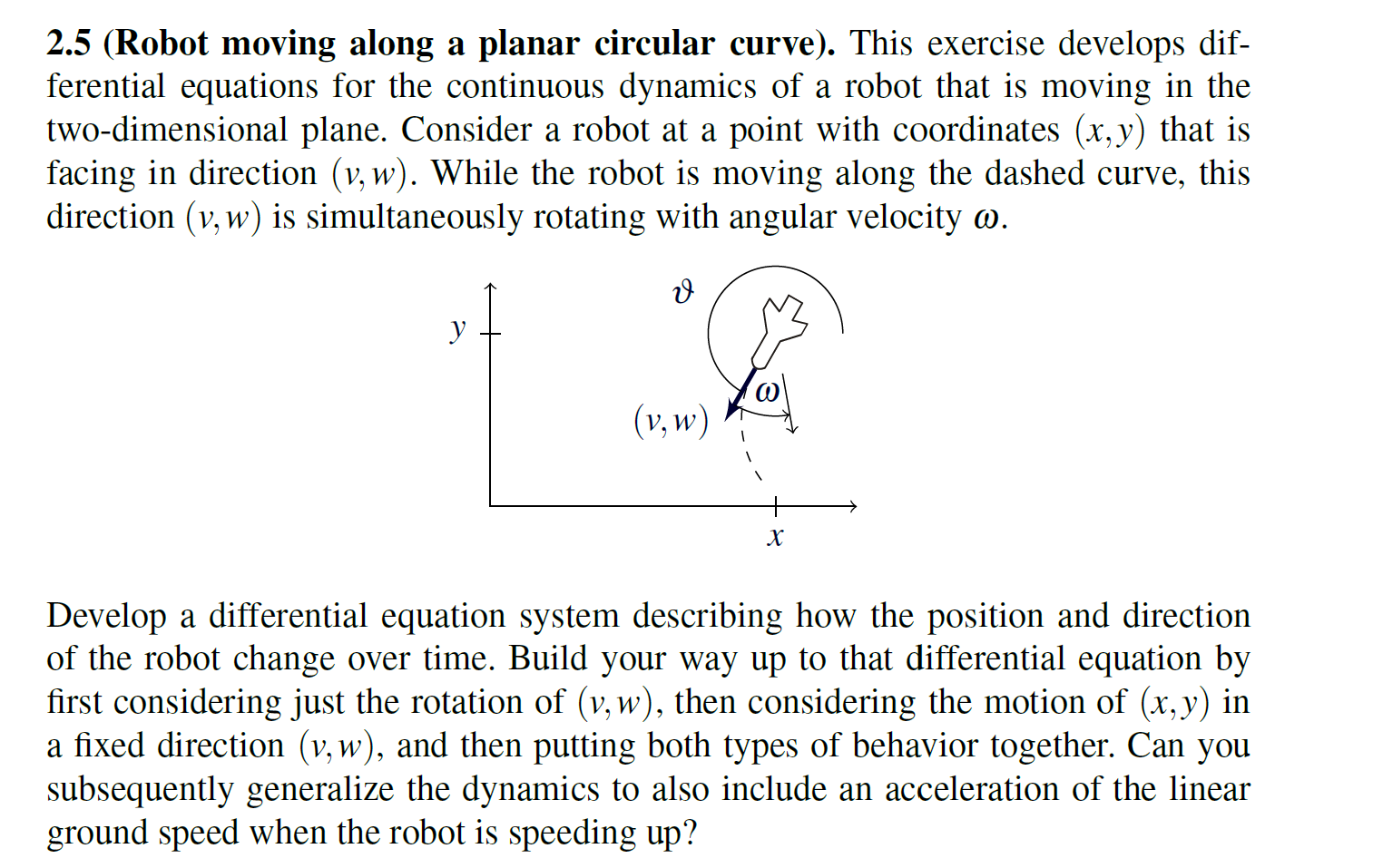
Question: 2 . 5 ( Robot moving along a planar circular curve ) . This exercise develops differential equations for the continuous dynamics of a robot
Robot moving along a planar circular curve This exercise develops differential equations for the continuous dynamics of a robot that is moving in the twodimensional plane. Consider a robot at a point with coordinates x y that is facing in direction v w While the robot is moving along the dashed curve, this direction v w is simultaneously rotating with angular velocity omega
Develop a differential equation system describing how the position and direction of the robot change over time. Build your way up to that differential equation by first considering just the rotation of v w then considering the motion of x y in a fixed direction v w and then putting both types of behavior together. Can you subsequently generalize the dynamics to also include an acceleration of the linear ground speed when the robot is speeding up
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


