Question: 2 Monopoly Pricing (a) Graph demand for a market Where P(y) = 100 13;. Label this demand curve D. 2 points 2 (b) Calculate the

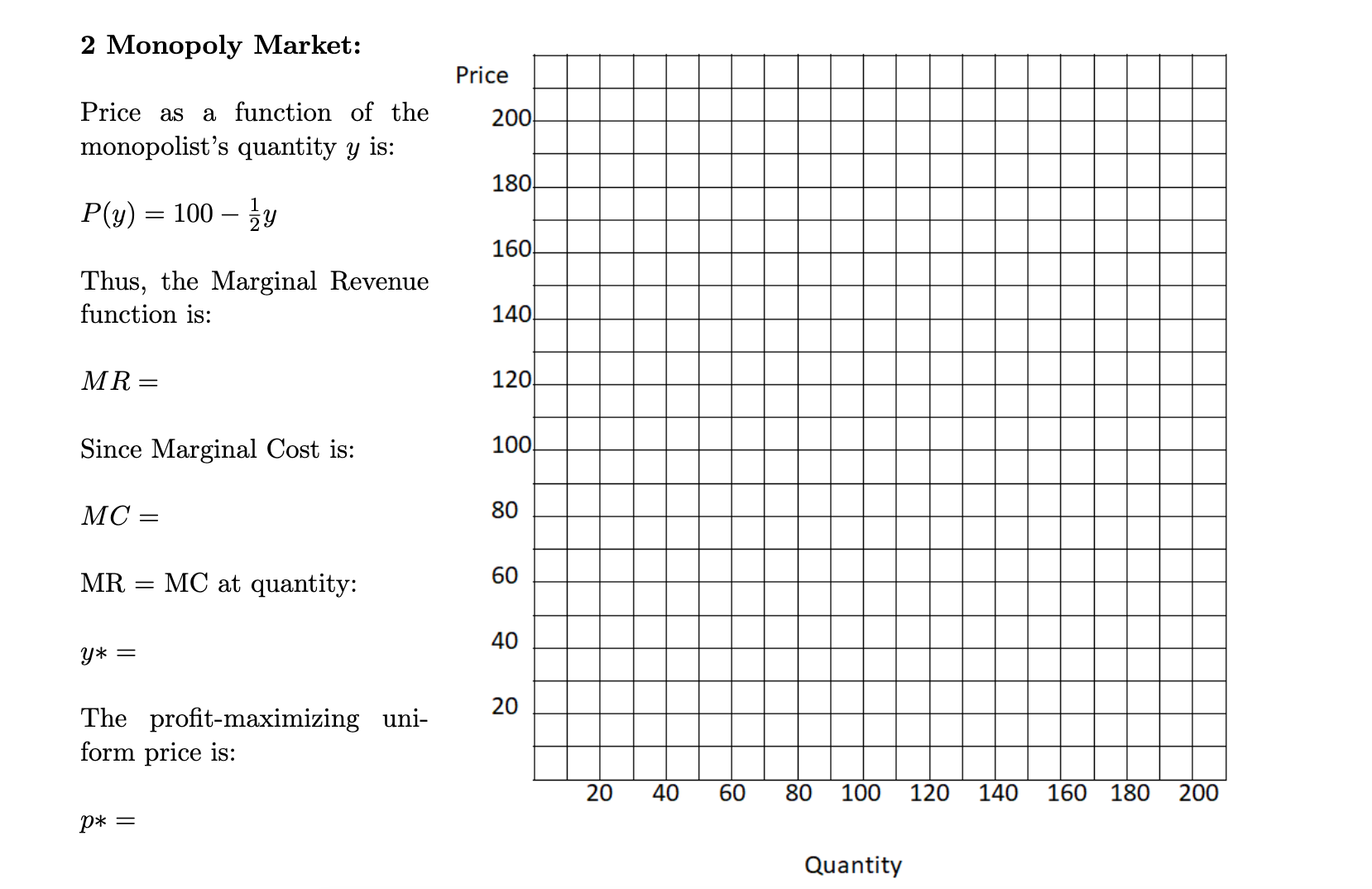

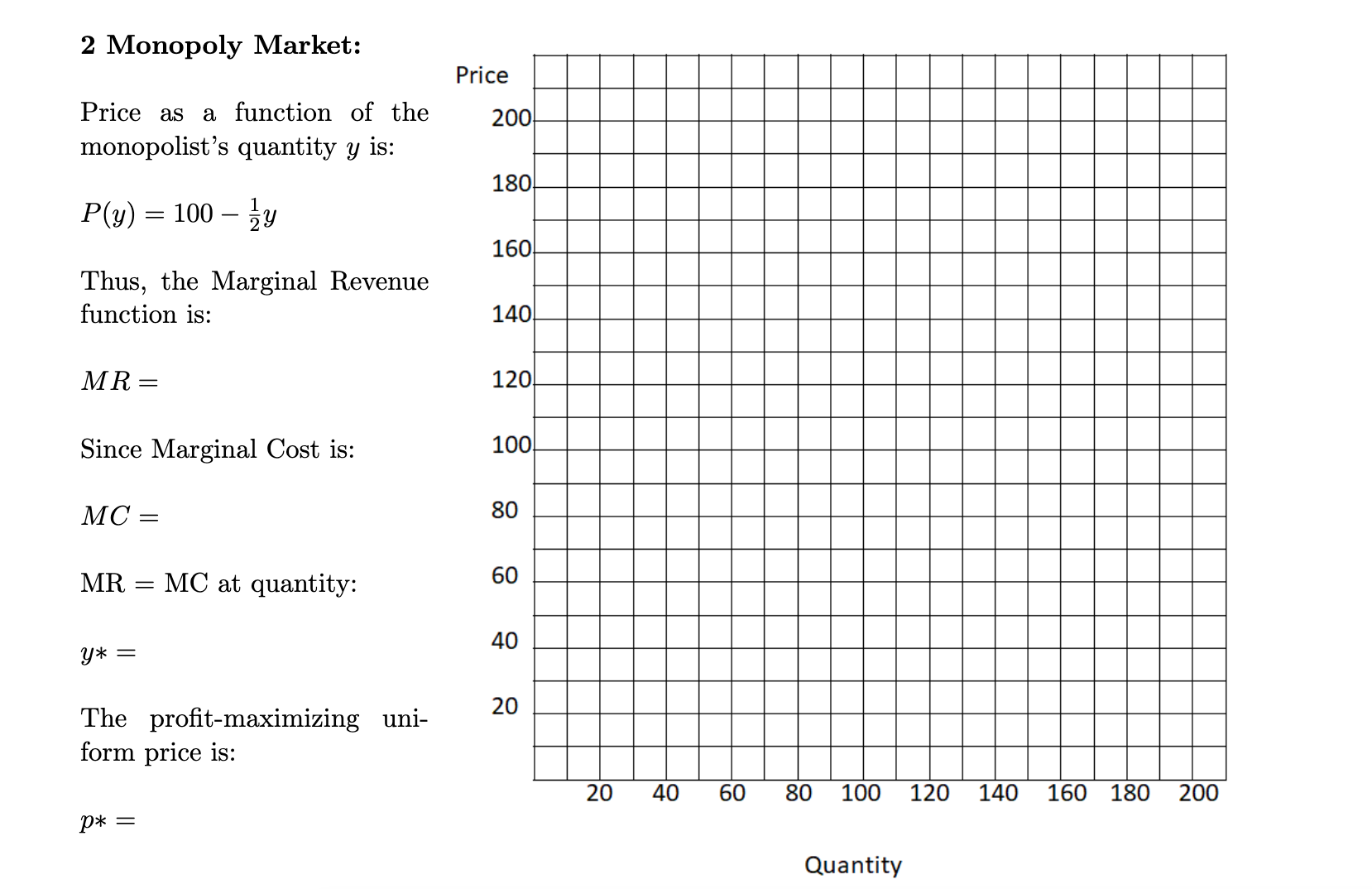
2 Monopoly Pricing (a) Graph demand for a market Where P(y) = 100 13;. Label this demand curve D. 2 points 2 (b) Calculate the Marginal Revenue function for a monopolist in this market. Graph this Marginal Revenue function in the same graph, labeling it MR. (2 points) (0) Calculate and graph the Marginal Cost curve in the same graph (labeling it MC, when the monopolist's total cost function is C(y) = 403; + 90 (2 points) (d) Identify the monopolist's prot-maximizing quantity and price, and mark that price-quantity point with a star on the demand curve in your graph. (2 points) (8) Outline the Producer Surplus and Consumer Surplus areas in your graph, and shade in the Deadweight Loss. (2 points) 2 Monopoly Market: Price Price as a function of the 200 monopolist's quantity y is: 180 P(y) = 100 - zy 160 Thus, the Marginal Revenue function is: 140 MR = 120 Since Marginal Cost is: 100 MC = 80 MR = MC at quantity: 60 y* = 40 The profit-maximizing uni- 20 form price is: 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 P* = Quantity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


