Question: 1-please, send the complete code of this program implementation of the binomial heap. 2- Find attached the code to implement the following two functions: -
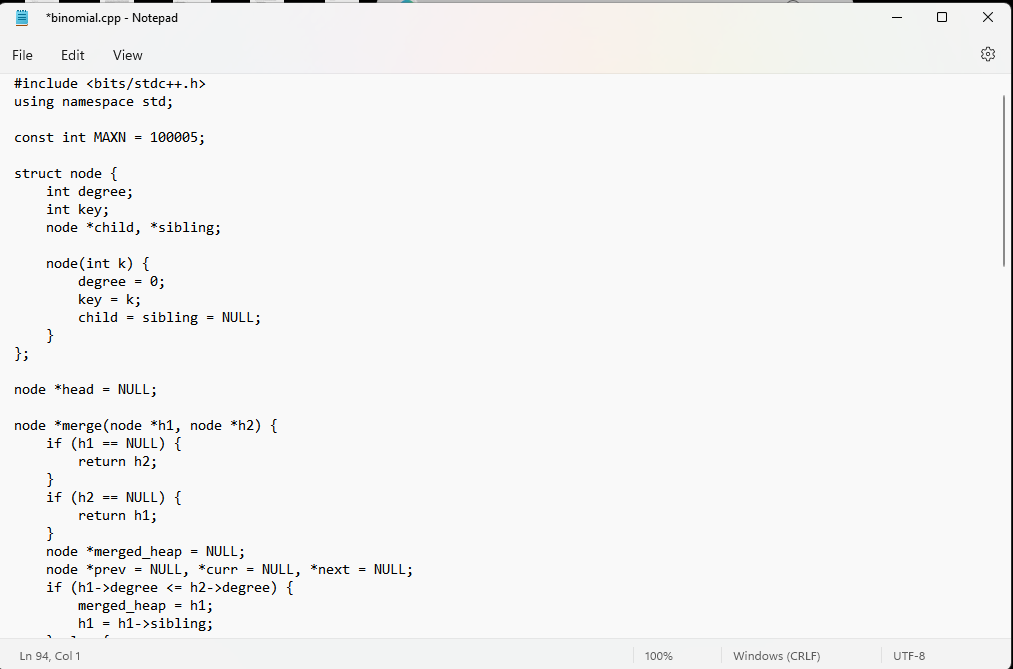
