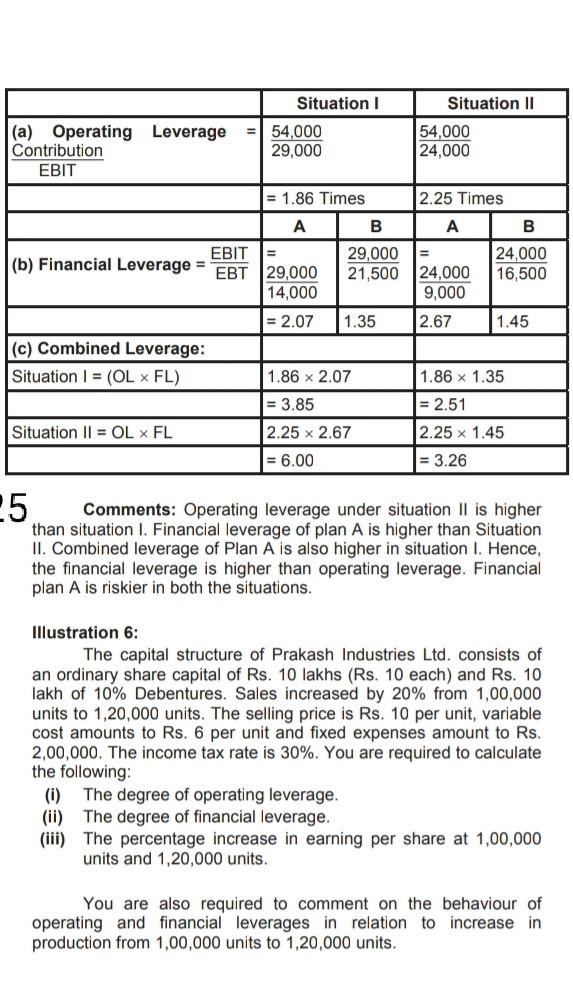
Question: 25 Situation ! Situation 11 (a) Operating Leverage Contribution EBIT 54,000 29,000 54,000 24,000 = 1.86 Times 2.25 Times A B A B 24,000 16,500
25
Situation ! Situation 11 (a) Operating Leverage Contribution EBIT 54,000 29,000 54,000 24,000 = 1.86 Times 2.25 Times A B A B 24,000 16,500 = 24,000 9,000 2.67 1.45 EBIT 29,000 (b) Financial Leverage = EBT 29,000 21,500 14,000 = 2.07 1.35 (c) Combined Leverage: Situation 1 = (OL ~ FL) 1.86 x 2.07 = 3.85 Situation 11 = OL ~ FL 2.25 x 2.67 = 6.00 1.86 x 1.35 1 = 2.51 2.25 x 1.45 = 3.26 25 Comments: Operating leverage under situation II is higher than situation I. Financial leverage of plan A is higher than Situation II. Combined leverage of Plan A is also higher in situation I. Hence, the financial leverage is higher than operating leverage. Financial plan A is riskier in both the situations. Illustration 6: The capital structure of Prakash Industries Ltd. consists of an ordinary share capital of Rs. 10 lakhs (Rs. 10 each) and Rs. 10 lakh of 10% Debentures. Sales increased by 20% from 1,00,000 units to 1,20,000 units. The selling price is Rs. 10 per unit, variable cost amounts to Rs. 6 per unit and fixed expenses amount to Rs. 2,00,000. The income tax rate is 30%. You are required to calculate the following: (0) The degree of operating leverage. (ii) The degree of financial leverage. (iii) The percentage increase in earning per share at 1,00,000 units and 1,20,000 units. You are also required to comment on the behaviour of operating and financial leverages in relation to increase in production from 1,00,000 units to 1,20,000 units
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


