Question: $1,000 is $1,000, except when you have to wait. In this typical delayed discounting study, researchers asked a group of high school seniors planning to
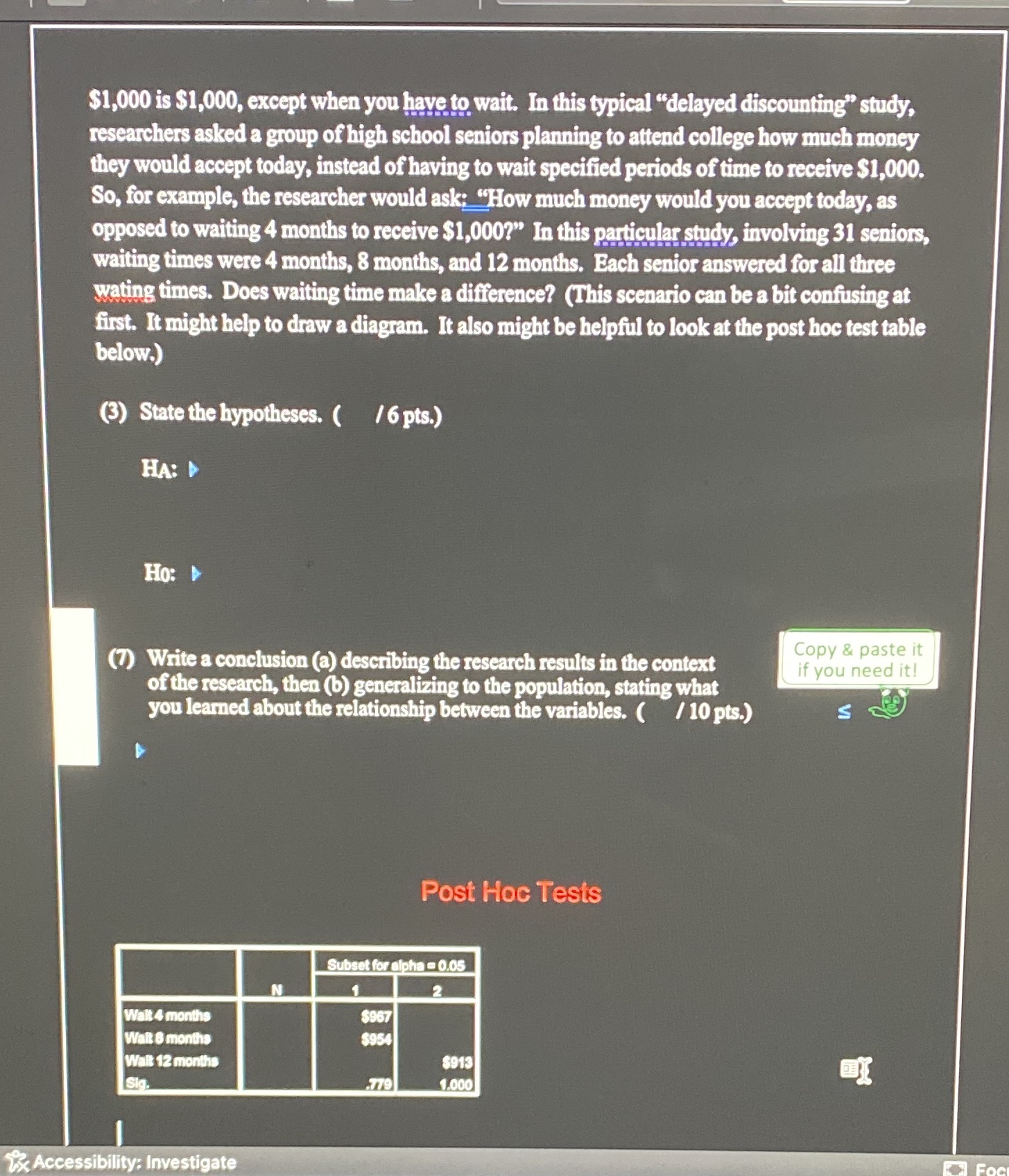
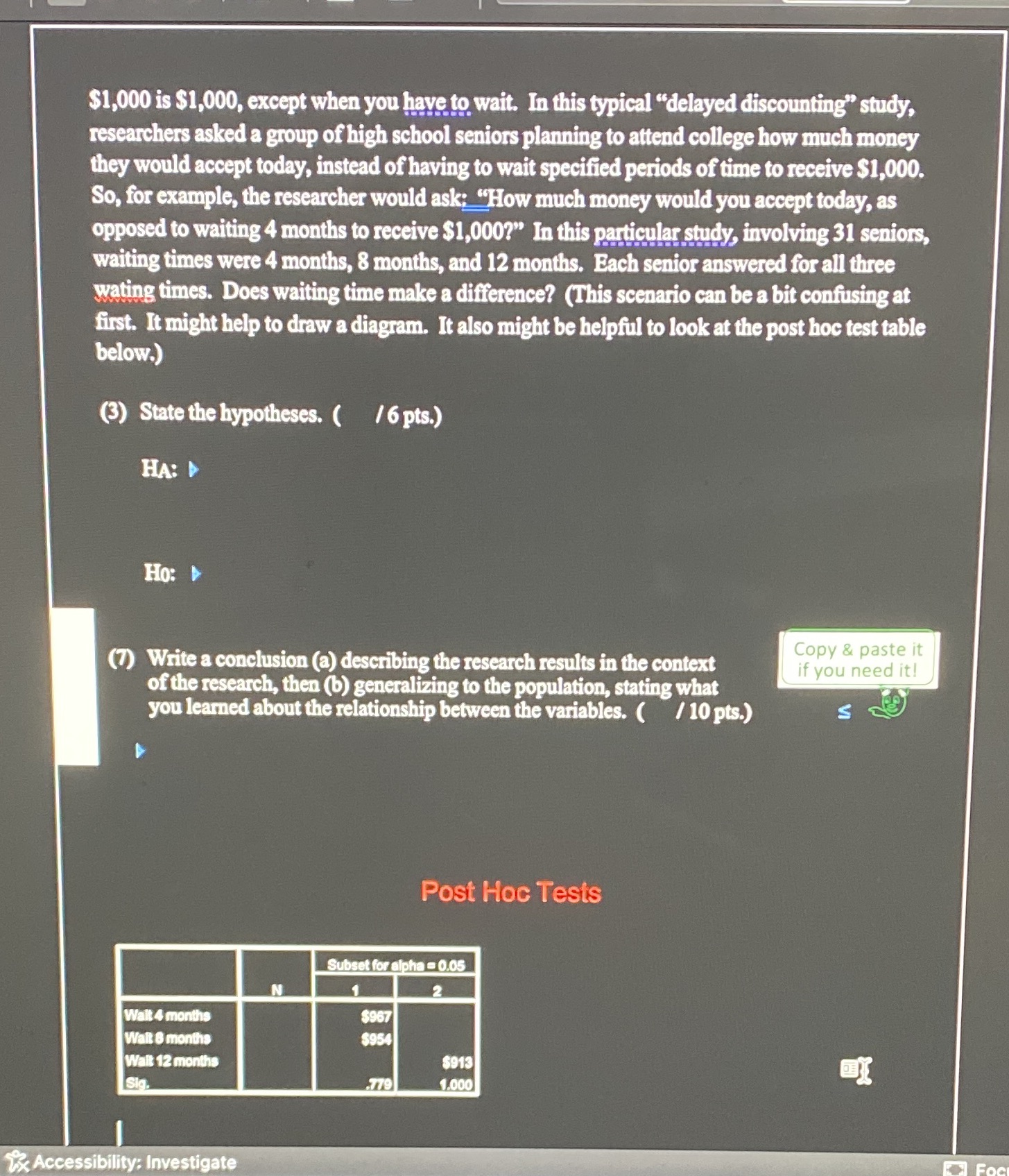
$1,000 is $1,000, except when you have to wait. In this typical "delayed discounting" study, researchers asked a group of high school seniors planning to attend college how much money they would accept today, instead of having to wait specified periods of time to receive $1,000. So, for example, the researcher would ask: "How much money would you accept today, as opposed to waiting 4 months to receive $1,000?" In this particular study, involving 31 seniors, waiting times were 4 months, 8 months, and 12 months. Each senior answered for all three wating times. Does waiting time make a difference? (This scenario can be a bit confusing at first. It might help to draw a diagram. It also might be helpful to look at the post hoc test table below.) (3) State the hypotheses. ( /6 pts.) HA: D Ho: (7) Write a conclusion (a) describing the research results in the context Copy & paste it if you need it! of the research, then (b) generalizing to the population, stating what you learned about the relationship between the variables. ( / 10 pts.) S Post Hoc Tests Subset for alpha = 0.05 Wait 4 months $967 Walt 8 months $954 Wait 12 months $913 .779 1.000 Accessibility: Investigate
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


