Question: 2 ) Can you use a cooling tower at high altitude? Two things change: typical relative humidity values are lower and the air density is
Can you use a cooling tower at high altitude? Two things change: typical relative humidity values are lower and the air density is lower due to lower pressure
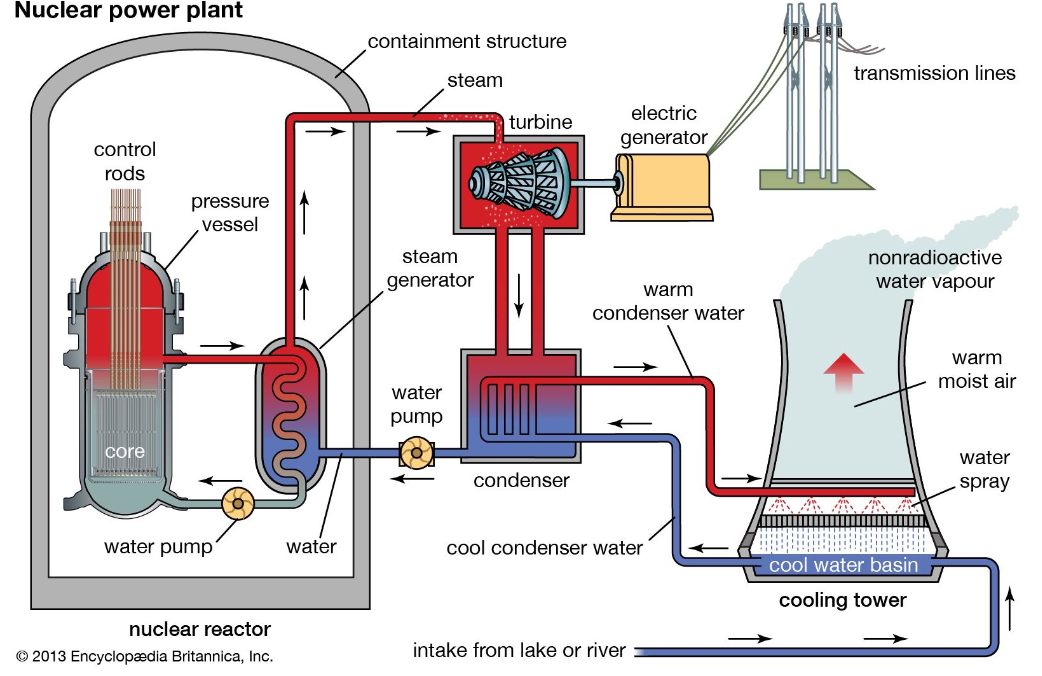
You have a power plant that produces MW electric a typical, large nuclear plant The boiler produces MW Heat is rejected in a cooling tower. Assume the generator is efficient.
You can site this plant in Savannah Georgia, which P atm and relative humidity is typically on a C day.
Or you can site in Logan, UT which P kPa and relative humidity is on a C day.
The water from the plant in both cases enters at C and leaves at C Makeup water is provided at C and the air exits the tower at relative humidity and C
Answer for each case:
a The mass flow rate of the makeup water
b The mass flow rate of the air
Remember that the condenser is a heat exchanger that transfers heat into the stream of water that goes to the cooling tower. You will need a mass and energy balance on this component.
Compare your makeup water flow rate to the Logan River. Its flowrate is in the neighborhood of ftsec
The mass flow rate of air in each case is a figure related to the height of the cooling tower, so more costs more capital.
Your conclusion is Nuclear power plant
c Encyclopdia Britannica, Inc.
intake from lake or river
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


