Question: 2. 3. 4. 5. Overview: You are to write two programs, Interface and Server. After initialization, the Interface will use the fork system call and


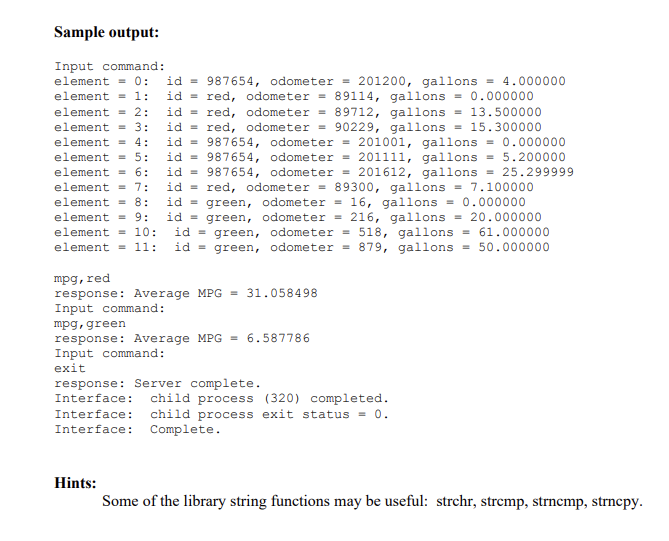
2. 3. 4. 5. Overview: You are to write two programs, Interface and Server. After initialization, the Interface will use the fork system call and an exec system call to start the execution of the Server. The Interface will accept commands from the console and send them to the Server for execution. After executing the command, the Server will send the output to the Interface for display on the console. Pipes: The Interface will need to create the pipes to be used for communication between itself and the Server prior to doing the fork. Use two pipes, one for sending commands to the Server and one for sending the response to the Interface. Interface: In addition to tasks described elsewhere, the Interface must pass the pipe file descriptor values to the Server. Use the arguments on the exec command for this purpose. The Interface should also detect the final exit status of the Server and display an appropriate message. Server: When the Server initializes, it must do two things before entering its loop accepting commands. First, it must initialize an array of structures (records) using the data in a local file called gasData. Second, it should display the contents of the array so it is easy to verify that the initialization occurred correctly. The records will keep track of the gas consumption of a set of cars. Each structure in the array is to consist of the following fields: id: this is the identifier of the car (a character string of up to 8 characters). odometer: the reading on the odometer at the time of fill-up (integer). gallons: Number of gallons to fill up the tank (float). You are to create and use a typedef for the record structure. gasData: each line of this ASCII file is to contain the data for one record of the array of structures. Each line is expected to be in the form: id odometer gallons where a single space is used as a delimiter. 6. 7. 8. 9. Makefile: Write a makefile to control the compilation of your programs. Commands: Three commands must be processed: mpg, This is to compute the average miles per gallon for the vehicle identified by the label . It is to be the average over all records maintained by Server for the designated vehicle. list, This will list all of the entries identified by the label in increasing order of the odometer reading. exit After processing this command, the Server should terminate in a normal manner. After detecting the termination of the Server, the Interface should print relevant information and exit normally. System calls: You should view this exercise as an opportunity to try out various system calls. Detailed documentation of the system calls can be found in the associated man pages. At a minimum, you are expected to use the following system calls: fork, some type of exec call (such as execl), pipe, read, write, exit, waitpid, close. In addition your code is to check the response from the system calls for errors, display an appropriate error message and take appropriate action. In many cases that action may be just to call exit with a unique number selected. Readability: Your program must be written using good C programming conventions: Variable names and function names should be descriptive of what they represent Use indentation to show the structure of the program. Typically this means using indentation with for, while, do-while, if, and switch statements as well as indenting the body of functions. Indentation should show the nesting level of the statements involved. Include some in-line documentation to give a high level view of what the program and groups of statements is/are doing. 10. Sample output: Input command: element = 0: id = 987654, odometer = 201200, gallons = 4.000000 element = 1: id = red, odometer = 89114, gallons = 0.000000 element = 2: id = red, odometer = 89712, gallons = 13.500000 element = 3: id = red, odometer = 90229, gallons = 15.300000 element = 4: id = 987654, odometer = 201001, gallons = 0.000000 element = 5: id = 987654, odometer = 201111, gallons = 5.200000 element = 6: id = 987654, odometer = 201612, gallons = 25.299999 element = 7: id = red, odometer = 89300, gallons = 7.100000 element = 8: id = green, odometer = 16, gallons = 0.000000 element = 9: id = green, odometer = 216, gallons = 20.000000 element = 10: id = green, odometer = 518, gallons = 61.000000 element = 11: id = green, odometer = 879, gallons = 50.000000 mpg, red response: Average MPG = 31.058498 Input command: mpg, green response: Average MPG = 6.587786 Input command: exit response: Server complete. Interface: child process (320) completed. Interface: child process exit status = 0. Interface: Complete. Hints: Some of the library string functions may be useful: strehr, strcmp, strncmp, strncpy. 