Question: 2. How do you know whether a random variable is continuous or discrete? 3. What is the difference between the two types of random variables?
2. How do you know whether a random variable is continuous or discrete?
3. What is the difference between the two types of random variables?
Classify the following random variables
discrete or continuous
1. the speed of a tricycle.
2. the number of female students.
3. the time needed to finish the module.
4. the amount of sugar in a cup of coffee.
5. The number of defective mobile phones produced by a manufacturer
Determine whether each of the following experiments/situations involve a discrete random variable or a continuous random variable.
1. choosing an even number less than 150
2. gathering information about the average monthly electric consumption in a certain household
3. tallying the number of family in a certain barangay that have one child
Identify whether the given experiment involves a discrete random variable or a continuous random variable.
1. getting the temperature of patient admitted in a hospital
2. collecting data about the weights of students in a certain school
3. the number of patient admitted in the hospital due to COVID-19
4. the number of no work no pay in a certain municipality caused by pandemic
5. the number of families that are members of 4P's in Quezon
6. the number of Balikbayan OFW arrive in the Philippines
7. the number of text messages received by a particular individual in a day
8. the number of possible outcomes in rolling a die
9. the amount of liquid in a 12 - ounce can of soda
10. the number of fouls committed by a basketball team during the games
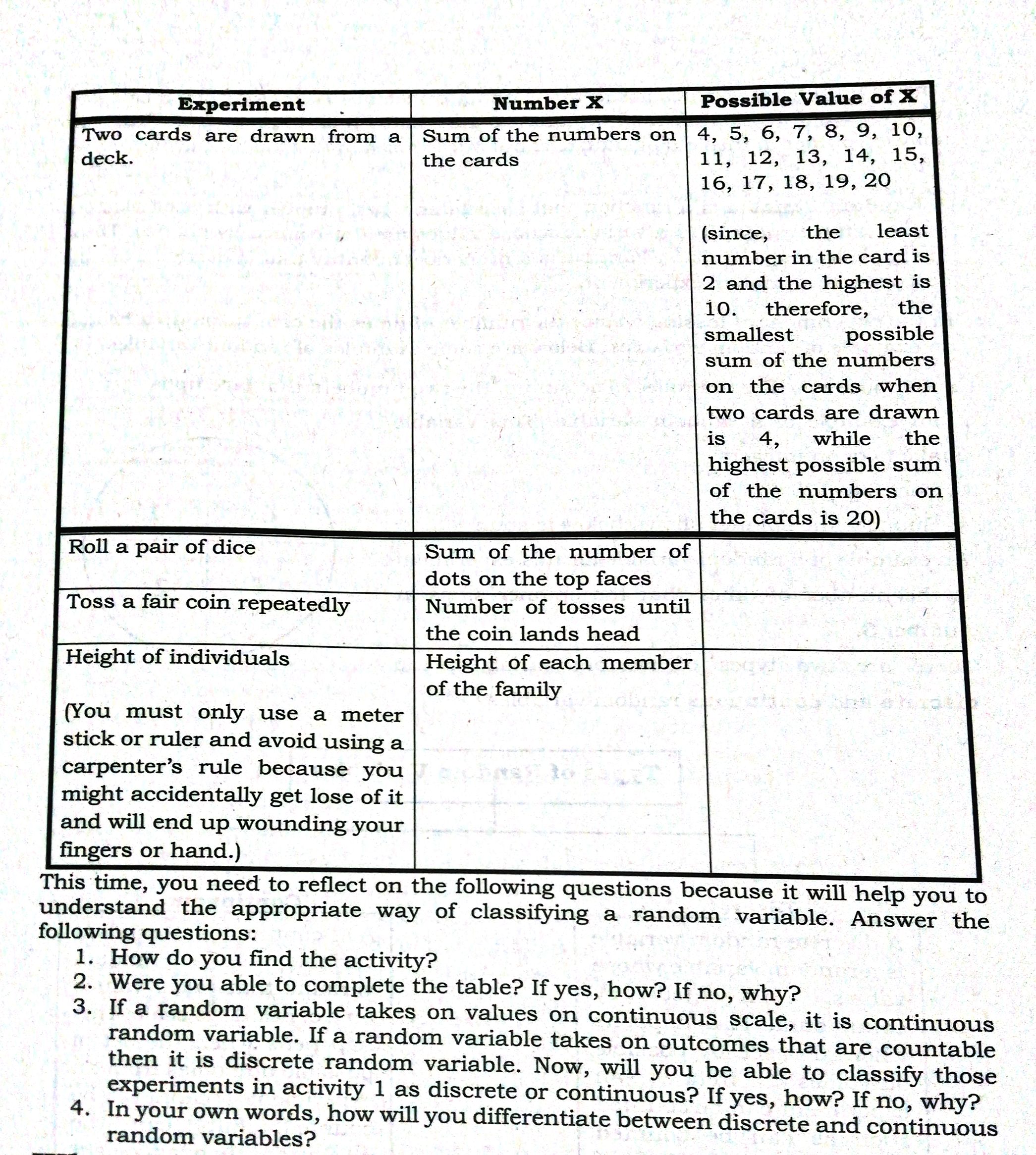
Experiment Number X Possible Value of X Two cards are drawn from a Sum of the numbers on 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, deck. the cards 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 (since, the least number in the card is 2 and the highest is 10. therefore, the smallest possible sum of the numbers on the cards when two cards are drawn is 4, while the highest possible sum of the numbers on the cards is 20) Roll a pair of dice Sum of the number of dots on the top faces Toss a fair coin repeatedly Number of tosses until the coin lands head Height of individuals Height of each member of the family You must only use a meter stick or ruler and avoid using a carpenter's rule because you might accidentally get lose of it and will end up wounding your fingers or hand.) This time, you need to reflect on the following questions because it will help you to understand the appropriate way of classifying a random variable. Answer the following questions: 1. How do you find the activity? 2. Were you able to complete the table? If yes, how? If no, why? 3. If a random variable takes on values on continuous scale, it is continuous random variable. If a random variable takes on outcomes that are countable then it is discrete random variable. Now, will you be able to classify those experiments in activity 1 as discrete or continuous? If yes, how? If no, why? 4. In your own words, how will you differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


