Question: 2. Rocket Engine Static Thrust: Consider a rocket engine attached to a test stand that is used to measure the thrust of the engine
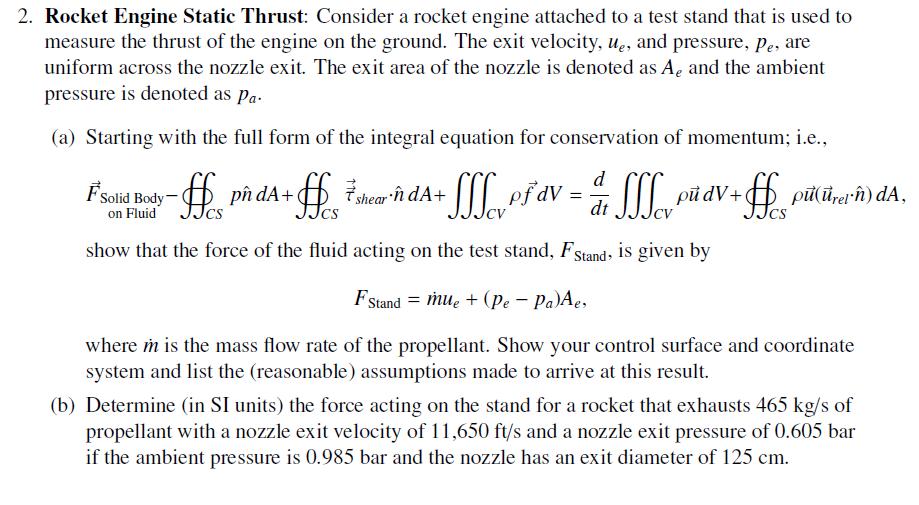
2. Rocket Engine Static Thrust: Consider a rocket engine attached to a test stand that is used to measure the thrust of the engine on the ground. The exit velocity, ue, and pressure, Pe, are uniform across the nozzle exit. The exit area of the nozzle is denoted as A, and the ambient pressure is denoted as pa (a) Starting with the full form of the integral equation for conservation of momentum; i.e., d FSolid Body- ff pn dA+ + ff * shear dA+ + + SSS pf dv = + SSS pu dv + g dt Se pudV+fpern) dA, CS on Fluid CS show that the force of the fluid acting on the test stand, FStand, is given by FStand mue + (Pe - Pa)Ae, where m is the mass flow rate of the propellant. Show your control surface and coordinate system and list the (reasonable) assumptions made to arrive at this result. (b) Determine (in SI units) the force acting on the stand for a rocket that exhausts 465 kg/s of propellant with a nozzle exit velocity of 11,650 ft/s and a nozzle exit pressure of 0.605 bar if the ambient pressure is 0.985 bar and the nozzle has an exit diameter of 125 cm.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


