Question: 13 14 - # Rolling Die 15 - ## Fair Die 16 Setup the experiment where we roll two fair six sided die independently, and
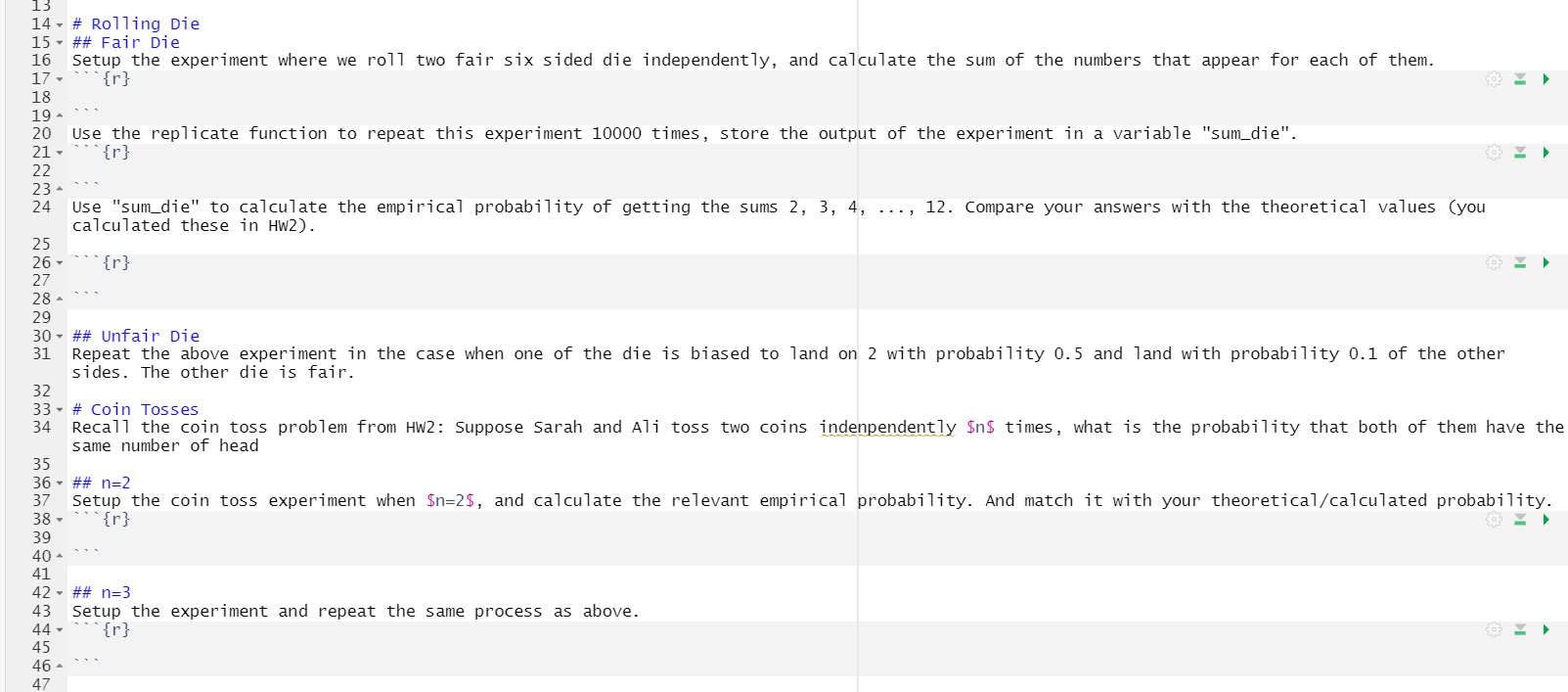

13 14 - # Rolling Die 15 - ## Fair Die 16 Setup the experiment where we roll two fair six sided die independently, and calculate the sum of the numbers that appear for each of them. 17, 18 19 - {r} 20 Use the replicate function to repeat this experiment 10000 times, store the output of the experiment in a variable "sum_die". 21 - {r} 22 23 - 24 Use "sum_die" to calculate the empirical probability of getting the sums 2, 3, 4, ..., 12. Compare your answers with the theoretical values (you calculated these in HW2). 25 26 - '{r} 27 28 - 29 30 - ## Unfair Die 31 Repeat the above experiment in the case when one of the die is biased to land on 2 with probability 0.5 and land with probability 0.1 of the other sides. The other die is fair. 32 33 - # Coin Tosses 34 Recall the coin toss problem from HW2: Suppose Sarah and Ali toss two coins indenpendently $n$ times, what is the probability that both of them have the same number of head 35 36 - ## n=2 37 Setup the coin toss experiment when $n=2$, and calculate the relevant empirical probability. And match it with your theoretical/calculated probability. 38 - {r} 39 40 - 41 42 - ## n=3 43 Setup the experiment and repeat the same process as above. 44 - "*{r} 45 46 47 13 14 - # Rolling die 15 - ## Fair die 16 setup the experiment where we roll two fair six sided die independently, and calculate the sum of the numbers that appear for each of them. 17, ***{r} 18 19. 20 Use the replicate function to repeat this experiment 10000 times, store the output of the experiment in a variable "sum_die". 21 - 22 23 24 use "sum_die" to calculate the empirical probability of getting the sums 2, 3, 4, ..., 12. Compare your answers with the theoretical values (you calculated these in HW2). 25 26***{r} 27 28 29 30 - ## Unfair die 31 Repeat the above experiment in the case when one of the die is biased to land on 2 with probability 0.5 and land with probability 0.1 of the other sides. The other die is fair. 32 33 - # Coin Tosses 34 Recall the coin toss problem from Hw2: Suppose Sarah and Ali toss two coins indenpendently $n$ times, what is the