Question: 13. The classical Stokes' theorem asserts, typically, that if x: D R is a 2-segment and V is a vector field on R?, then I

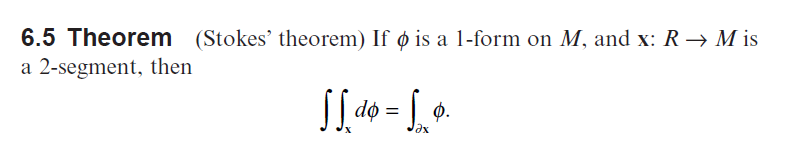
13. The classical Stokes' theorem asserts, typically, that if x: D R is a 2-segment and V is a vector field on R?, then I v ds - Slu(8xV)da. where V x V = curl V. Interpret this as a special case of Theorem 6.5. (Hint: Assume d - VEG F? du dv, and use Ex. 8 of Sec. 1.6.) This geometric result will be clarified later on. Note that Theorem 6.5 does not involve geometry. 6.5 Theorem (Stokes' theorem) If o is a 1-form on M, and x: R Mis a 2-segment, then SS.do = Sex 0. 13. The classical Stokes' theorem asserts, typically, that if x: D R is a 2-segment and V is a vector field on R?, then I v ds - Slu(8xV)da. where V x V = curl V. Interpret this as a special case of Theorem 6.5. (Hint: Assume d - VEG F? du dv, and use Ex. 8 of Sec. 1.6.) This geometric result will be clarified later on. Note that Theorem 6.5 does not involve geometry. 6.5 Theorem (Stokes' theorem) If o is a 1-form on M, and x: R Mis a 2-segment, then SS.do = Sex 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


