Question: 2.1Element Uniqueness problem asks that given a set of integers whether any two of them are equal. There is a simple way to reduce EU
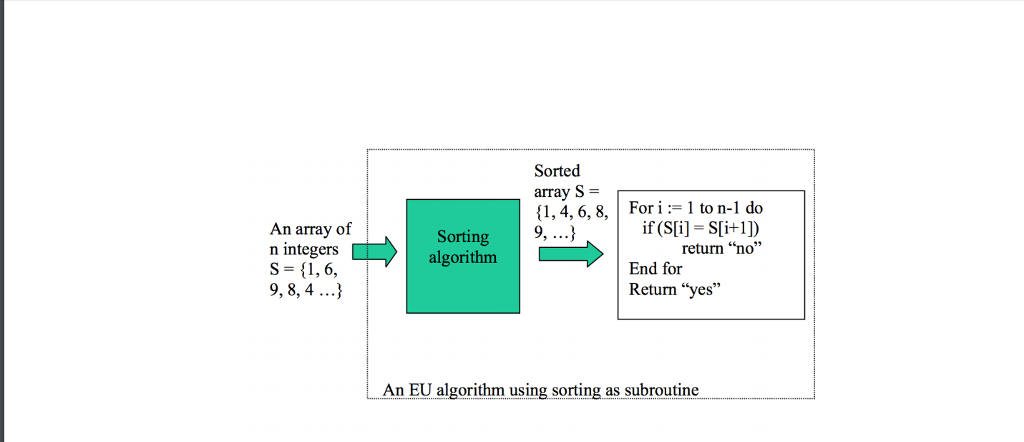
2.1Element Uniqueness problem asks that given a set of integers whether any two of them are equal. There is a simple way to reduce EU to sorting. As shown in the following figure, we just sort the list and then scan for adjacent duplicate. This reduction provides an O(nlogn) algorithm for EU problem. Can we use this reduction to prove (nlogn) is the lower bound for EU? Why?
2.2 Suppose we have proven that (nlogn) is the lower bound for EU. Now prove (nlogn) is also the lower bound for Closest Pair Problem (given a set of n points in the plane, determine the two points that are closet to each other).
An array of n integers S {1,6, 9,8, 4... Sorted array S 1, 4, 6, 8, For i 1 to n-1 do if (Sli] S[i+1D Sorting return "no" algorithm End for Return "yes" An EU algorithm using sorting as subroutine L
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


