Question: 2. ( 30 points) Use the following table for the properties of the ternary system given in the previous question. The pressures are all given

![decimal point. Wilson's correlation for K value for component i is Ki=P(PC)iexp[5.373(1+i)(1T(TC)i)]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/09/66da67eb5a43b_48266da67eaebd89.jpg)
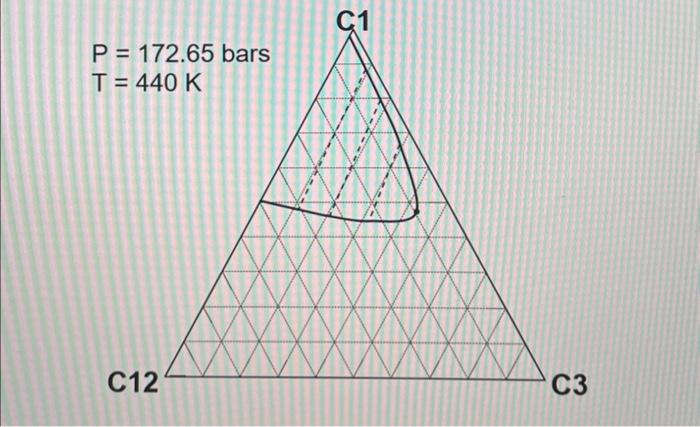
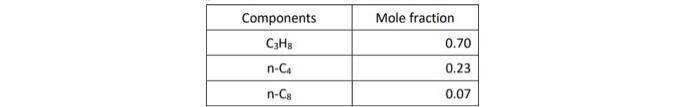
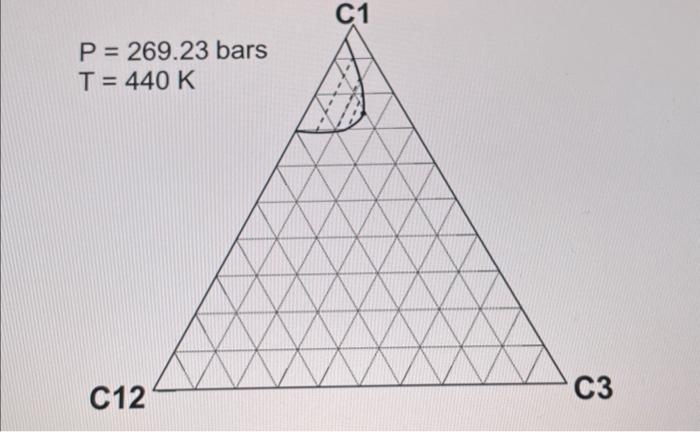
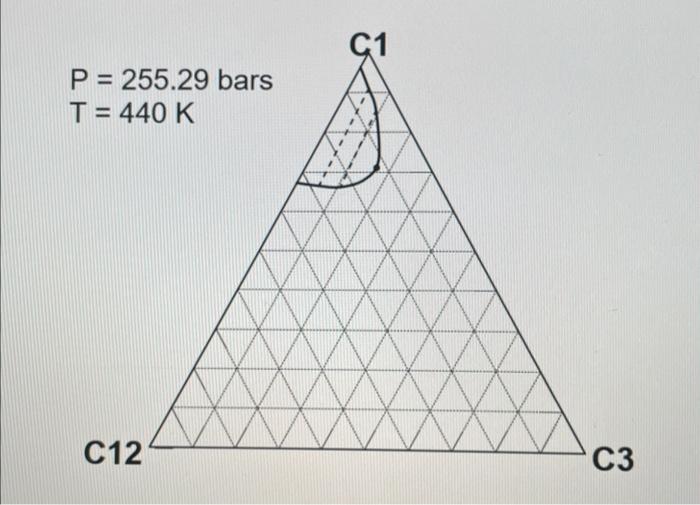
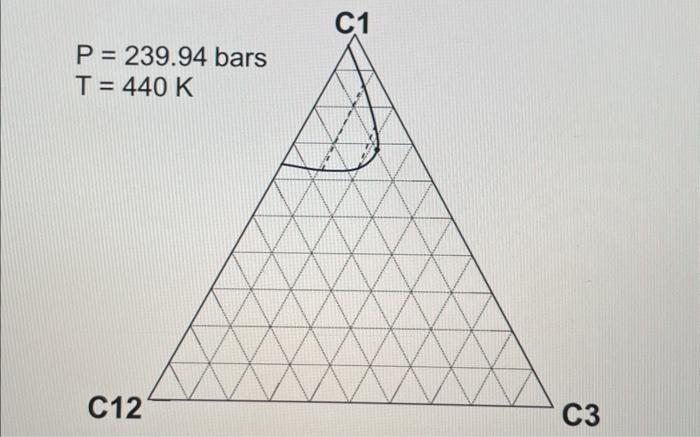
2. ( 30 points) Use the following table for the properties of the ternary system given in the previous question. The pressures are all given as absolute pressure (bara). Table 1 Properties for the gas-condensate components a. (6 points) Calculate K values for C1,C3, and C12 at 190.72 bars and 440K using Wilson's correlation. Give 4 digits after the decimal point. Wilson's correlation for K value for component i is Ki=P(PC)iexp[5.373(1+i)(1T(TC)i)] b. (10 points: 4+6 ) Consider the mixture of 50mol%C1,20mol%C3, and 30mol%C12 at 440K. Estimate a bubble point pressure of this mixture using Raoult's law. To answer the question, you can use Wilson's correlation (the numerator) and Table 1 to estimate the vapor pressure of each component at 440K. c. (5 points) What is the actual K value for C1 at 190.72 bars and 440K on the basis of the ternary diagrams given? d. (4 points: 2+2 ) Comparison between parts a and c clearly indicates that Wilson's correlation is not accurate for this ternary system at 190.72 bars and 440K. This is because Raoult's law (the basis for Wilson's correlation) assumes for the gas-phase fugacities and for the liquid-phase fugacities in the formulation. Fill in the blanks. \begin{tabular}{|c|r|} \hline Components & Mole fraction \\ \hline C3H8 & 0.70 \\ \hline nC4 & 0.23 \\ \hline nC8 & 0.07 \\ \hline \end{tabular} 2. ( 30 points) Use the following table for the properties of the ternary system given in the previous question. The pressures are all given as absolute pressure (bara). Table 1 Properties for the gas-condensate components a. (6 points) Calculate K values for C1,C3, and C12 at 190.72 bars and 440K using Wilson's correlation. Give 4 digits after the decimal point. Wilson's correlation for K value for component i is Ki=P(PC)iexp[5.373(1+i)(1T(TC)i)] b. (10 points: 4+6 ) Consider the mixture of 50mol%C1,20mol%C3, and 30mol%C12 at 440K. Estimate a bubble point pressure of this mixture using Raoult's law. To answer the question, you can use Wilson's correlation (the numerator) and Table 1 to estimate the vapor pressure of each component at 440K. c. (5 points) What is the actual K value for C1 at 190.72 bars and 440K on the basis of the ternary diagrams given? d. (4 points: 2+2 ) Comparison between parts a and c clearly indicates that Wilson's correlation is not accurate for this ternary system at 190.72 bars and 440K. This is because Raoult's law (the basis for Wilson's correlation) assumes for the gas-phase fugacities and for the liquid-phase fugacities in the formulation. Fill in the blanks. \begin{tabular}{|c|r|} \hline Components & Mole fraction \\ \hline C3H8 & 0.70 \\ \hline nC4 & 0.23 \\ \hline nC8 & 0.07 \\ \hline \end{tabular}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


