Question: 2. Problem 8.06 (Expected Returns) eBook Problem Walk-Through Stocks A and B have the following probability distributions of expected future returns: E Probability 0.1 0.1
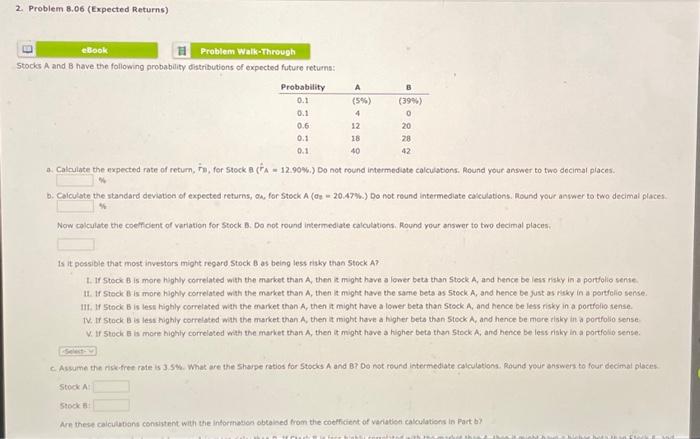
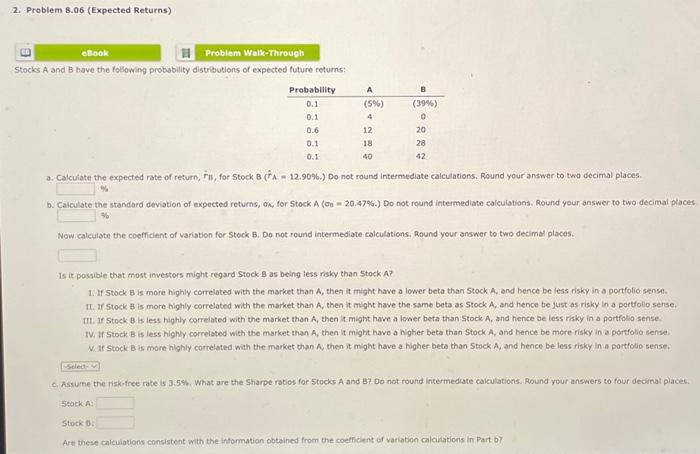
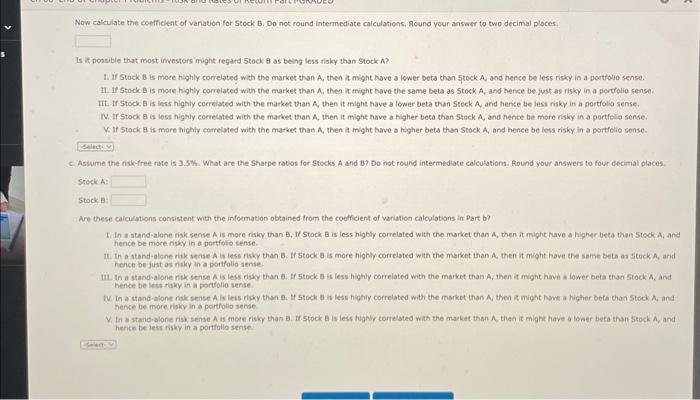
Stocks A and B have the following probability distributions of expected future returns: a. Calrulate the expected rate of return, rm, for 5t0k a (rA=12.90%.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. b. Calculate the standard devisten of expected returns, on, for steck A (Oe =20.47%.) Do not reund intermediate cakculations. Mound your ankner to two decimal places. Now colculate the coeffclent of variation for Stock B. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. Is it pessible that most investors might regard Stock B as being less risk than 5 tock A ? 1. If 5tock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then in might have a lower beta than Stock A, and hence be less rithy in a portfolio sente 14. If 5 teck B is more highly correlated with the maket than A, then it might have the samie bets as 5 teck A, and hence be just as r isky in a portfilio sense. IIt. If Stock B is lest highly correlated with the enarket than A, then it might have a lower beta than 5 Fock A, and henco be less risky in a gortfolio sense. IV. If Stock B is less highly correlathd with the market than A, then it might have a higher bets than Stock A, and hence be more tisky in a portfollo sense. V. If stock E is more highly correletod wati the market than A, then it might have a higher beto than stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfollo sense. c. Aswume the nskefree rate is 3.5 \%. What are the shape ratios for Stocks A and 8 ? Do not round intermediate calculotions. Round yeur answers to four idecimat places. stockA stock f Are these calculubans consistent with the insorthadion obtaked from the coefficient of variatien calculations in Part b) is A and B have the following probability distributions of expected future returns: a: Calculate the expected rate of return, r11, for stock B(r^A=12.90%6 ) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. \% b. Calnulate the standard deviation of expected retums, a, for 5tock.A(0i=20.47%.) Do not round intermediate calculations: Round your answer to two decimal places Now calculate the coefficient of variation for Stock B. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. Is it possible that most investors might regard Stock B as being less risky than 5 tock A ? 1. If Stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beta than Stock A, and bence be less risky in a portfolio sense. 1I. If Stock B is more Bighly correlated with the market than A, then it might have the same beta as Stock A, and hence be just as risky in a portfolio sense. II. If Stock B is less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a lewer beta than Stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfolio sense. IV. If Stock B is less highy correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than Stock A, and hence be more risky in a portfolio sense. V. If stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than Stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfolio sense. c. Assume the risk-tree rate is 3.55\%. What are the Sharpe raties for 5 tocks A and B ? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to four decinal places. stock A: Stock 6 . Art these calcuiations consistent with the intormation obteined from the coefficent of variation calcilations in Part by Now caiculate the coefficent of variation for Stock B. Do not round intermediate caiculations. Round your answer to two decimal ploces: Is it ponsible that most investors imight regard 5 tock B as being less risky than Stock A ? 