2. 3. 4. 5. Overview: You are to write two programs, Interface and Server. After initialization, the Interface will use the fork system call and an exec system call to start the execution of the Server. The Interface will accept commands from the console and send them to the Server for execution. After executing the command, the Server will send the output to the Interface for display on the console. Pipes: The Interface will need to create the pipes to be used for communication between itself and the Server prior to doing the fork. Use two pipes, one for sending commands to the Server and one for sending the response to the Interface. Interface: In addition to tasks described elsewhere, the Interface must pass the pipe file descriptor values to the Server. Use the arguments on the exec command for this purpose. The Interface should also detect the final exit status of the Server and display an appropriate message. Server: When the Server initializes, it must do two things before entering its loop accepting commands. First, it must initialize an array of structures (records) using the data in a local file called gasData. Second, it should display the contents of the array so it is easy to verify that the initialization occurred correctly. The records will keep track of the gas consumption of a set of cars. Each structure in the array is to consist of the following fields: id: this is the identifier of the car (a character string of up to 8 characters). odometer: the reading on the odometer at the time of fill-up (integer). gallons: Number of gallons to fill up the tank (float). You are to create and use a typedef for the record structure. gasData: each line of this ASCII file is to contain the data for one record of the array of structures. Each line is expected to be in the form: id odometer gallons where a single space is used as a delimiter. 6. 7. 8. 9. Makefile: Write a makefile to control the compilation of your programs. Commands: Three commands must be processed: mpg, This is to compute the average miles per gallon for the vehicle identified by the label . It is to be the average over all records maintained by Server for the designated vehicle. list, This will list all of the entries identified by the label in increasing order of the odometer reading. exit After processing this command, the Server should terminate in a normal manner. After detecting the termination of the Server, the Interface should print relevant information and exit normally. System calls: You should view this exercise as an opportunity to try out various system calls. Detailed documentation of the system calls can be found in the associated man pages. At a minimum, you are expected to use the following system calls: fork, some type of exec call (such as execl), pipe, read, write, exit, waitpid, close. In addition your code is to check the response from the system calls for errors, display an appropriate error message and take appropriate action. In many cases that action may be just to call exit with a unique number selected. Readability: Your program must be written using good C programming conventions: Variable names and function names should be descriptive of what they represent Use indentation to show the structure of the program. Typically this means using indentation with for, while, do-while, if, and switch statements as well as indenting the body of functions. Indentation should show the nesting level of the statements involved. Include some in-line documentation to give a high level view of what the program and groups of statements is/are doing. 10. Sample output: Input command: element = 0: id = 987654, odometer = 201200, gallons = 4.000000 element = 1: id = red, odometer = 89114, gallons = 0.000000 element = 2: id = red, odometer = 89712, gallons = 13.500000 element = 3: id = red, odometer = 90229, gallons = 15.300000 element = 4: id = 987654, odometer = 201001, gallons = 0.000000 element = 5: id = 987654, odometer = 201111, gallons = 5.200000 element = 6: id = 987654, odometer = 201612, gallons = 25.299999 element = 7: id = red, odometer = 89300, gallons = 7.100000 element = 8: id = green, odometer = 16, gallons = 0.000000 element = 9: id = green, odometer = 216, gallons = 20.000000 element = 10: id = green, odometer = 518, gallons = 61.000000 element = 11: id = green, odometer = 879, gallons = 50.000000 mpg, red response: Average MPG = 31.058498 Input command: mpg, green response: Average MPG = 6.587786 Input command: exit response: Server complete. Interface: child process (320) completed. Interface: child process exit status = 0. Interface: Complete. Hints: Some of the library string functions may be useful: strehr, strcmp, strncmp, strncpy






