Question: 14.1 SUMMARY . A vector-valued function is a function of the form A sample is shown fort cate with a diagram the position vectors r

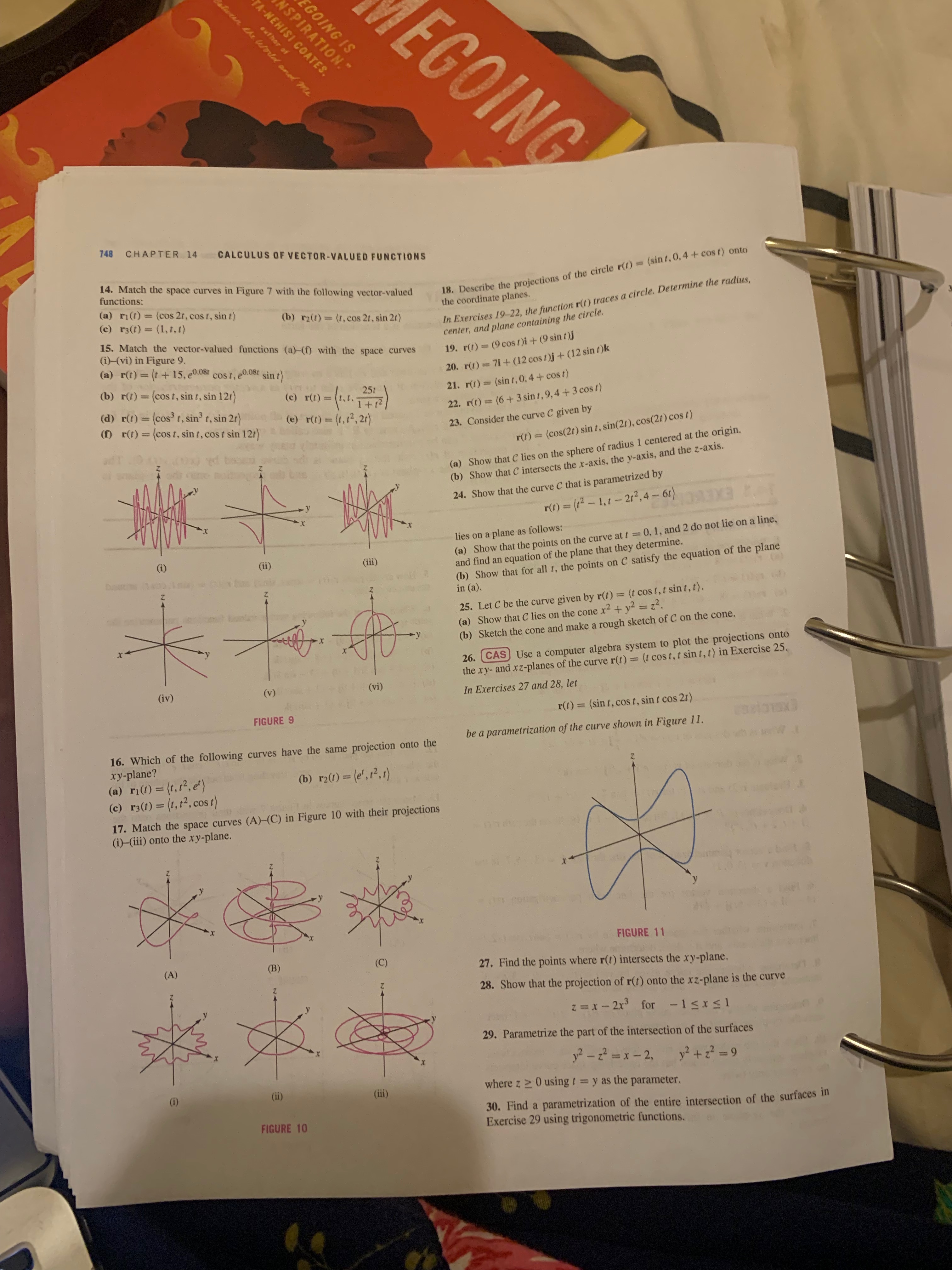

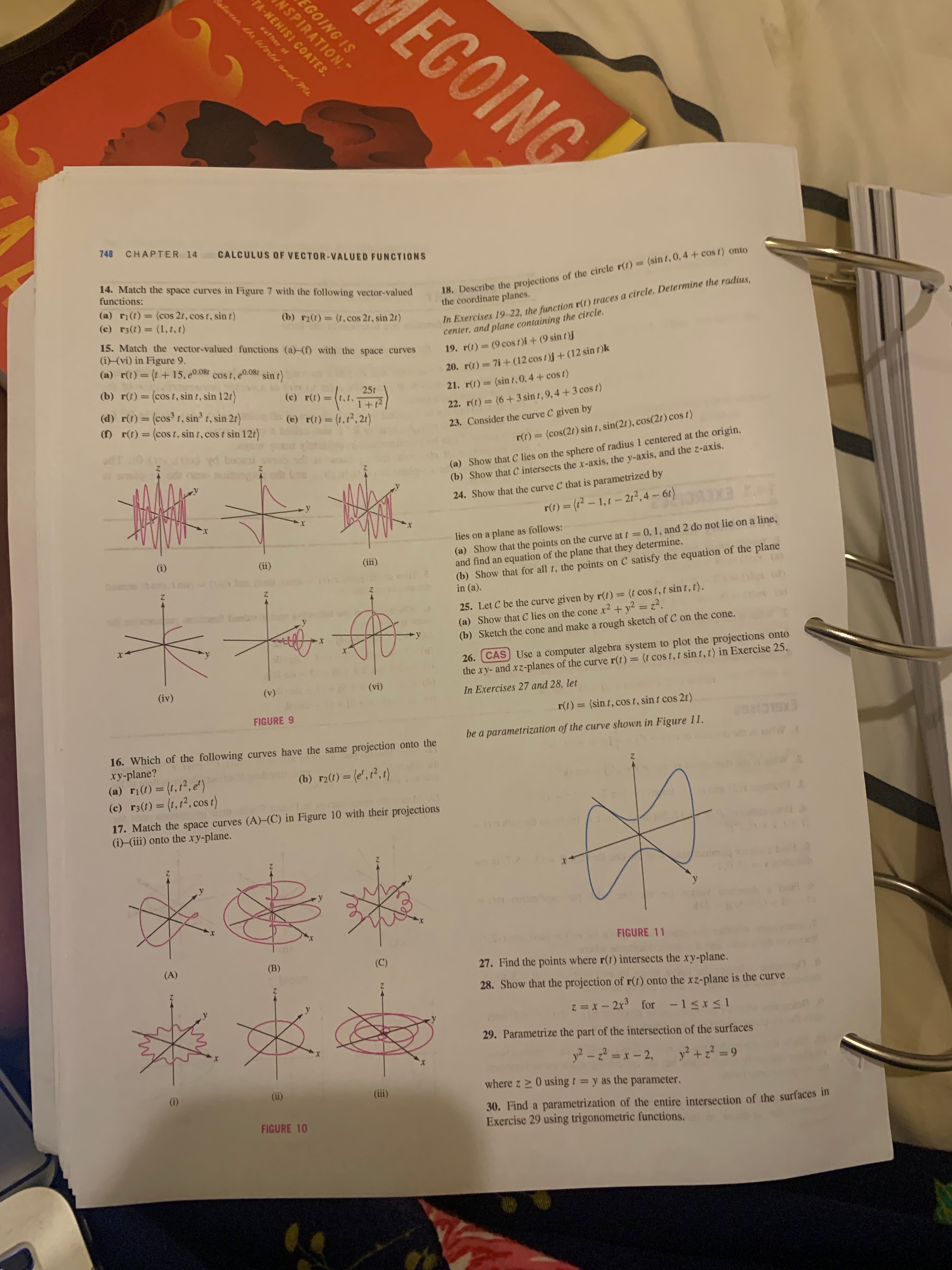
14.1 SUMMARY . A vector-valued function is a function of the form A sample is shown fort cate with a diagram the position vectors r ( t ) = (x (1 ) . y (1), z(1) > = x(1)i + >(1)j+ z(1)k (10 - DZ + 1 . We often think of f as time and r() as a moving vector whose terminal point traces out a path as a function of time. We refer to r() as a vector parametrization of the calculate the linear path, or simply as a path. (b) 21 - 31 . The underlying curve C traced by r(t) is the set of all points (x(t), y(t). z(1)) in R for onents and length of t t in the domain of r(). A curve in R' is also called a space curve. Every curve C can be parametrizationy many ways. - (9) The projection of r(t) onto the xy-plane is the curve traced by (x(1), y(t), 0). The projection onto the xz-plane is (x(t), 0, z(t)), and the projection onto the yz-plane is w - AC, where A (0, y(1), z(t)). 14.1 EXERCISES FIGURE 26 Preliminary Questions 1. Which one of the following does not parametrizatio (a) ri(1) = (8 - 1,21, 31) 5. How do the paths ri(t) = (cost, sint) and r2(f) = (sing, cost) around (b) r2(1) =13i-713j+ 13k the unit circle differ? (c) 13(1) = (8- 413, 2+ 512, 913) 6. Which three of the following vector-valued functions parametrizat same space curve? 2. What is the projection of r(!) = fi + 14j + elk onto the xz-plane? (a) (-2 + cost)i + 9j + (3 - sint)k 3. Which projection of (cost, cos 2t, sint) is a circle? (b) (2 + cost)i - 9j + (-3 - sint)k and b in the pa 4. What is the center of the circle with the following parametrization? (c) (-2 + cos 31)i + 9j + (3 - sin 3t)k (d) (-2 - cost)i + 9j + (3 + sint)k of the point r (1 ) = (-2+ cost)i+2j +(3 - sin1)k (e) (2 + cost)i + 9j + (3+ sint)k - (02's) + Exercises (2, 3) has leng direction from 1. What is the domain of r(1) = e'i + -j + ( +1)-3k? 12. Show that the path given