Question: 2. A volatile solvent (solute A ) is dried from the surface of a polymer film using the process shown in the figure below. The

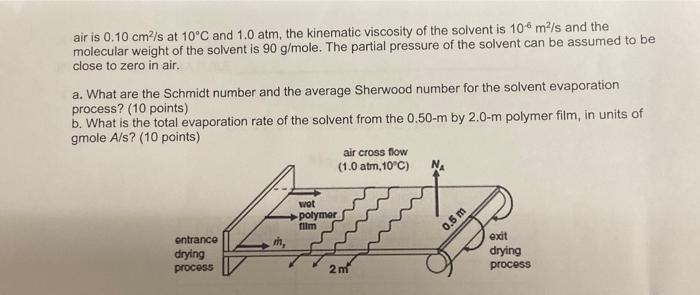
2. A volatile solvent (solute A ) is dried from the surface of a polymer film using the process shown in the figure below. The wet polymer film enters the drying process. Both the top and bottom surfaces of the polymer film are exposed to a cross flow of air. The evaporation rate of the solvent from the polymer film is limited by external convection mass transfer. During the drying process, the width of the thin polymer film is 50cm, and the length of the polymer film is 2.0m. The flowing air has a bulk velocity of 0.5m/s, temperature of 10C, and total system pressure of 1.0atm. The wet polymer film is also maintained at 10C, and the evaporation process is assumed to be limited by convection mass transfer. The vapor pressure of the solvent at 10C is 0.1atm. The diffusion coefficient of the solvent in air is 0.10cm2/s at 10C and 1.0 atm, the kinematic viscosity of the solvent is 106m2/s and the molecular weight of the solvent is 90g/mole. The partial pressure of the solvent can be assumed to be close to zero in air. a. What are the Schmidt number and the average Sherwood number for the solvent evaporation process? (10 points) b. What is the total evaporation rate of the solvent from the 0.50m by 2.0m polymer film, in units of gmole A/s ? (10 points)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


