Question: 1- Write a C++ program to implement the Example on Chapter 6 - Lecture 1 Slide 5. You need to print a table like Table

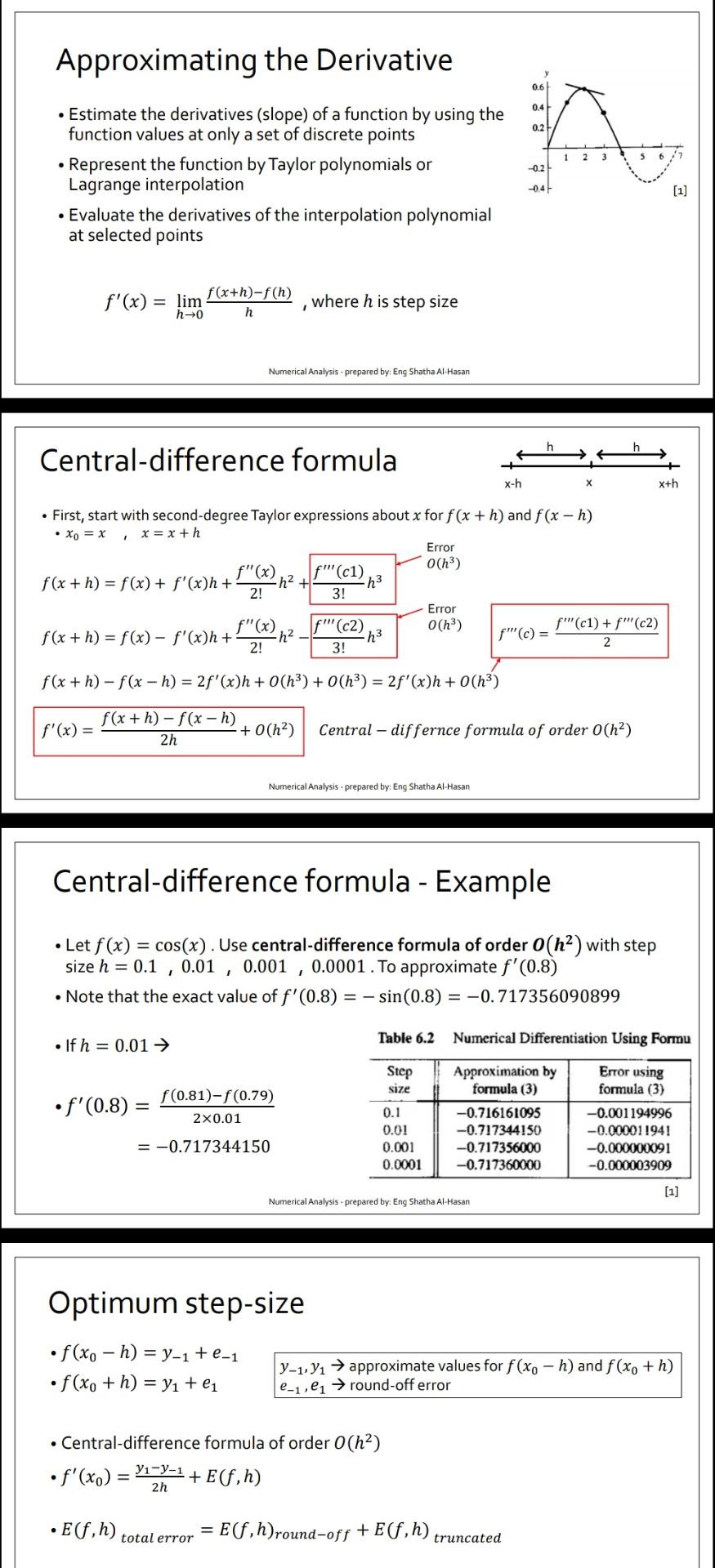

1- Write a C++ program to implement the Example on Chapter 6 - Lecture 1 Slide 5. You need to print a table like Table 6.2 and to find optimum step size from the table (minimum error). 2- Complete your program by implementing the Example on Chapter 6 - Lecture 1 Slide 8. And compare the result with optimum step size found on part 1 above. Approximating the Derivative 0.6 0.41 0.2 Estimate the derivatives (slope) of a function by using the function values at only a set of discrete points Represent the function by Taylor polynomials or Lagrange interpolation Evaluate the derivatives of the interpolation polynomial at selected points A -0.2 -04 [1] f(x+h)-f(h) f'(x) = lim h0 h 1 where his step size Numerical Analysis - prepared by: Eng Shatha Al-Hasan Central-difference formula x-h x+h First, start with second-degree Taylor expressions about x for f(x + h) and f(x - h) Xo = x , x= x + Error o(hu) f(x + h) = f(x) + f'(x)h + h2 + f''(c1) h3 2! 3! Error f"(x) f"(c2) O(h) f''(c1) + f''(c2) f(x + h) = f(x) - f'(x)h + h2 f"(c) = 2! 3! 2 f"(x) h3 f(x +h)-f(x - h) = 2f'(x)h + O(h3) + O(h3) = 2f'(x)h + O(h3) f'(x) = f(x+h)-f(x - h) + 0(h) 2h Central - differnce formula of order O(h) Numerical Analysis - prepared by: Eng Shatha Al-Hasan Central-difference formula - Example Let f(x) = cos(x). Use central-difference formula of order 0(ha) with step size h = 0.1 0.01, 0.001 0.0001. To approximate f'(0.8) Note that the exact value of f'(0.8) = sin(0.8) = -0.717356090899 . If h = 0.01 Table 6.2 Numerical Differentiation Using Formu Error using formula (3) f'(0.8) = f(0.81)-f(0.79) 20.01 Step size 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.0001 Approximation by formula (3) -0.716161095 -0.717344150 -0.717356000 -0.717360000 = -0.717344150 -0.001194996 -0.000011941 -0.000000091 -0.000003909 Numerical Analysis - prepared by: Eng Shatha Al-Hasan Optimum step-size f(xo - h) = y-1 +e-1 f(xo + h) = y + e1 y-1,91 approximate values for f(xo - h) and f(xo+h) e-1,ei round-off error Central-difference formula of order 0(h) f'(x) Y-y-1 +E(f,h) 2h E(f,h) = total error Elf,h)round-off + E(f,h) truncated Central-difference formula - Example Let f(x) = cos(x). Use central-difference formula of order O(ha) with step size h = 0.1, 0.01 , 0.001 , 0.0001 . To approximate f'(0.8) Note that the exact value of f'(0.8) = - sin(0.8) = -0.717356090899 If h = 0.01 Table 6.2 Numerical Differentiation Using Formu Step Error using formula (3) size f'(0.8) = f(0.81)-f(0.79) 2x0.01 Approximation by formula (3) -0.716161095 -0.717344150 -0.717356000 -0.717360000 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.0001 = -0.717344150 -0.001194996 -0.0000! !941 -0.000000091 -0.000003909 [1] Numerical Analysis - prepared by: Eng Shatha Al-Hasan Optimum step-size f(xo - h) = y-1 +e-1 f(xo + h) = 91 +41 Y-1,91 approximate values for f(xo - h) and f(xo +h) e-1,ei round-off error Central-difference formula of order 0(ha) f'(x) Y-y-1 + Ef,h) 2h Ef,h) - Elf,h)round-off + Ef,h) total error truncated Numerical Analysis - prepared by: Eng Shatha Al-Hasan Optimum step-size (cont'd) Elf,h) total error E(f, h)round-off + E(f,h) truncated ei-e-1 + 2h h2 f(3)(C) 3! Assume: le-il se,leil Se, M = max{\f(3)(x)}} Then, error bound: \E(f,h) > 2 Mh2 + 2h 6 To find optimum value of h: a(h) = 0 h = 1 = ($) Numerical Analysis - prepared by: Eng Shatha Al-Hasan Optimum step-size - Example Let f(x) = cos(x) and = 0.5 x 10-9. Find optimum step size for Central-difference formula of order O(h2) \f(3)(x) = sin(x)] = 1 M= 1 (3x0.5X10-9 .h= h = = = 0.001144714 1 Note that from previous example, optimum step size h = 0.001
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


