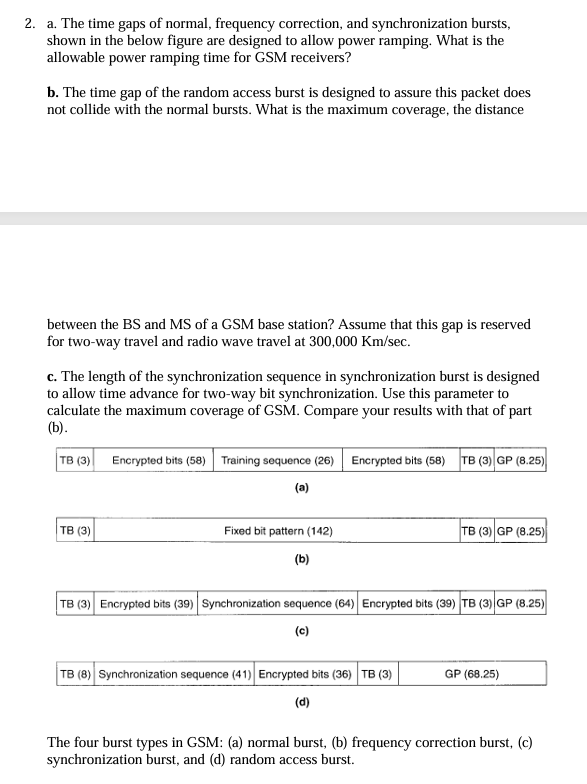
Question: 2 . a . The time gaps of normal, frequency correction, and synchronization bursts, shown in the below figure are designed to allow power ramping.
a The time gaps of normal, frequency correction, and synchronization bursts, shown in the below figure are designed to allow power ramping. What is the allowable power ramping time for GSM receivers?
b The time gap of the random access burst is designed to assure this packet does not collide with the normal bursts. What is the maximum coverage, the distance
between the BS and MS of a GSM base station? Assume that this gap is reserved for twoway travel and radio wave travel at mathrmKmmathrmsec
c The length of the synchronization sequence in synchronization burst is designed to allow time advance for twoway bit synchronization. Use this parameter to calculate the maximum coverage of GSM Compare your results with that of part b
a
b
c
d
The four burst types in GSM: a normal burst, b frequency correction burst, c synchronization burst, and d random access burst.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


