Question: 25 20 20 mV Time (msec) Transmembrane potential, mv -25 -50! 2 Outward current lonic current mA/cm2 Inward current Figure 5.8. Illustrative Example of the
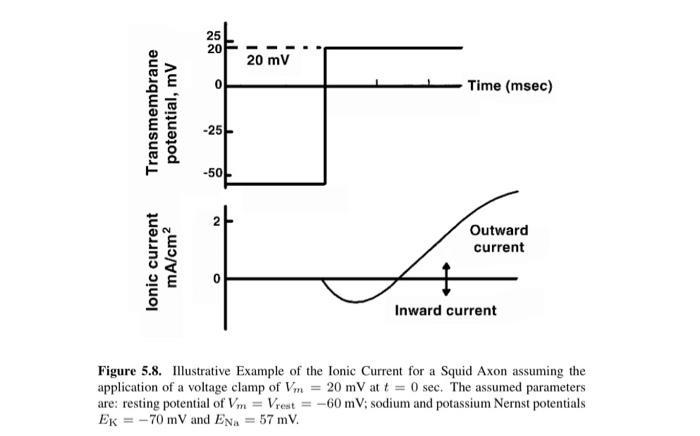

25 20 20 mV Time (msec) Transmembrane potential, mv -25 -50! 2 Outward current lonic current mA/cm2 Inward current Figure 5.8. Illustrative Example of the Ionic Current for a Squid Axon assuming the application of a voltage clamp of Vm = 20 mV at t = 0 sec. The assumed parameters are: resting potential of Vm = Vreat = -60 mV; sodium and potassium Nernst potentials EK = - 70 mV and Ena = 57 mV. ercises 4347 picture a voltage clamp that shifts from Vm at -60 mV to Vm = 15 mV. At first clamp is performed with the normal composition of (Na); = 15 mM and (Na), = 180 mM. The early current is carried by which ion, and crossing in which direction? The steady-state current is carried by which ion, and crossing in which direction? If the voltage clamp is repeated such that the sodium current is abolished, what extracellular medium changes are necessary? (Be specific and quantitative.) If the voltage clamp at Vm = 15 mV is conducted with 10% sodium seawater ([Na]. = 18.0 mM), how does the sodium current magnitude and time course compare with that under normal conditions? (Be specific and quantitative.) How does the potassium ion flow compare during the voltage clamp under normal, zero sodium flux, 10% sodium seawater conditions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


