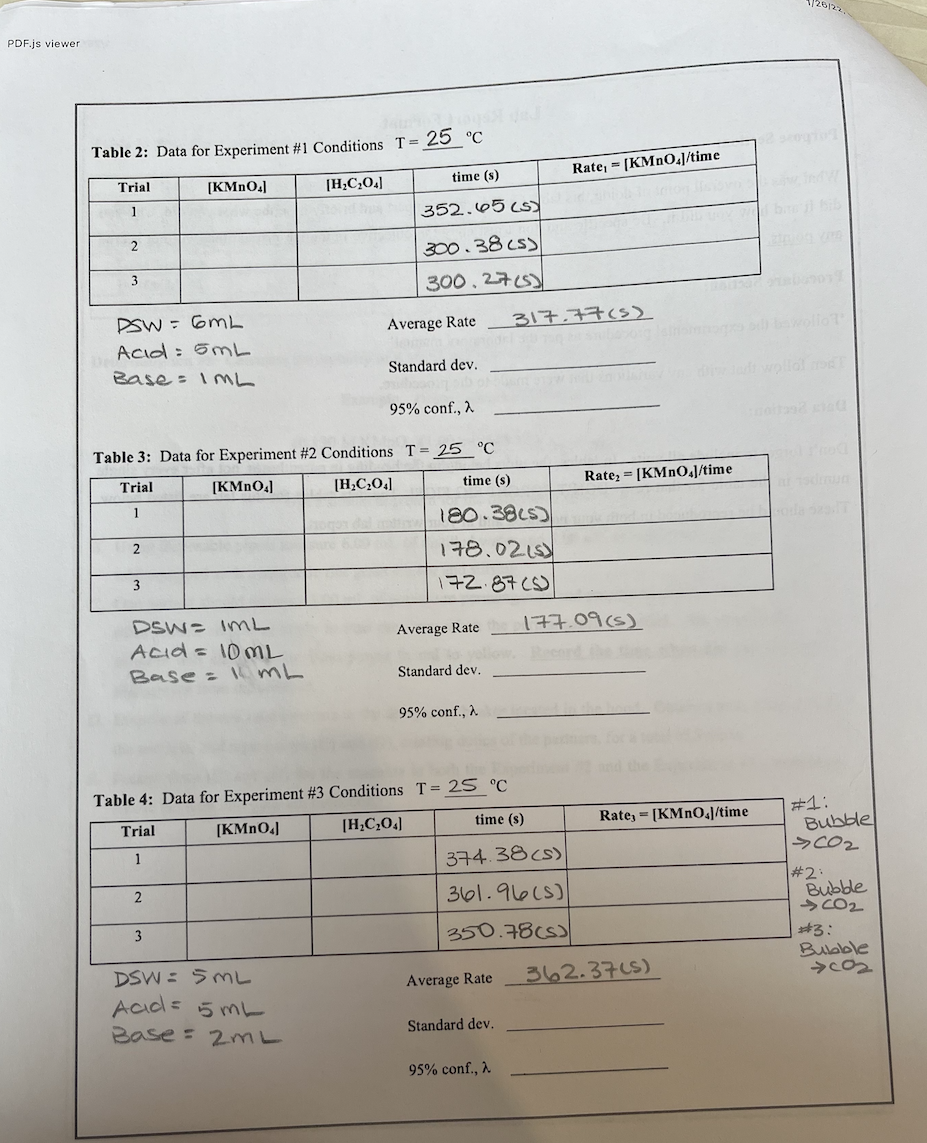
Question: 128122 PDF.js viewer Table 2: Data for Experiment #1 Conditions T= 25C Rate, = [KMnO.J/time time (s) Trial [KMnO4] [H,C20.] 1 352.6565 2 300.38 (5)
![25C Rate, = [KMnO.J/time time (s) Trial [KMnO4] [H,C20.] 1 352.6565 2](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f84622b53c6_91366f8462200c15.jpg)
128122 PDF.js viewer Table 2: Data for Experiment #1 Conditions T= 25C Rate, = [KMnO.J/time time (s) Trial [KMnO4] [H,C20.] 1 352.6565 2 300.38 (5) 3 300,27153 Average Rate 317.77(s) DOW= 6ML Acid: 5ML Base: IML Standard dev. 95% conf., a Rate = [KMnO.J/time Table 3: Data for Experiment #2 Conditions T = 25C Trial [KMnO4) [H,C,0:1 time (s) 1 180.3825) 2 178.021) 3 172 87(6) 177.09 (5) Average Rate Dow= IML Acid = 10ML Base = 1 ML Standard dev. 95% conf., a Rate; = [KMnO.J/time #1: Table 4: Data for Experiment #3 Conditions T = 25 C Trial [KMn0.] [H,C,0) time (s) 1 374.38 (s) 2 361.96(s) Bubble >CO2 #2 : Bubble CO2 #3: Bubble cos 3 350.78cs) Average Rate 362.3715) DSW 5ML Acd= 5 mL Base: 2ML Standard dev. 95% conf., a Determination of Reaction Order: The results from the various pairs of experiments will now be combined to find X and Y. The conditions for Experiments #1 and #2 differ by the oxalic acid concentration, [H2C,04). We can therefore use Eqn. 4 to give the reaction order with respect oxalic acid: Eqn. 4 Y In (rate,/rate) In ([H,C,0,1,/[H,C,0.12) Substitute your values of rate, and rate, to obtain Y; remember that In" is natural log not log base 10. Now we can use results from Experiments #1 and #3 to get a similar expression for the reaction order with respect to potassium permanganate. X= In (rate, /rate) In ([KMnO,1,/[KMn0,1) Eqn. 5 Substitute your values of rate, and ratez to obtain X. Now we can write the overall rate equation, substituting numbers for X and Y: rate = k [KMnO4]*[H_C204] Then we can solve for the rate constant, k, using data from any of the three experiments. Eqn. 6 k= rate [KMnO.]*[H,C,0.1" The units of k depend on the values of X and Y. The rate has units of mol/L's. Therefore, the rate constant has units of mol(1-X-Y)/L (1-X-Y) .s. As an example, if X = 1.5 and Y=0.5, the units of k are mol(-1.5-0.5)/L (1-1.5-0.5) -s = mol/L's=L/mol-s. Reaction Order Data: Reaction Order X (rounded to nearest 10 h) Reaction Order Y (rounded earest 10') Overall Order of Reaction X+Y Rate constant, k (with proper units) 128122 PDF.js viewer Table 2: Data for Experiment #1 Conditions T= 25C Rate, = [KMnO.J/time time (s) Trial [KMnO4] [H,C20.] 