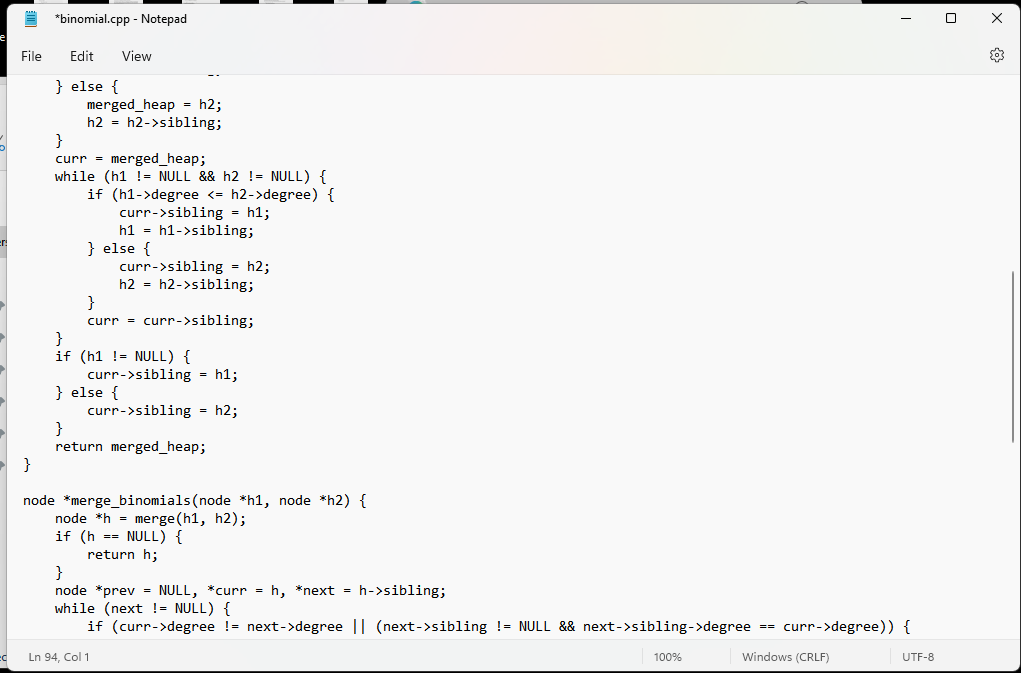
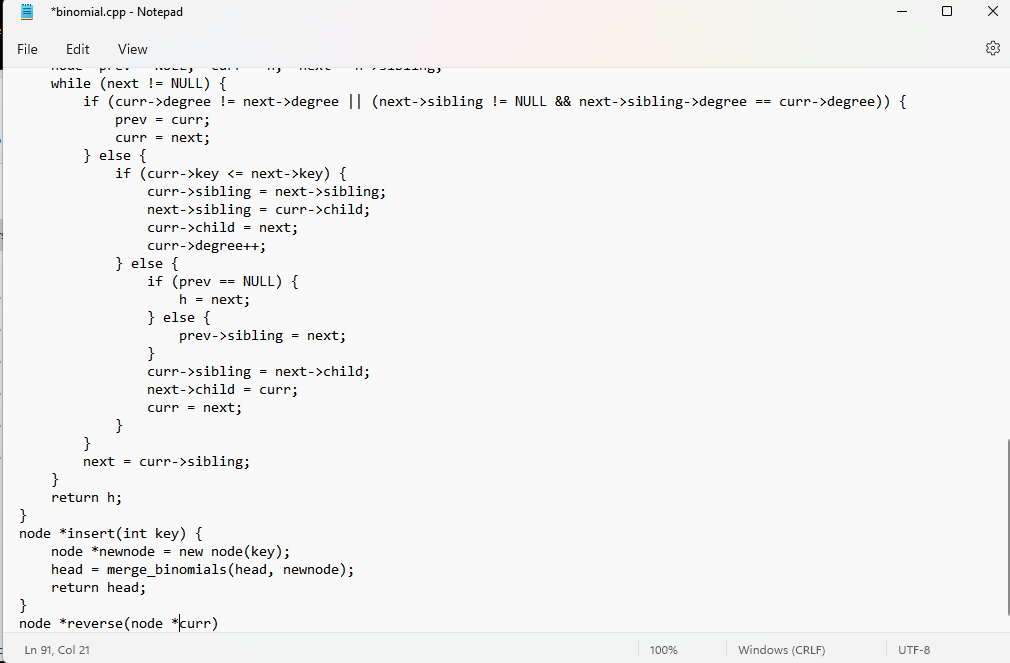
1-please, send the complete code of this program implementation of the binomial heap.