1. If Stock B is moce highly correiated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beta than 5 tock A and hence be less risky in a porttolio sense. II. If Stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have the same beta as Stock A, and hence be fust as risky in a portfolio sense. IIt. If Stock B is less highly coerelated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beta than Stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfolo sense. N. If Stock B is lest highiy correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beto than stock A, and hence be more risky in a portfolio sense. V. If Stock 8 is more highiy comelated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than Stock A, and hence be iess risky in a portflio sense. c. Aswume the risk-free rate is 3.5\%. What are the Sharpe ratios for Stocks A and 87 Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to four ifecimal places. steck A: stock B Are these caicyltions consistent with the information obtained from the coefficient of veriation calculations in part b? I. In a stand-alone rik sense A is more risky than B, If Stock B is less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than 5 tock A, and hence be more risky in a portiolio sense. If. In a stand-alone rikk sense A is less fisky than B. If stock B is more highy correlated with the market than A, then it might have the same Beta as stock A, and hence be just as rikky in a portfolig aense. 141. In a stand-alone ritk sense A is less risy than B. If 5 tock B is less highly correiated with the market than A, then it might have i fower beta than stock A, and hence be ints risk in il portolio sense. W. in a stand-alone risk sense A is leis risky than e. If 5 tock 8 is iess highly correlated with the markot than A, then it might have a higher bets chan Stock A, and hence be more risky in a portfolio sense V. In a stand.alone risk sense A is mere risky than B. If stock B is less higNy comelsted with the macket than A, then it might have a lower beta than Seock A, and hence be less misy in a portfulio sense. Stocks A and B have the following probability distributions of expected future returns: a. Calrulate the expected rate of return, rm, for 5t0k a (rA=12.90%.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. b. Calculate the standard devisten of expected returns, on, for steck A (Oe =20.47%.) Do not reund intermediate cakculations. Mound your ankner to two decimal places. Now colculate the coeffclent of variation for Stock B. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. Is it pessible that most investors might regard Stock B as being less risk than 5 tock A ? 1. If 5tock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then in might have a lower beta than Stock A, and hence be less rithy in a portfolio sente 14. If 5 teck B is more highly correlated with the maket than A, then it might have the samie bets as 5 teck A, and hence be just as r isky in a portfilio sense. IIt. If Stock B is lest highly correlated with the enarket than A, then it might have a lower beta than 5 Fock A, and henco be less risky in a gortfolio sense. IV. If Stock B is less highly correlathd with the market than A, then it might have a higher bets than Stock A, and hence be more tisky in a portfollo sense. V. If stock E is more highly correletod wati the market than A, then it might have a higher beto than stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfollo sense. c. Aswume the nskefree rate is 3.5 \%. What are the shape ratios for Stocks A and 8 ? Do not round intermediate calculotions. Round yeur answers to four idecimat places. stockA stock f Are these calculubans consistent with the insorthadion obtaked from the coefficient of variatien calculations in Part b) is A and B have the following probability distributions of expected future returns: a: Calculate the expected rate of return, r11, for stock B(r^A=12.90%6 ) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. \% b. Calnulate the standard deviation of expected retums, a, for 5tock.A(0i=20.47%.) Do not round intermediate calculations: Round your answer to two decimal places Now calculate the coefficient of variation for Stock B. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. Is it possible that most investors might regard Stock B as being less risky than 5 tock A ? 1. If Stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beta than Stock A, and bence be less risky in a portfolio sense. 1I. If Stock B is more Bighly correlated with the market than A, then it might have the same beta as Stock A, and hence be just as risky in a portfolio sense. II. If Stock B is less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a lewer beta than Stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfolio sense. IV. If Stock B is less highy correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than Stock A, and hence be more risky in a portfolio sense. V. If stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than Stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfolio sense. c. Assume the risk-tree rate is 3.55\%. What are the Sharpe raties for 5 tocks A and B ? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to four decinal places. stock A: Stock 6 . Art these calcuiations consistent with the intormation obteined from the coefficent of variation calcilations in Part by Now caiculate the coefficent of variation for Stock B. Do not round intermediate caiculations. Round your answer to two decimal ploces: Is it ponsible that most investors imight regard 5 tock B as being less risky than Stock A ? 1. If Stock B is moce highly correiated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beta than 5 tock A and hence be less risky in a porttolio sense. II. If Stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have the same beta as Stock A, and hence be fust as risky in a portfolio sense. IIt. If Stock B is less highly coerelated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beta than Stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfolo sense. N. If Stock B is lest highiy correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beto than stock A, and hence be more risky in a portfolio sense. V. If Stock 8 is more highiy comelated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than Stock A, and hence be iess risky in a portflio sense. c. Aswume the risk-free rate is 3.5\%. What are the Sharpe ratios for Stocks A and 87 Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to four ifecimal places. steck A: stock B Are these caicyltions consistent with the information obtained from the coefficient of veriation calculations in part b? I. In a stand-alone rik sense A is more risky than B, If Stock B is less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than 5 tock A, and hence be more risky in a portiolio sense. If. In a stand-alone rikk sense A is less fisky than B. If stock B is more highy correlated with the market than A, then it might have the same Beta as stock A, and hence be just as rikky in a portfolig aense. 141. In a stand-alone ritk sense A is less risy than B. If 5 tock B is less highly correiated with the market than A, then it might have i fower beta than stock A, and hence be ints risk in il portolio sense. W. in a stand-alone risk sense A is leis risky than e. If 5 tock 8 is iess highly correlated with the markot than A, then it might have a higher bets chan Stock A, and hence be more risky in a portfolio sense V. In a stand.alone risk sense A is mere risky than B. If stock B is less higNy comelsted with the macket than A, then it might have a lower beta than Seock A, and hence be less misy in a portfulio sense
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


