Question: 11.2. Greedy Algorithm to the TSP We've seen how we can formulate the TSP as a Linear Programming problem. Unfortunately, as we mentioned earlier, the
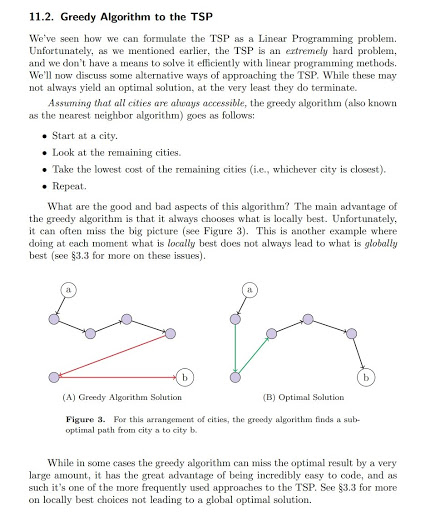
11.2. Greedy Algorithm to the TSP We've seen how we can formulate the TSP as a Linear Programming problem. Unfortunately, as we mentioned earlier, the TSP is an extremely hard problem. and we don't have a means to solve it efficiently with linear programming methods. We'll now discuss some alternative ways of approaching the TSP. While these may not always yield an optimal solution, at the very least they do terminate. Assuming that all cities are always accessible, the greedy algorithm (also known as the nearest neighbor algorithm) goes as follows: . Start at a city. . Look at the remaining cities. . Take the lowest cost of the remaining cities (i.c., whichever city is closest). . Repeat. What are the good and bad aspects of this algorithm? The main advantage of the greedy algorithm is that it always chooses what is locally best. Unfortunately. it can often miss the big picture (see Figure 3). This is another example where doing at each moment what is locally best does not always lead to what is globally best (see $3.3 for more on these issues). (A) Greedy Algorithm Solution (B) Optimal Solution Figure 8. For this arrangement of cities, the greedy algorithm finds a sub- optimal path from city a to city b. While in some cases the greedy algorithm can miss the optimal result by a very large amount, it has the great advantage of being incredibly easy to code, and as such it's one of the more frequently used approaches to the TSP. See $3.3 for more on locally best choices not leading to a global optimal solution
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


