Question: 2. Tomasulo's Algorithm (II) In this problem, we consider an in-order fetch, out-of-order dispatch, and out-of-order retirement execution engine that employs Tomasulo's algorithm. This engine
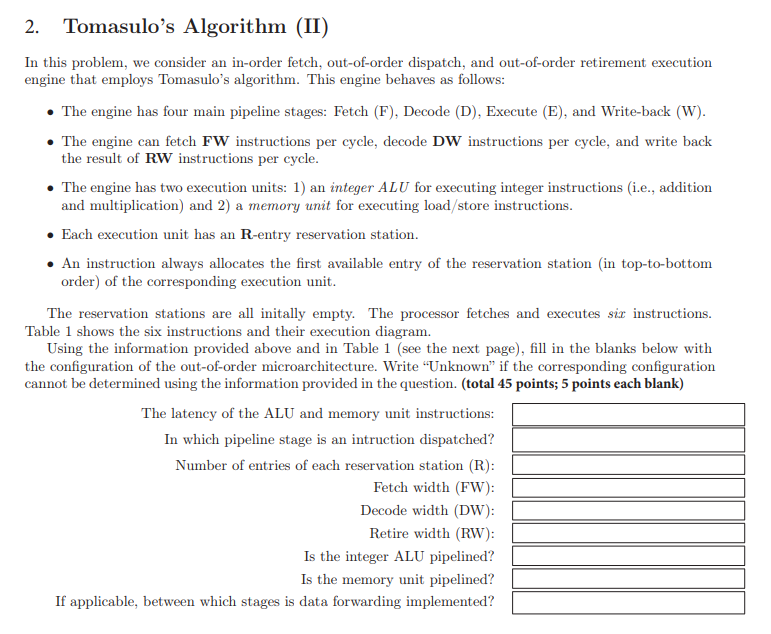
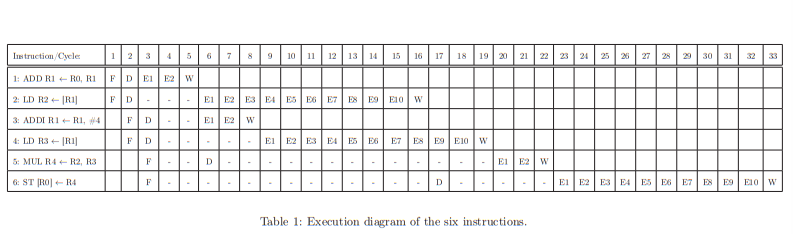
2. Tomasulo's Algorithm (II) In this problem, we consider an in-order fetch, out-of-order dispatch, and out-of-order retirement execution engine that employs Tomasulo's algorithm. This engine behaves as follows: The engine has four main pipeline stages: Fetch (F), Decode (D), Execute (E), and Write-back (W). The engine can fetch FW instructions per cycle, decode DW instructions per cycle, and write back the result of RW instructions per cycle. The engine has two execution units: 1) an integer ALU for executing integer instructions (i.e., addition and multiplication) and 2) a memory unit for executing load/store instructions. Each execution unit has an R-entry reservation station. An instruction always allocates the first available entry of the reservation station (in top-to-bottom order) of the corresponding execution unit. The reservation stations are all initally empty. The processor fetches and executes siz instructions. Table 1 shows the six instructions and their execution diagram. Using the information provided above and in Table 1 (see the next page), fill in the blanks below with the configuration of the out-of-order microarchitecture. Write "Unknown" if the corresponding configuration cannot be determined using the information provided in the question. (total 45 points; 5 points each blank) The latency of the ALU and memory unit instructions: In which pipeline stage is an intruction dispatched? Number of entries of each reservation station (R): Fetch width (FW): Decode width (DW): Retire width (RW): Is the integer ALU pipelined? Is the memory unit pipelined? If applicable, between which stages is data forwarding implemented? 7 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 30 31 E1 E2 E3 E4 ES ES ET ES ES ELOW Instruction Cycle 12 1: ADD R1 -- RO, RL F D E1 E2 W 2: LD R2-TR11 FD. 3. ADDIRIRI, 4 FD 4: LD 13 --|R1] FD G: MUL RA -- R2, R3 F 6: ST RO-R4 F EIE2 w E1 E2 E3 EA ESTE ES ELOW D E1 - D E1 E2 E3 E4 ES E6 EES 19 ELOW Table 1: Execution diagram of the six instructions, 2. Tomasulo's Algorithm (II) In this problem, we consider an in-order fetch, out-of-order dispatch, and out-of-order retirement execution engine that employs Tomasulo's algorithm. This engine behaves as follows: The engine has four main pipeline stages: Fetch (F), Decode (D), Execute (E), and Write-back (W). The engine can fetch FW instructions per cycle, decode DW instructions per cycle, and write back the result of RW instructions per cycle. The engine has two execution units: 1) an integer ALU for executing integer instructions (i.e., addition and multiplication) and 2) a memory unit for executing load/store instructions. Each execution unit has an R-entry reservation station. An instruction always allocates the first available entry of the reservation station (in top-to-bottom order) of the corresponding execution unit. The reservation stations are all initally empty. The processor fetches and executes siz instructions. Table 1 shows the six instructions and their execution diagram. Using the information provided above and in Table 1 (see the next page), fill in the blanks below with the configuration of the out-of-order microarchitecture. Write "Unknown" if the corresponding configuration cannot be determined using the information provided in the question. (total 45 points; 5 points each blank) The latency of the ALU and memory unit instructions: In which pipeline stage is an intruction dispatched? Number of entries of each reservation station (R): Fetch width (FW): Decode width (DW): Retire width (RW): Is the integer ALU pipelined? Is the memory unit pipelined? If applicable, between which stages is data forwarding implemented? 7 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 30 31 E1 E2 E3 E4 ES ES ET ES ES ELOW Instruction Cycle 12 1: ADD R1 -- RO, RL F D E1 E2 W 2: LD R2-TR11 FD. 3. ADDIRIRI, 4 FD 4: LD 13 --|R1] FD G: MUL RA -- R2, R3 F 6: ST RO-R4 F EIE2 w E1 E2 E3 EA ESTE ES ELOW D E1 - D E1 E2 E3 E4 ES E6 EES 19 ELOW Table 1: Execution diagram of the six instructions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