by r(t) = (e- sint, e-cost, e-) intersects irection from the sphere x2 + y2 + z? = 4 once, traveling from outside the sphere to in- 2. What is the domain of r(s) = esi+ sj + cos sk? side as t goes from -co to co. angle of 30 13. Match the space curves in Figure 7 with their projections onto the 47 with th 3. Evaluate r(2) and r(-1) for r(t) = (sin Et, 12, (12 + 1)-1). xy-plane in Figure 8. site to v = 4. Does either of P = (4, 11, 20) or @ = (-1, 6, 16) lie on the path r(1) = opposite t (1+ 1, 2+ 12, 14)? It = A JO 5. Find a vector parametrization of the line through P = (3, -5, 7) in the -) = n jo direction v = (3, 0, 1). 6. Find a direction vector for the line with parametrization r(t) = 4- thi+ (2+51)j+ =ck. 7. Determine whether the space curve given by r(t) = (sint, cost/2, t) (A ) (C) intersects the z-axis, and if it does, determine where. FIGURE 7 8. Determine whether the curve given by r(t) = (12, 12 - 21 - 3, 1 -3) intersects the x-axis, and if it does, determine where. 9. Determine whether the space curve given by r(t) = (t, 13, 12 + 1) inter- sects the xy-plane, and if it does, determine where. 10. Show that the path given by r(t) = (cost, cos(2t), sint) intersects the xy-plane infinitely many times, but the underlying space curve intersects the xy-plane only twice. (ii) (iii) 11. Show that the space curve given by r(t) = (1 - cos(2t), t + sint, 12) (i) intersects the yz-plane in infinitely many points but does not cross FIGURE 8 through it.SPIRAT GOING IS A-NEHISI COATES. EGOING 748 CHAPTER 14 CALCULUS OF VECTOR-VALUED FUNCTIONS functions: 14. Match the space curves in Figure 7 with the following vector-valued 18. Describe the projections of the circle r(f) = (sint, 0.4 + cost) onto (a) ri(t) = (cos 2t, cost, sint) (c) 13(t) = (1, t, 1) (b) r2(1) = (t, cos 2t, sin 2t) the coordinate planes. In Exercises 19-22, the function r(t) traces a circle. Determine the radius, 15. Match the vector-valued functions (a)-(f) with the space curves center, and plane containing the circle. i) (vi) in Figure 9. 