Question: 2. Write a program to simulate the following scenario. You should use the queue.h header file defined in the lecture notes. There is a supermarket
2. Write a program to simulate the following scenario. You should use the queue.h
header file defined in the lecture notes.
There is a supermarket that has only 4 cashiers, numbered 0, 1, 2 and 3. Therefore, in general, customers form four queues, waiting to check out in front of each of these three cashiers. For simplicity, we assume that at most one customer comes to check out every minute. When a customer comes, he will first check which of these three queues is the shortest, and will then join the shortest queue. If a customer finds that there are two queues of the same length, then he will prefer cashier 0 to cashier 1, cashier 1 to cashier 2, and cashier 2 to cashier 3, because cashier 0 is the closest to the exit. A customer starts to check out as soon as the customer before him in the queue finishes checking out.
The input to the program is read from a file. The first line in the file specifies the information of the customer who comes in the first minute; the second line specifies the information of the customer who comes in the second minute, and so on. An empty line indicates that no customer comes in that minute. Each line contains two numbers. The first is an integer that indicates the number of minutes the customer needs to wait while being served at a cashier. The second is a floating point number that indicates the total price of the goods he buys. There are one or more spaces between these two numbers. For example, if the file contains only the following five lines:
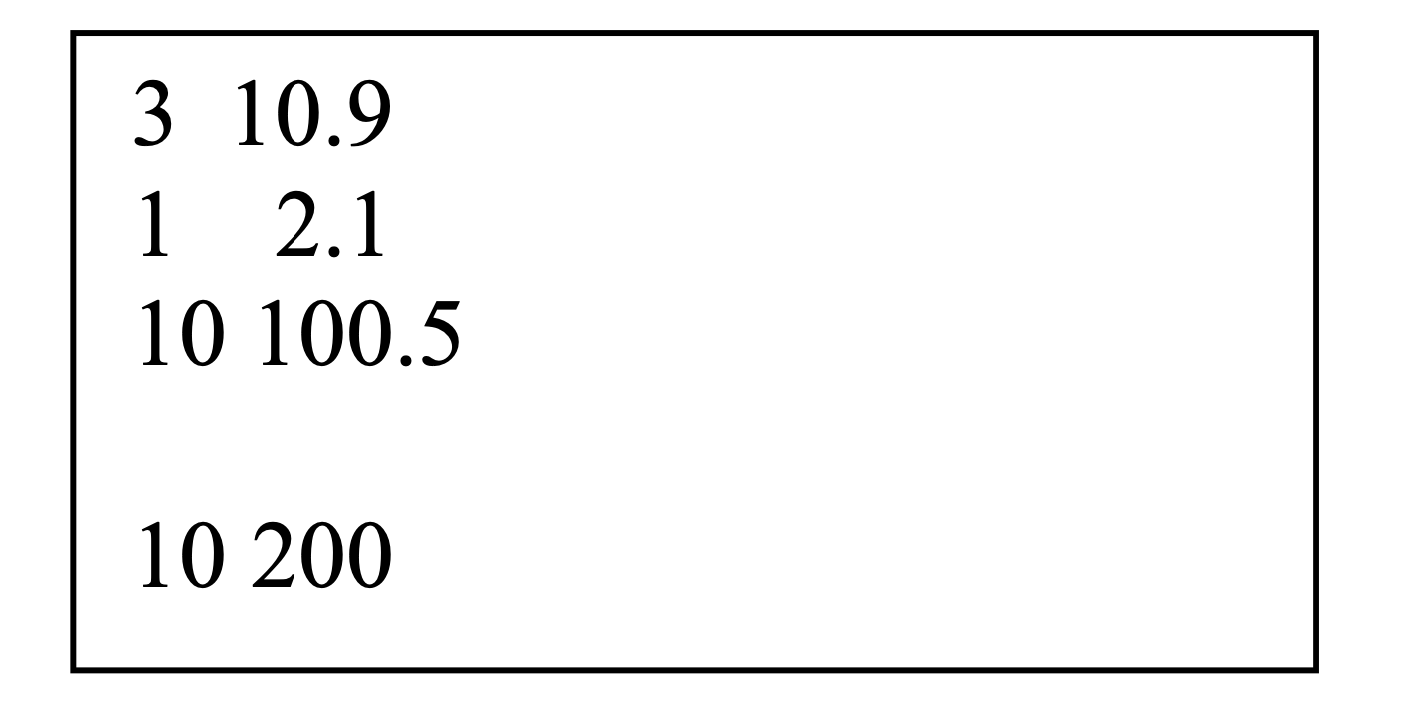
Then it means that there are totally 4 customers: the first comes in the first minute, the second in the second minute, etc., and no customer comes in the fourth minute. The first customer will need to spend 3 minutes checking out, and he will need to pay $10.9; the second customer will need to spend 1 minute checking out, and he will need to pay $2.1, and so on. No more customers will come after the fourth customer (who comes in the fifth minute) is served. You may also assume that there is no error in the input data, so no error checking is necessary.
Write a program (supermarket.c) that reads an input file (file name is supermarket.dat). The total number of lines in the input file is not known in advance. The program performs the simulation, and outputs the following information
1. The average time(over all four counters)a customer needs to wait after he joins a queue until he starts to check out.
2.The total amount of money each oft he cashiers receives.
