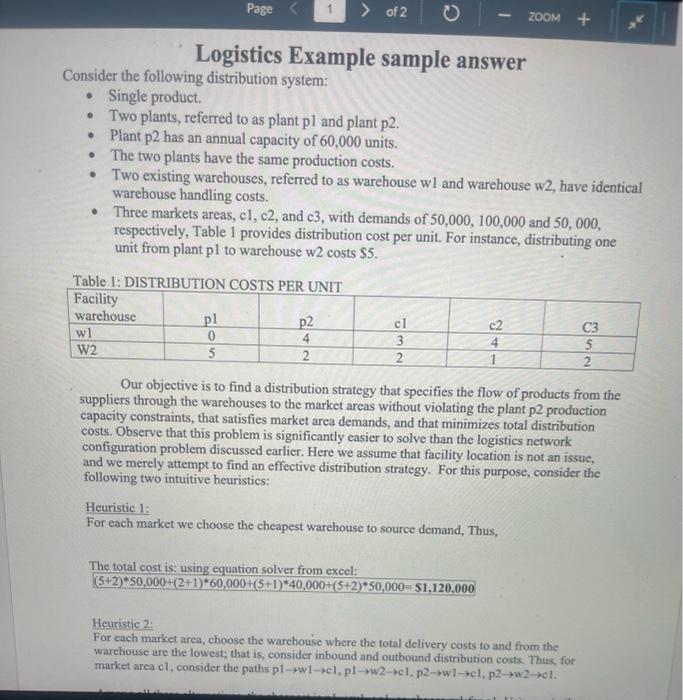
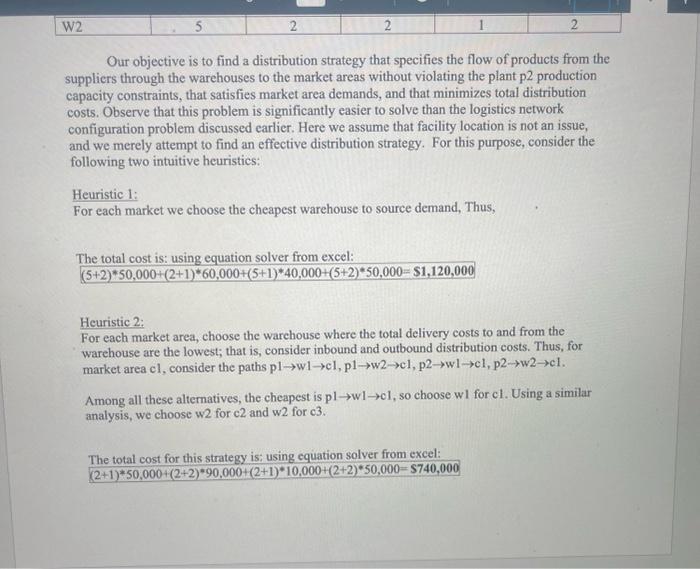
Logistics Example sample answer Consider the following distribution system: - Single product. - Two plants, referred to as plant pl and plant p2. - Plant p2 has an annual capacity of 60,000 units. - The two plants have the same production costs. - Two existing warehouses, referred to as warehouse wl and warehouse w2, have identical warehouse handling costs. - Three markets areas, c1, c2, and c3, with demands of 50,000,100,000 and 50,000 , respectively, Table 1 provides distribution cost per unit. For instance, distributing one unit from plant p1 to warehouse w2 costs $5. Our objective is to find a distribution strategy that specifies the flow of products from the suppliers through the warehouses to the market areas without violating the plant p2 production capacity constraints, that satisfies market area demands, and that minimizes total distribution costs. Observe that this problem is significantly easier to solve than the logistics network configuration problem discussed earlier. Here we assume that facility location is not an issue, and we merely attempt to find an effective distribution strategy. For this purpose, consider the following two intuitive heuristics: Heuristic 1: For each market we choose the cheapest warchouse to source demand, Thus, The total cost is: using equation solver from excel: (5+2)50,000+(2+1)60,000+(5+1)40,000+(5+2)50,000=$1,120,000 Heuristic 2: For euch market area, choose the warehouse where the total delivery costs to and from the warchouse are the lowest; that is, consider inbound and outbound distribution costs. Thus, for Our objective is to find a distribution strategy that specifies the flow of products from the suppliers through the warehouses to the market areas without violating the plant p2 production capacity constraints, that satisfies market area demands, and that minimizes total distribution costs. Observe that this problem is significantly easier to solve than the logistics network configuration problem discussed earlier. Here we assume that facility location is not an issue, and we merely attempt to find an effective distribution strategy. For this purpose, consider the following two intuitive heuristics: Heuristic 1: For each market we choose the cheapest warehouse to source demand, Thus, The total cost is: using equation solver from excel: Thetotalcostis:usingequationsolverfromexcel:(5+2)50,000+(2+1)60,000+(5+1)40,000+(5+2)50,000=$1,120,000 Heuristic 2: For each market area, choose the warchouse where the total delivery costs to and from the warehouse are the lowest; that is, consider inbound and outbound distribution costs. Thus, for market area cl, consider the paths plw1cl,plw2cl,p2wlcl,p2w2cl. Among all these alternatives, the cheapest is plwlcl, so choose wl for cl. Using a similar analysis, we choose w 2 for c2 and w 2 for 3 . The total cost for this strategy is: using equation solver from excel: (2+1)50,000+(2+2)90,000+(2+1)10,000+(2+2)50,000=$740,000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