19. r(1) = (9 cost)i + (9 sint) (a) r(t) = (1+ 15, e0.08 cost, e0.08 sint 20. r(1) = 71 + (12 cost)j + (12 sint)k (b) r(t) = (cost, sint, sin 12t) 21. r(1) = (sin t, 0.4 + cost) (d) r(t) = (cost, sin' t, sin 2t) (c) r(1) = (1.1. 1+ 12 ) 22. r(1) = (6 + 3 sint, 9,4 + 3 cost) if) r(t) = (cost, sint, cost sin 12t) (e) r(t) = (1, 12, 21) 23. Consider the curve C given by r(t) = (cos(2t) sin t, sin(2t), cos(2t) cost) (a) Show that C lies on the sphere of radius 1 centered at the origin. b) Show that C intersects the x-axis, the y-axis, and the z-axis. 24. Show that the curve C that is parametriz r(1) = (12 - 1,1-212, 4-61) lies on a plane as follows: (i) (ii) (a) Show that the points on the curve at t = 0, 1, and 2 do not lie on a line, (iii) and find an equation of the plane that they determine. (b) Show that for all t, the points on C satisfy the equation of the plane in (a). 25. Let C be the curve given by r(t) = (t cost, t sint, t). a) Show that C lies on the cone x2 + y? = z. b) Sketch the cone and make a rough sketch of C on the cone. 26. CAS Use a computer algebra system to plot the projections onto (iv) (v ) the xy- and xz-planes of the curve r(1) = (t cost, t sint, t) in Exercise 25. (vi) In Exercises 27 and 28, let FIGURE 9 r(t) = (sint, cost, sint cos 2t) 16. Which of the following curves have the same projection onto the be a parametrization of the curve shown in Figure 11. xy-plane? (a) ri(1) = (t, 12, er) (b) 12(1) = (e', 12, 1) (c) 13(1) = (t, 12, cost) 17. Match the space curves (A)-(C) in Figure 10 with their projections (i) (iii) onto the xy-plane. FIGURE 11 (A) (B) 27. Find the points where r() intersects the xy-plane. 28. Show that the projection of r(t) onto the xz-plane is the curve z = x - 2x3 for - 1 5 x 1 29. Parametrization the intersection of the surfaces 12 - 22 = x-2, 12+ 2 2 = 9 (1i) (iji) where z 2 0 using t = y as the parameter. FIGURE 10 30. Find a parametrization of the entire intersection of the surfaces in Exercise 29 using trigonometric functions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