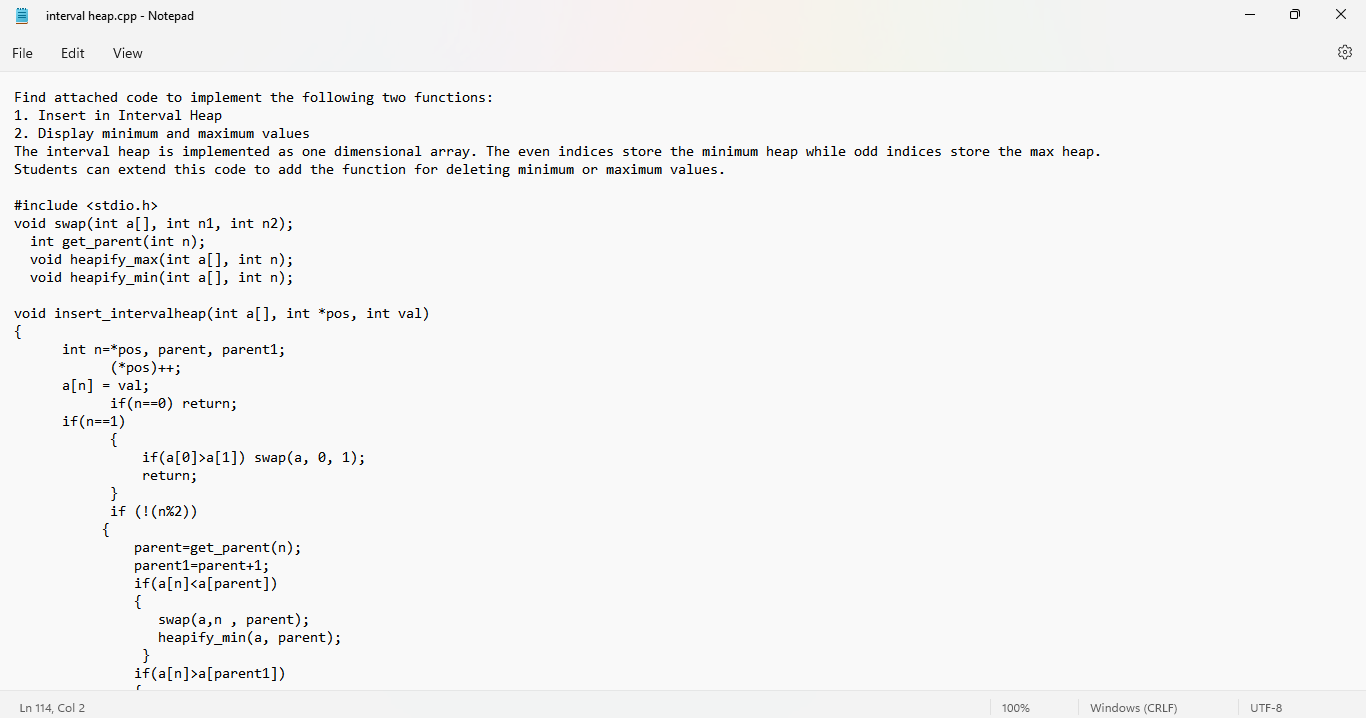
2- Find attached the code to implement the following two functions: - Insert in Interval Heap - Display minimum and maximum values The interval heap is implemented as a one-dimensional array. The even indices store the minimum heap while odd indices store the max heap. Students can extend this code to add the function for deleting minimum or maximum values.
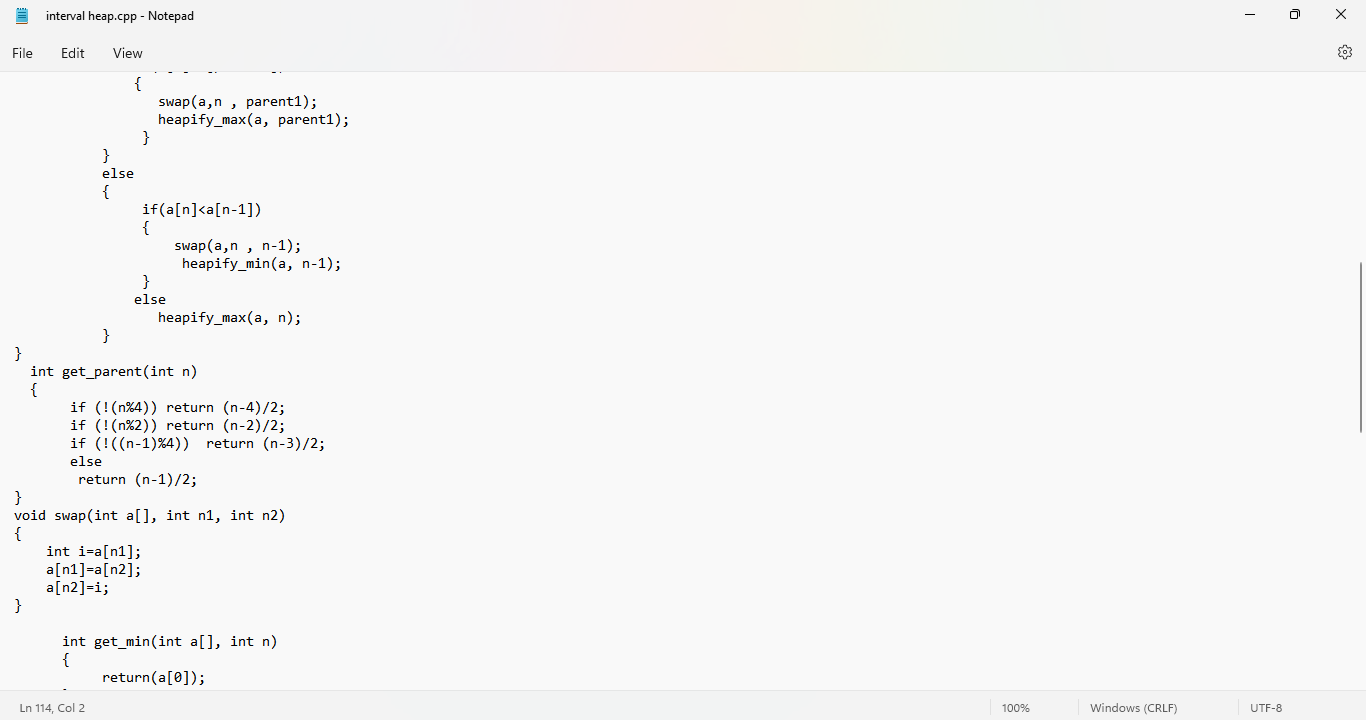
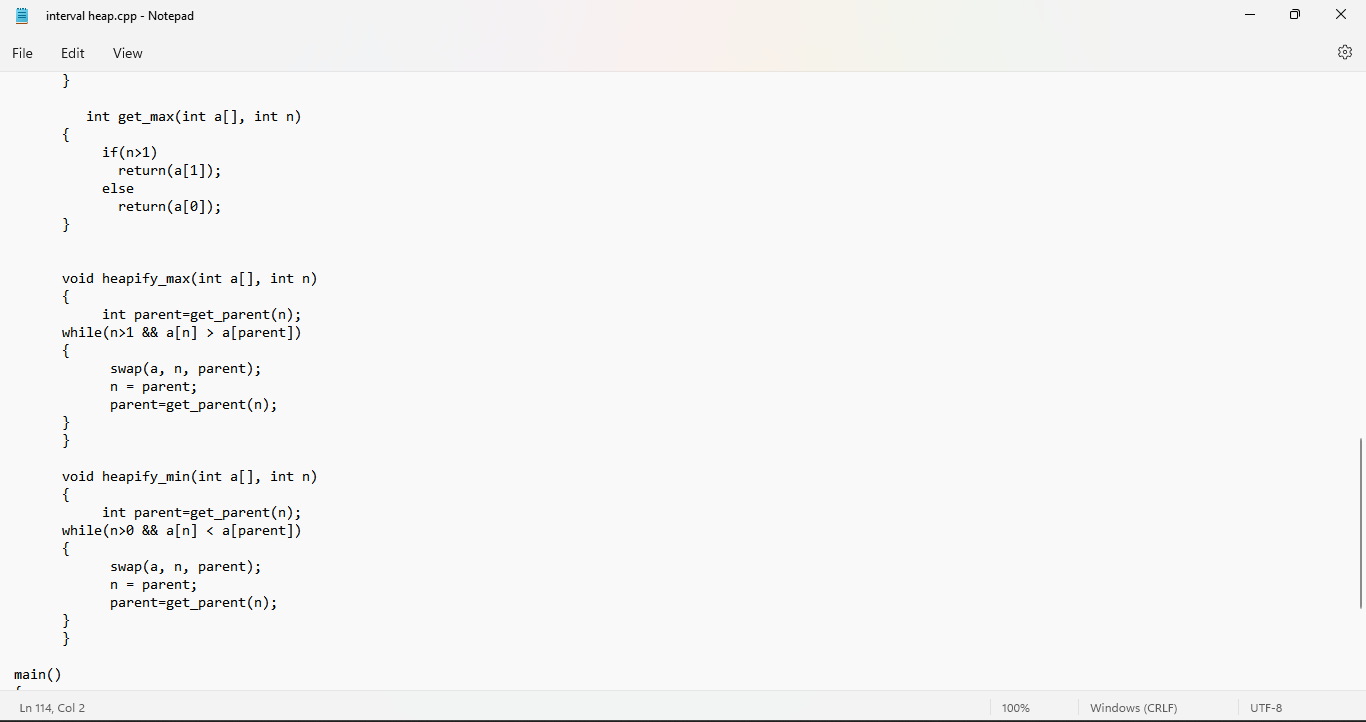
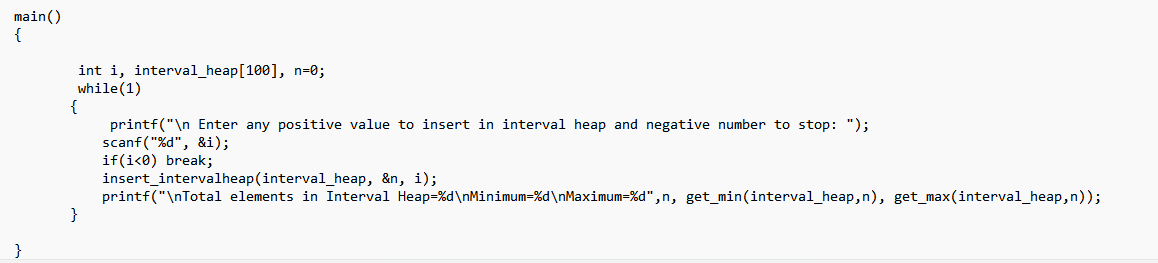
View *binomial.cpp - Notepad File Edit View \} else \{ merged_heap =h2; h2 = h2->sibling; \} curr = merged_heap; while (h1 != NULL \&\& h2!=NULL){ if (h1->degree =h2> degree) \{ curr->sibling = h1; h1 = h1->sibling; \} else \{ cur r> sibling =h2; h2 = h2->sibling; \} curr = curr > sibling; \} if (h1 != NULL) \{ curr->sibling =h1; \} else \{ curr sibling =h2; \} return merged_heap; \} node *merge_binomials(node *h1, node *h2) \{ node h=merge(h1,h2); if (h==NULL){ return h; \} node *prev = NULL, curr =h, next =h> sibling; while (next != NULL) \{ if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling != NULL \&\& next->sibling->degree == curr > degree)) \{ Ln 94, Col 1 \begin{tabular}{l|l} 100% & Windows (CRLF) \end{tabular} UTF-8 *binomial.cpp - Notepad File Edit View while (next != NULL) \{ if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling != NULL \&\& next->sibling->degree == curr > degree)) \{ prev = curr; curr = next; \} else \{ if (curr->key key) \{ curr->sibling = next->sibling; next > sibling = curr > child; curr->child = next; curr->degreet+; \} else \{ if (prev == NULL) \{ h= next; \} else \{ prev->sibling = next; \} curr sibling = next > child next > child = curr; curr = next; \} \} next = curr > sibling; \} return h; \} node *insert(int key) \{ node *newnode = new node(key); head = merge_binomials (head, newnode ); return head; \} node *reverse(node Kurr) Ln 91, Col 21 \begin{tabular}{l|l} 100% & Windows (CRLF) \end{tabular} UTF-8 Find attached code to implement the following two functions: 1. Insert in Interval Heap 2. Display minimum and maximum values The interval heap is implemented as one dimensional array. The even indices store the minimum heap while odd indices store the max heap. Students can extend this code to add the function for deleting minimum or maximum values. void swap(int a[], int n1, int n2 ); int get_parent(int n ); void heapify_max(int a[], int n); void heapify_min(int a[], int n ); void insert_intervalheap(int a[], int *pos, int val) \{ interval heap.cpp - Notepad File Edit View interval heap.cpp - Notepad File Edit View \} void heapify_max(int a[], int n ) \{ int parent=get_parent (n); while (n>1 \&\& a[n]>a[ parent ]) \{ swap(a, n, parent ); n = parent; parent=get_parent (n); \} \} void heapify_min(int a[], int n ) \{ int parent = get_parent (n); while (n>0 \&\& a[n]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