probability that both of them have the same number of head 13 14 - # Rolling Die 15 - ## Fair Die 16 Setup the experiment where we roll two fair six sided die independently, and calculate the sum of the numbers that appear for each of them. 17, 18 19 - {r} 20 Use the replicate function to repeat this experiment 10000 times, store the output of the experiment in a variable "sum_die". 21 - {r} 22 23 - 24 Use "sum_die" to calculate the empirical probability of getting the sums 2, 3, 4, ..., 12. Compare your answers with the theoretical values (you calculated these in HW2). 25 26 - '{r} 27 28 - 29 30 - ## Unfair Die 31 Repeat the above experiment in the case when one of the die is biased to land on 2 with probability 0.5 and land with probability 0.1 of the other sides. The other die is fair. 32 33 - # Coin Tosses 34 Recall the coin toss problem from HW2: Suppose Sarah and Ali toss two coins indenpendently $n$ times, what is the probability that both of them have the same number of head 35 36 - ## n=2 37 Setup the coin toss experiment when $n=2$, and calculate the relevant empirical probability. And match it with your theoretical/calculated probability. 38 - {r} 39 40 - 41 42 - ## n=3 43 Setup the experiment and repeat the same process as above. 44 - "*{r} 45 46 47 13 14 - # Rolling die 15 - ## Fair die 16 setup the experiment where we roll two fair six sided die independently, and calculate the sum of the numbers that appear for each of them. 17, ***{r} 18 19. 20 Use the replicate function to repeat this experiment 10000 times, store the output of the experiment in a variable "sum_die". 21 - 22 23 24 use "sum_die" to calculate the empirical probability of getting the sums 2, 3, 4, ..., 12. Compare your answers with the theoretical values (you calculated these in HW2). 25 26***{r} 27 28 29 30 - ## Unfair die 31 Repeat the above experiment in the case when one of the die is biased to land on 2 with probability 0.5 and land with probability 0.1 of the other sides. The other die is fair. 32 33 - # Coin Tosses 34 Recall the coin toss problem from Hw2: Suppose Sarah and Ali toss two coins indenpendently $n$ times, what is the probability that both of them have the same number of head
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


