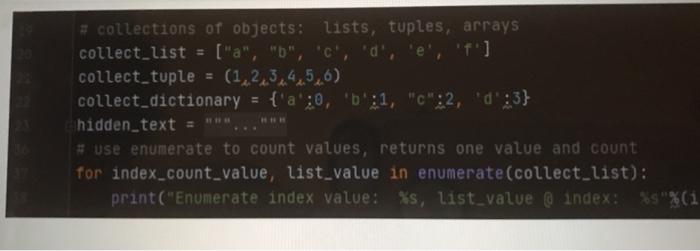
Question: 1box 2 3 4 5 6 # collections of objects: lists, tuples, arrays collect_list = [a, b, 'c': 'd', 'e',''] collect_tuple = (1,2,3,4,5,6) collect_dictionary =
![tuples, arrays collect_list = ["a", "b", 'c': 'd', 'e',''] collect_tuple = (1,2,3,4,5,6)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3cc9296709_65066f3cc92284c9.jpg)
 1box
1box 2
2 3
3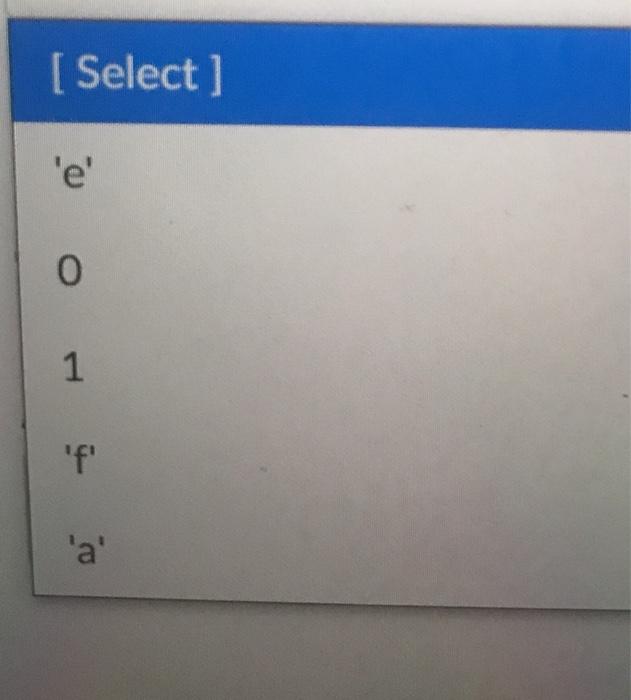 4
4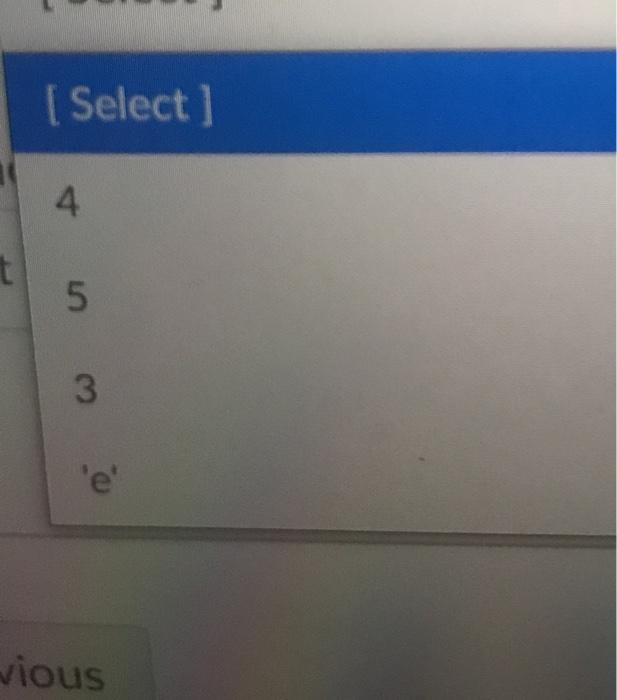 5
5![every cycle of the loop, starting at [Select ] and ending at](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3cc966c86c_65466f3cc960c2d6.jpg) 6
6# collections of objects: lists, tuples, arrays collect_list = ["a", "b", 'c': 'd', 'e',''] collect_tuple = (1,2,3,4,5,6) collect_dictionary = {'a': 0, 'b': 1, "C":2, 'd':3} hidden_text = # use enumerate to count values, returns one value and count for index_count_value, list_value in enumerate(collect_list): print("Enumerate index value: %s, list_value @ index: Ss"% Consider the for loop on line 37-38. This loop uses enumerate() to count the number of items in collect_list. The variable index_count_value becomes a new integer every cycle of the loop, starting at [Select ] and ending at [Select] Likewise, the variable list_value becomes a new element of collect_list every cycle of the loop, starting at [ Select] and ending with [ Select] V For example, when list_value contains "e", index_count_value is equal to [Select] Also, when index_count value is equal to 3, list_value contains [ Select ] [ Select] [ Select] 2 O le 1 'a' [Select] [ Select] 5 3 6 7 Select ] 1 'a' 'b' 0 [ Select] O 1 'f 'a' [ Select] 4 5 3 vious [ Select] [ Select] 'd e 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


