Question: 2 Multiple choice, Short Answer, Fill in the blank (6 points total, 1 each) 1. Consumer surplus is defined as: (a) The total amount spent
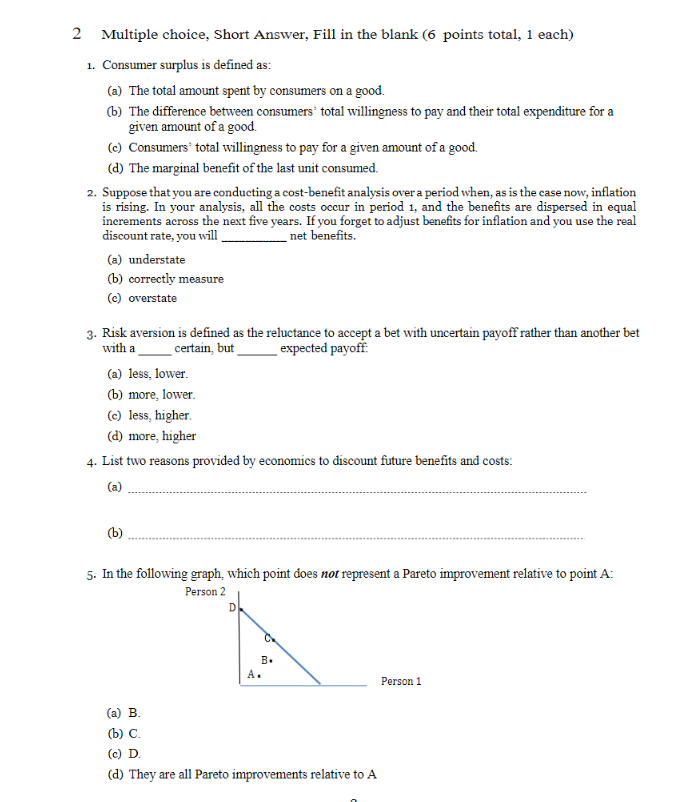

2 Multiple choice, Short Answer, Fill in the blank (6 points total, 1 each) 1. Consumer surplus is defined as: (a) The total amount spent by consumers on a good. (b) The difference between consumers' total willingness to pay and their total expenditure for a given amount of a good. (c) Consumers' total willingness to pay for a given amount of a good. (d) The marginal benefit of the last unit consumed. 2. Suppose that you are conducting a cost-benefit analysis over a period when, as is the case now, inflation is rising. In your analysis, all the costs occur in period 1, and the benefits are dispersed in equal increments across the next five years. If you forget to adjust benefits for inflation and you use the real discount rate, you will _ net benefits. (a) understate (b) correctly measure (c) overstate 3. Risk aversion is defined as the reluctance to accept a bet with uncertain payoff rather than another bet with a certain, but expected payoff: (a) less, lower. (b) more, lower. (c) less, higher. (d) more, higher 4. List two reasons provided by economics to discount future benefits and costs: (a) ( b ) 5. In the following graph, which point does not represent a Pareto improvement relative to point A: Person 2 D B. A . Person 1 (a) B. (b) C. (C) D. (d) They are all Pareto improvements relative to A6. If prices in a secondary market as result of a policy, we can ignore secondary market impacts of that policy. (a) Don't change (b) Increase (e) Decrease
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


