Question: 2-2. Charge Conservation and Electric Current In an electrolyte solution of uniform composition the current density i and electrical potential are related as i= where
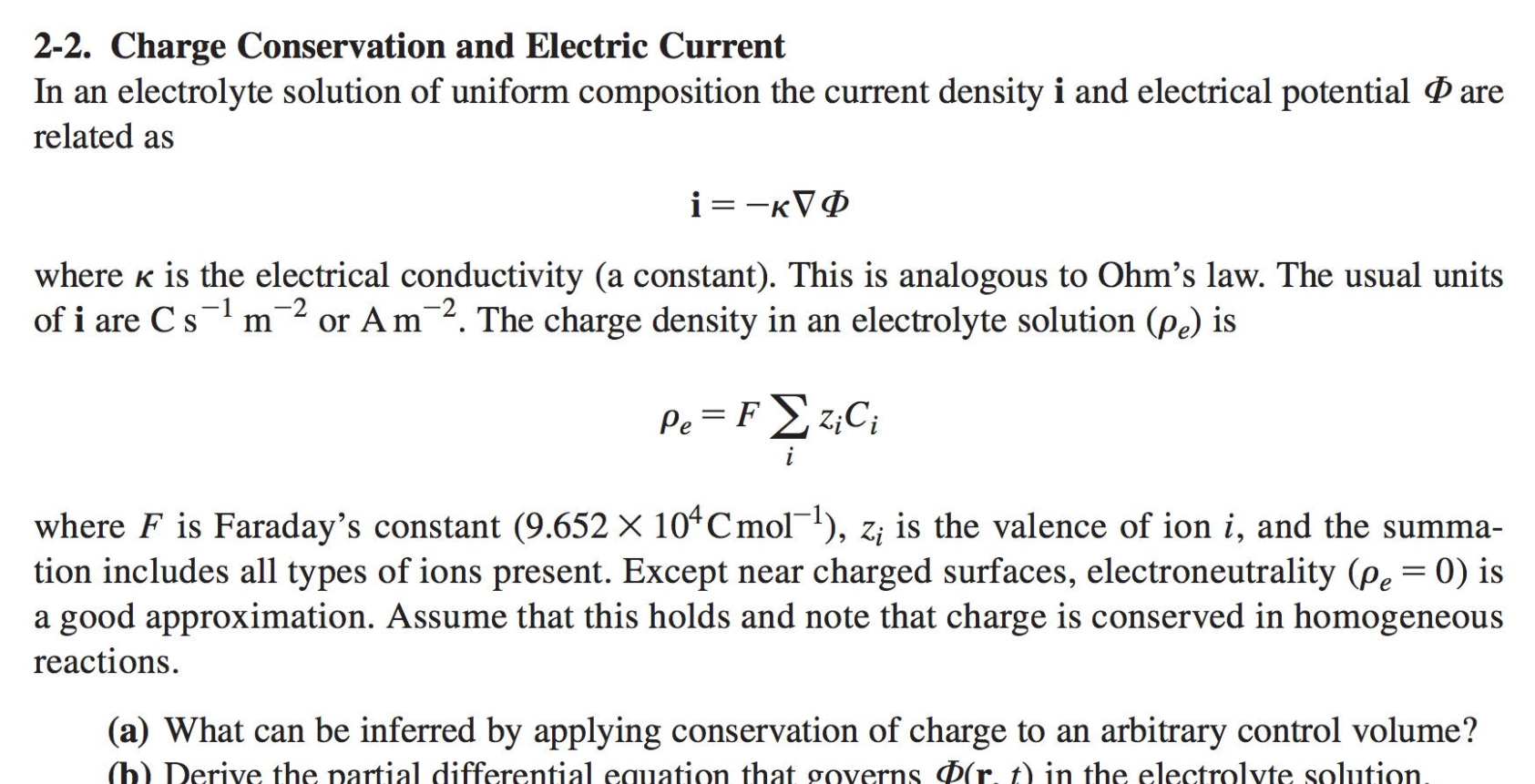
2-2. Charge Conservation and Electric Current In an electrolyte solution of uniform composition the current density i and electrical potential are related as i= where is the electrical conductivity (a constant). This is analogous to Ohm's law. The usual units of i are Cs1m2 or Am2. The charge density in an electrolyte solution (e) is e=FiziCi where F is Faraday's constant (9.652104Cmol1),zi is the valence of ion i, and the summation includes all types of ions present. Except near charged surfaces, electroneutrality (e=0) is a good approximation. Assume that this holds and note that charge is conserved in homogeneous reactions. (a) What can be inferred by applying conservation of charge to an arbitrary control volume? 2-2. Charge Conservation and Electric Current In an electrolyte solution of uniform composition the current density i and electrical potential are related as i= where is the electrical conductivity (a constant). This is analogous to Ohm's law. The usual units of i are Cs1m2 or Am2. The charge density in an electrolyte solution (e) is e=FiziCi where F is Faraday's constant (9.652104Cmol1),zi is the valence of ion i, and the summation includes all types of ions present. Except near charged surfaces, electroneutrality (e=0) is a good approximation. Assume that this holds and note that charge is conserved in homogeneous reactions. (a) What can be inferred by applying conservation of charge to an arbitrary control volume
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


