Question: 2 . Dislocation pileup ( 5 0 points ) Driven by an external shear stress ( tau ) , an edge dislocation
Dislocation pileup points
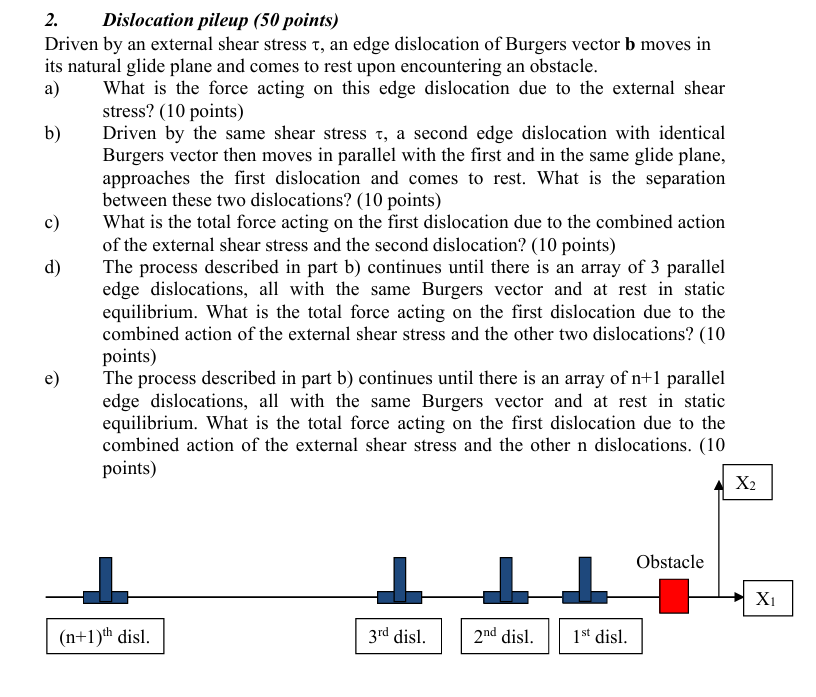
Driven by an external shear stress tau an edge dislocation of Burgers vector mathbfb moves in its natural glide plane and comes to rest upon encountering an obstacle.
a What is the force acting on this edge dislocation due to the external shear stress? points
b Driven by the same shear stress tau a second edge dislocation with identical Burgers vector then moves in parallel with the first and in the same glide plane, approaches the first dislocation and comes to rest. What is the separation between these two dislocations? points
c What is the total force acting on the first dislocation due to the combined action of the external shear stress and the second dislocation? points
d The process described in part b continues until there is an array of parallel edge dislocations, all with the same Burgers vector and at rest in static equilibrium. What is the total force acting on the first dislocation due to the combined action of the external shear stress and the other two dislocations? points
e The process described in part b continues until there is an array of mathrmn parallel edge dislocations, all with the same Burgers vector and at rest in static equilibrium. What is the total force acting on the first dislocation due to the combined action of the external shear stress and the other n dislocations. points
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