1 352.6565 2 300.38 (5) 3 300,27153 Average Rate 317.77(s) DOW= 6ML Acid: 5ML Base: IML Standard dev. 95% conf., a Rate = [KMnO.J/time Table 3: Data for Experiment #2 Conditions T = 25C Trial [KMnO4) [H,C,0:1 time (s) 1 180.3825) 2 178.021) 3 172 87(6) 177.09 (5) Average Rate Dow= IML Acid = 10ML Base = 1 ML Standard dev. 95% conf., a Rate; = [KMnO.J/time #1: Table 4: Data for Experiment #3 Conditions T = 25 C Trial [KMn0.] [H,C,0) time (s) 1 374.38 (s) 2 361.96(s) Bubble >CO2 #2 : Bubble CO2 #3: Bubble cos 3 350.78cs) Average Rate 362.3715) DSW 5ML Acd= 5 mL Base: 2ML Standard dev. 95% conf., a Determination of Reaction Order: The results from the various pairs of experiments will now be combined to find X and Y. The conditions for Experiments #1 and #2 differ by the oxalic acid concentration, [H2C,04). We can therefore use Eqn. 4 to give the reaction order with respect oxalic acid: Eqn. 4 Y In (rate,/rate) In ([H,C,0,1,/[H,C,0.12) Substitute your values of rate, and rate, to obtain Y; remember that In" is natural log not log base 10. Now we can use results from Experiments #1 and #3 to get a similar expression for the reaction order with respect to potassium permanganate. X= In (rate, /rate) In ([KMnO,1,/[KMn0,1) Eqn. 5 Substitute your values of rate, and ratez to obtain X. Now we can write the overall rate equation, substituting numbers for X and Y: rate = k [KMnO4]*[H_C204] Then we can solve for the rate constant, k, using data from any of the three experiments. Eqn. 6 k= rate [KMnO.]*[H,C,0.1" The units of k depend on the values of X and Y. The rate has units of mol/L's. Therefore, the rate constant has units of mol(1-X-Y)/L (1-X-Y) .s. As an example, if X = 1.5 and Y=0.5, the units of k are mol(-1.5-0.5)/L (1-1.5-0.5) -s = mol/L's=L/mol-s. Reaction Order Data: Reaction Order X (rounded to nearest 10 h) Reaction Order Y (rounded earest 10') Overall Order of Reaction X+Y Rate constant, k (with proper units)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


