Question: 2. Using the incremental-cost approach, determine the net present value in favor of (or against) purchasing the new truck? (Negotive amounts should be indicated with
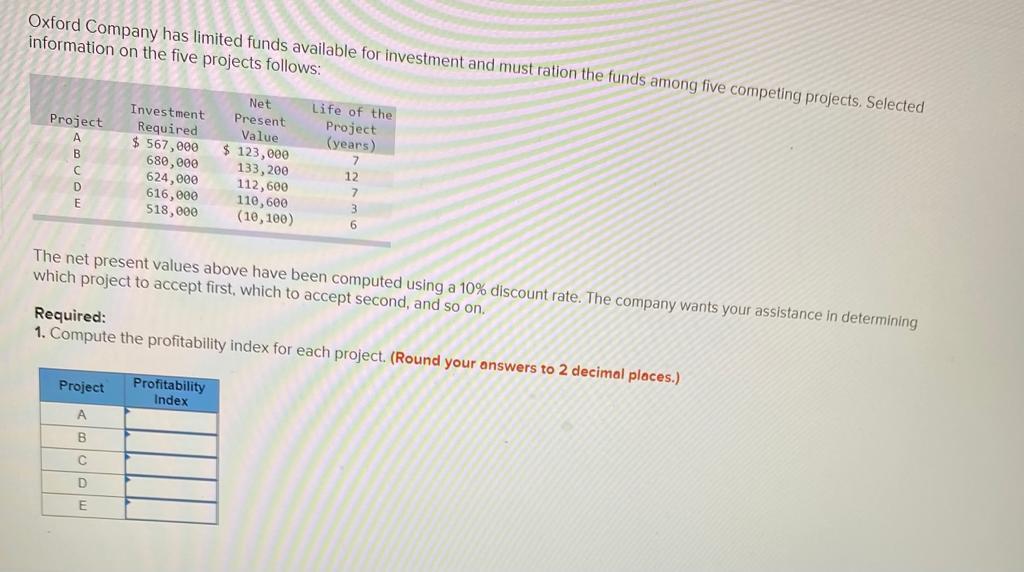
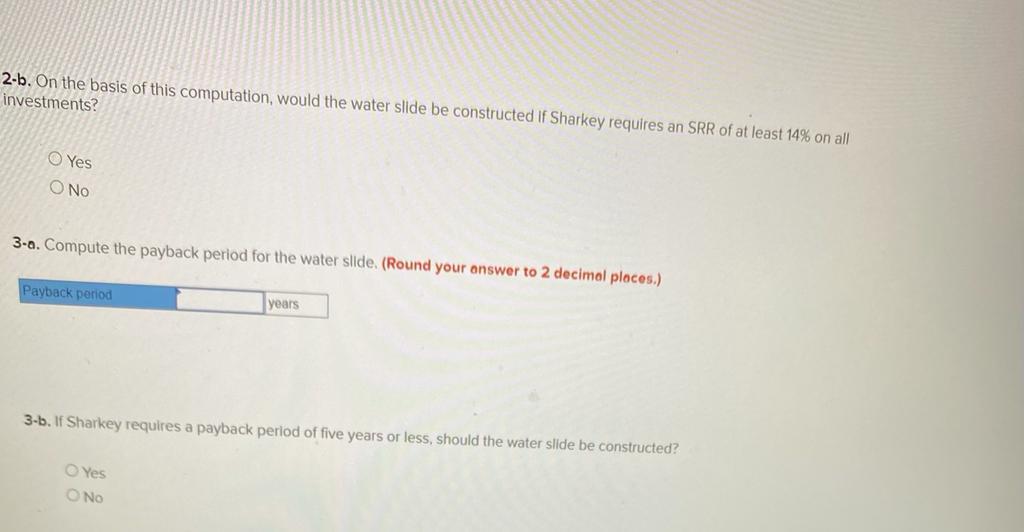
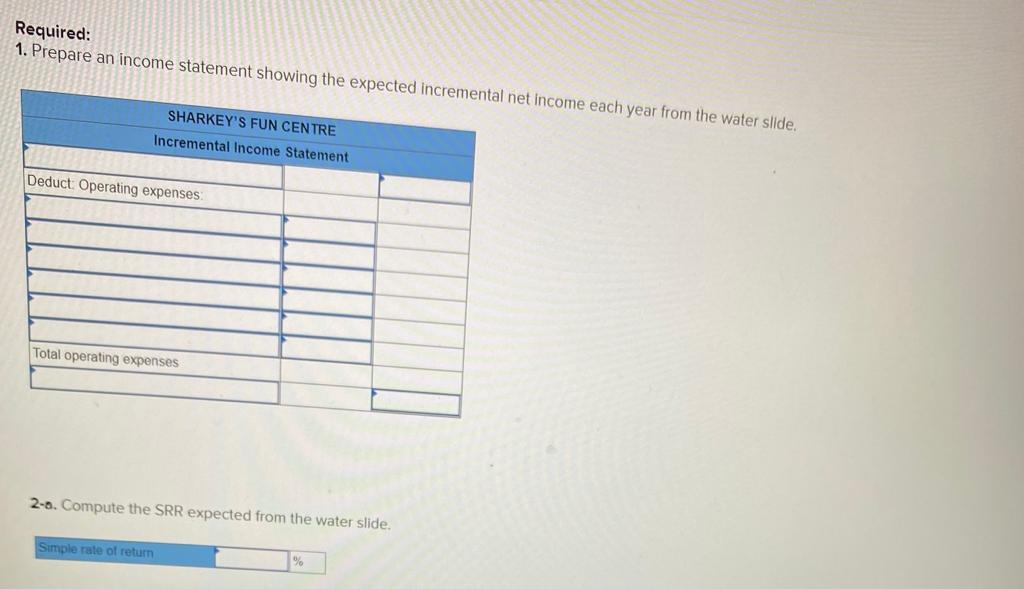
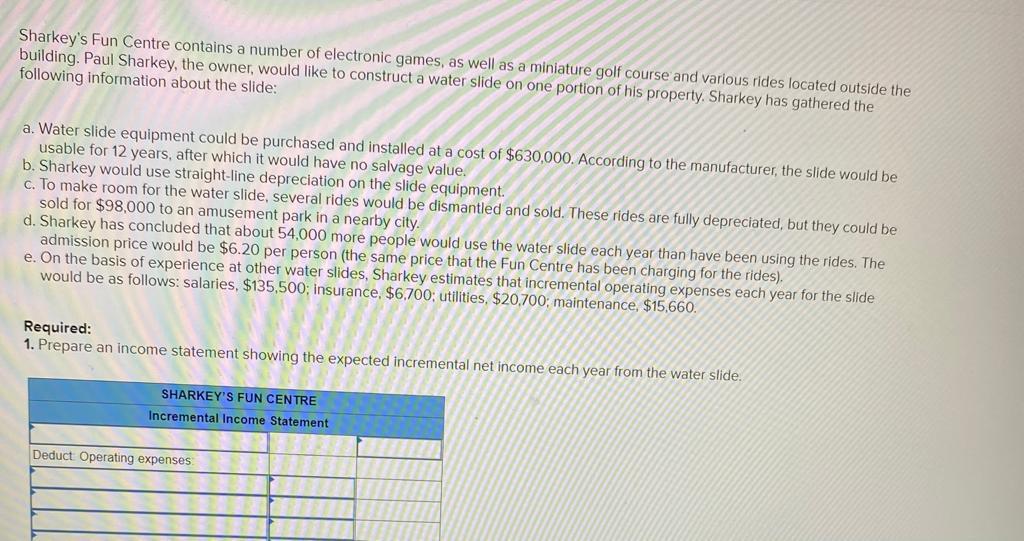
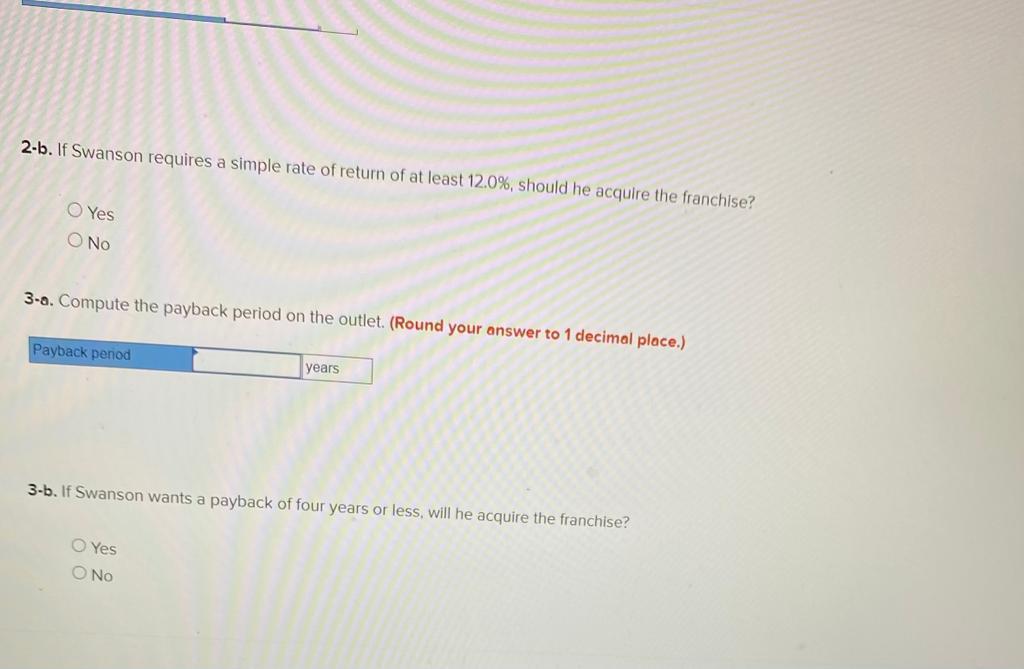
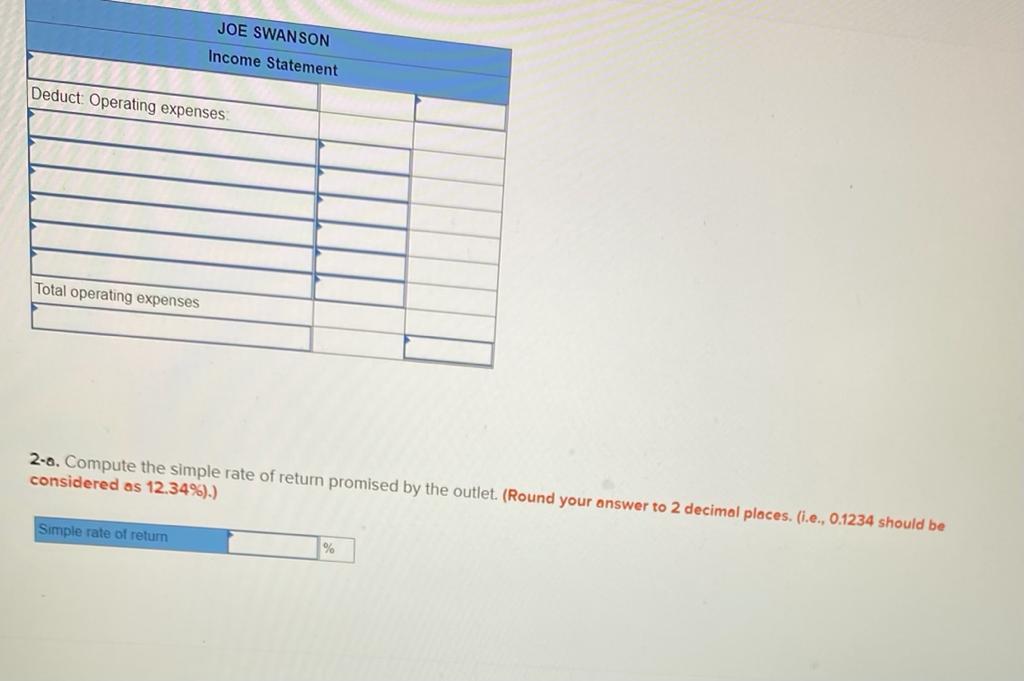
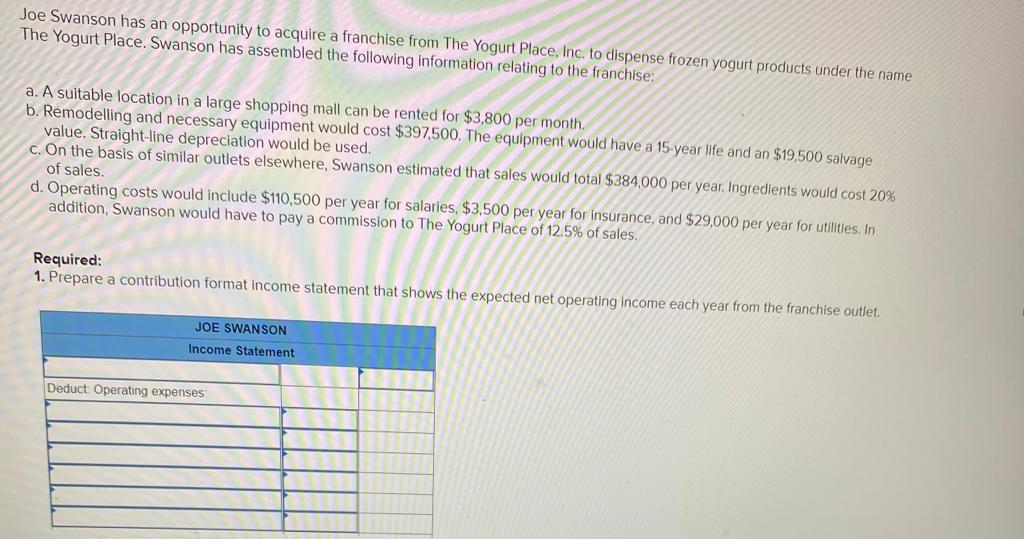
2. Using the incremental-cost approach, determine the net present value in favor of (or against) purchasing the new truck? (Negotive amounts should be indicated with a minus sign. Round discount factor(s) to 3 decimal place.) Net present value rei uperaung Income P 3,02 b. Sell the property. A realty company has offered to purchase the property by paying $216,000 immediately and $33,750 per year for the next 15 years. Control of the property would go to the realty company immediately. To sell the property, Martinas would need to pay the mortgage off, which could be done by making a lump-sum payment of $136,500. Click here to view Exhibit 10-1 and Exhibit 10-2 to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Required: Assume that Martinas requires a 12% rate of return. Compute net present value in favor of (or against) keeping the property using the total-cost approach. (Round discount factor(s) to 3 decimal places and other intermediate calculations to the nearest dollar amount.) Net present value Oxford