3.The total number of customers each of the cashiers serves.
You should represent a customer as a structure defined as
struct customer { int checkoutTime;
float payment;
};
We also define a type customerT for customers, as follows:
typedef struct customer *customerT;
The values of the fields should be properly initialized when a Customer structure is created for a customer. The type of queue elements in the queue.h header file and the queue implementation file queue.c should therefore be modified from int to customerT.
A cashier is an object of the following class:
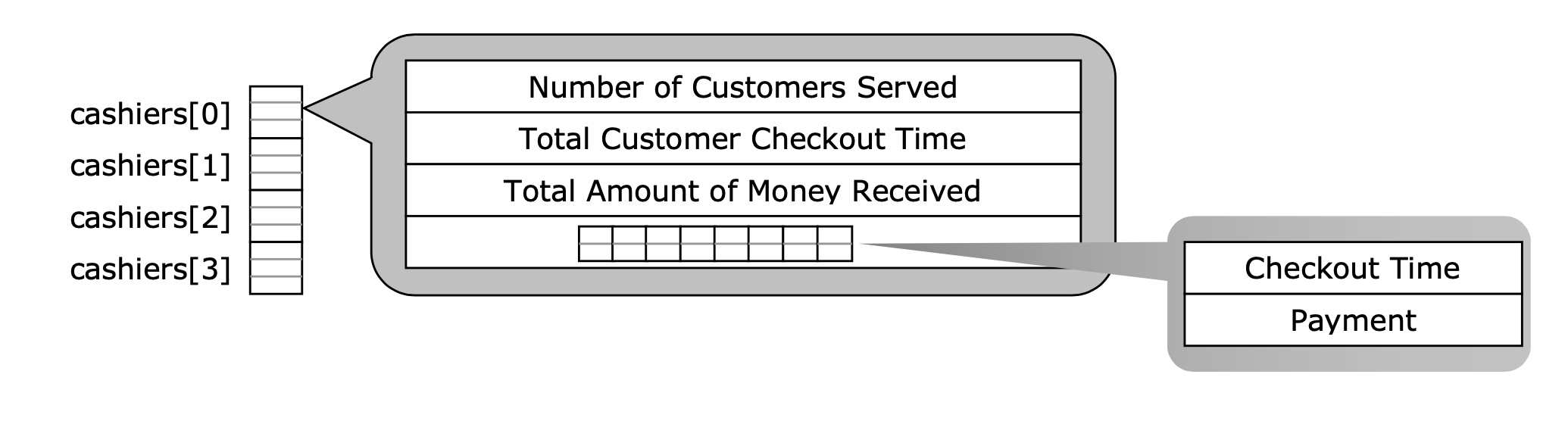
struct cashier { int numberOfCustomersServed; /* This should be initialized to 0 */ int totalCustomerWaitingTime; /* This should be initialized to 0 */ float totalAmountReceived; /* This should be initialized to 0 */
queueADT customerQ; /* This should be initialized to an empty queue */;
/* This is a Queue of customer structures*/
}
We also define a type cashierT for cashiers, as follows:
typedef struct cashier cashierT;
Finally, the three cashiers should be implemented as an array in main:
cashierT[4] cashiers;
The following diagram shows the picture as seen by you (who are supposed not to know the contents of queue.c).
/*
Queue.c
*/
#include
#include "queue.h"
#include
struct queueCDT{
queueElementT front;
queueElementT tail;
};
queueADT EmptyQueue(){
queueADT queue;
queue = (queueADT)malloc(sizeof(*queue));
queue->front = 0;
queue->tail = 0;
return queue;
}
void Enqueue(queueADT queue, queueElementT element){
if (queue->front == 0){
queue->front = element;
}
else {
queue->tail->next = element;
}
queue->tail = element;
}
queueElementT Dequeue(queueADT queue){
queueElementT result;
if (queue->front==0) {
printf("Queue is empty. "); exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
};
result = queue->front;
queue->front = queue->front->next;
return result;
}
int QueueLength(queueADT queue) {
int i = 0;
queueElementT tmp = queue->front;
while (tmp != 0){
i += 1;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
return i;
}
int QueueIsEmpty(queueADT queue) {
return (queue->front == 0);
}
/*
Queue.h
*/
#include "customer.h"
typedef struct queueCDT *queueADT;
typedef customerT queueElementT;
queueADT EmptyQueue(void);
void Enqueue(queueADT queue, queueElementT element);
queueElementT Dequeue(queueADT queue);
int QueueLength(queueADT queue);
int QueueIsEmpty(queueADT queue);
Your help would mean a lot to me, thanks.
3 10.9 12.1 10 100.5 10 200 cashiers[0] cashiers[1] cashiers[2] cashiers[3] Number of Customers Served Total Customer Checkout Time Total Amount of Money Received Checkout Time Payment 3 10.9 12.1 10 100.5 10 200 cashiers[0] cashiers[1] cashiers[2] cashiers[3] Number of Customers Served Total Customer Checkout Time Total Amount of Money Received Checkout Time Payment
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


