Question: 15. Unifiers and unification Write the most general unifier (MGU) of the two terms given, or None if no unification is possible. Write your answer
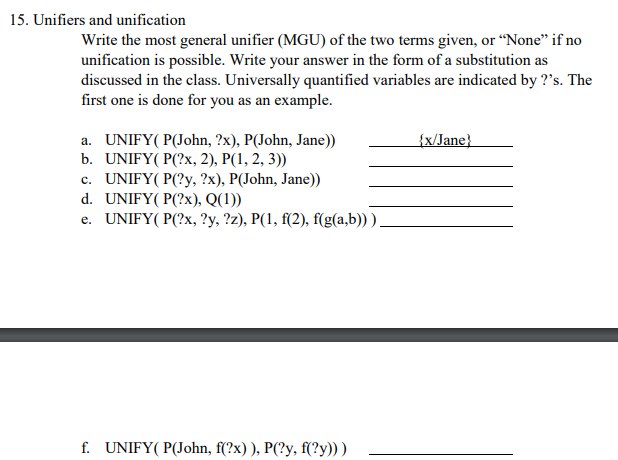
15. Unifiers and unification Write the most general unifier (MGU) of the two terms given, or "None" if no unification is possible. Write your answer in the form of a substitution as discussed in the class. Universally quantified variables are indicated by?'s. The first one is done for you as an example a. UNIFY( P(John, ?x), P(John, Jane)) x/Jane b. UNIFY( P(?x, 2), P(1, 2, 3)) c. UNIFY( P(?y, ?x), P(John, Jane)) d. UNIFY(P(2x), Q(I)) e. UNIFY(P(?x, 2y, ?z), P, 2), f(g(a,b))) f. UNIFY( P(John, f?x) ), P(?y, f?y))) 15. Unifiers and unification Write the most general unifier (MGU) of the two terms given, or "None" if no unification is possible. Write your answer in the form of a substitution as discussed in the class. Universally quantified variables are indicated by?'s. The first one is done for you as an example a. UNIFY( P(John, ?x), P(John, Jane)) x/Jane b. UNIFY( P(?x, 2), P(1, 2, 3)) c. UNIFY( P(?y, ?x), P(John, Jane)) d. UNIFY(P(2x), Q(I)) e. UNIFY(P(?x, 2y, ?z), P, 2), f(g(a,b))) f. UNIFY( P(John, f?x) ), P(?y, f?y)))
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