Company has limited funds available for investment and must ration the funds among five competing projects. Selected information on the five projects follows: Project A B D E Investment Required $ 567,000 680,000 624,000 616,000 518,000 Net Present Value $ $ 123,000 133,200 112,600 110,600 (10, 100) Life of the Project (years) 1 12 12 2 1 3 6 The net present values above have been computed using a 10% discount rate. The company wants your assistance in determining which project to accept first, which to accept second, and so on. Required: 1. Compute the profitability index for each project. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Project Profitability Index B D E 2-b. On the basis of this computation, would the water slide be constructed if Sharkey requires an SRR of at least 14% on all investments? Yes ONo 3-a. Compute the payback period for the water slide. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Payback period years 3-b. If Sharkey requires a payback period of five years or less, should the water slide be constructed? Yes No Required: 1. Prepare an income statement showing the expected incremental net income each year from the water slide. SHARKEY'S FUN CENTRE Incremental Income Statement Deduct Operating expenses Total operating expenses 2-a. Compute the SRR expected from the water slide. Simple rate of return Sharkey's Fun Centre contains a number of electronic games, as well as a miniature golf course and various rides located outside the building. Paul Sharkey, the owner, would like to construct a water slide on one portion of his property. Sharkey has gathered the following information about the slide: a. Water slide equipment could be purchased and installed at a cost of $630,000. According to the manufacturer, the slide would be usable for 12 years, after which it would have no salvage value. b. Sharkey would use straight-line depreciation on the slide equipment. c. To make room for the water slide, several rides would be dismantled and sold. These rides are fully depreciated, but they could be sold for $98,000 to an amusement park in a nearby city. d. Sharkey has concluded that about 54,000 more people would use the water slide each year than have been using the rides. The admission price would be $6.20 per person (the same price that the Fun Centre has been charging for the rides). e. On the basis of experience at other water slides, Sharkey estimates that incremental operating expenses each year for the slide would be as follows: salaries, $135,500; insurance, $6,700; utilities, $20,700; maintenance, $15,660. Required: 1. Prepare an income statement showing the expected incremental net income each year from the water slide. SHARKEY'S FUN CENTRE Incremental Income Statement Deduct Operating expenses 2-b. If Swanson requires a simple rate of return of at least 12.0%, should he acquire the franchise? O Yes O No 3-a. Compute the payback period on the outlet. (Round your answer to 1 decimal place.) Payback period years 3-b. If Swanson wants a payback of four years or less, will he acquire the franchise? Yes ONo JOE SWANSON Income Statement Deduct Operating expenses Total operating expenses 2-8. Compute the simple rate of return promised by the outlet. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places, (i.e., 0.1234 should be considered as 12.34%).) Simple rate of return % Joe Swanson has an opportunity to acquire a franchise from The Yogurt Place, Inc. to dispense frozen yogurt products under the name The Yogurt Place. Swanson has assembled the following information relating to the franchise: a. A suitable location in a large shopping mall can be rented for $3,800 per month b. Remodelling and necessary equipment would cost $397,500. The equipment would have a 15-year life and an $19,500 salvage value. Straight-line depreciation would be used. c. On the basis of similar outlets elsewhere, Swanson estimated that sales would total $384.000 per year. Ingredients would cost 20% of sales. d. Operating costs would include $110,500 per year for salaries, $3,500 per year for insurance, and $29,000 per year for utilities. In addition, Swanson would have to pay a commission to The Yogurt Place of 12.5% of sales. Required: 1. Prepare a contribution format income statement that shows the expected net operating income each year from the franchise outlet. JOE SWANSON Income Statement Deduct Operating expenses
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


