Question: 29 2 Staffing with the M/M/s Queue McNeese is determining the staffing level for their credit union located within the university, and has recently hired
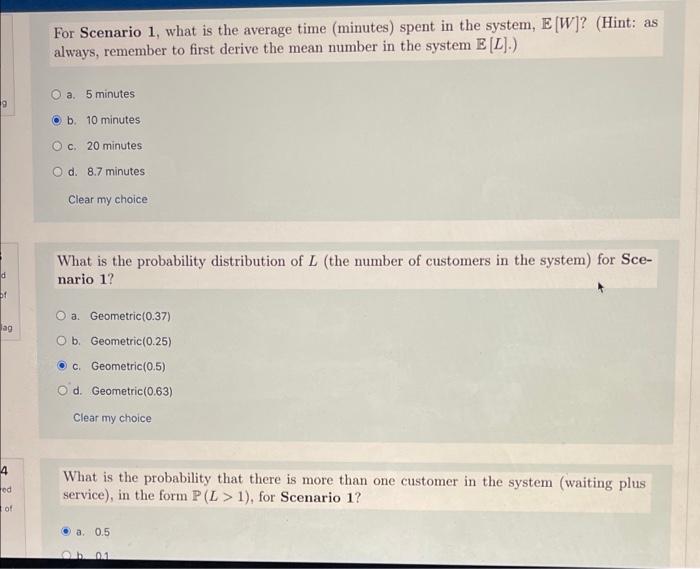
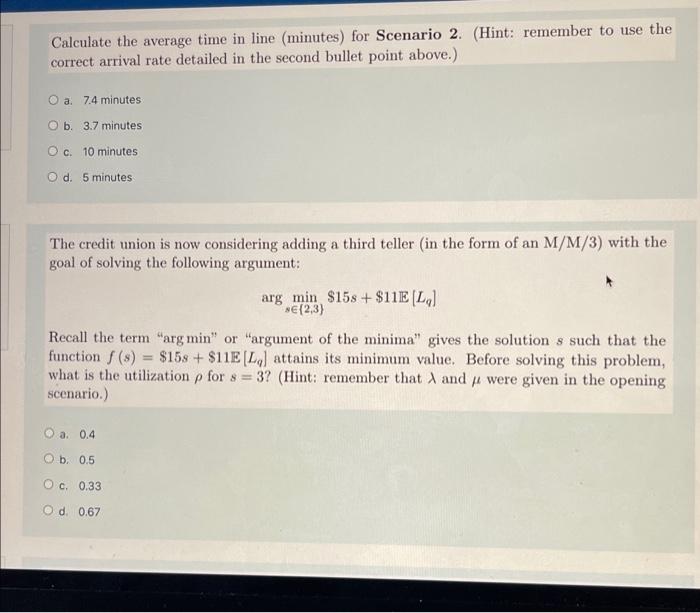
29 2 Staffing with the M/M/s Queue McNeese is determining the staffing level for their credit union located within the university, and has recently hired two tellers (servers). The beginning of the fall semester is their busiest time, with incoming freshmen and transfer students opening accounts. On average, it takes a teller E(T) = 10 minutes to successfully open an account (equivalent to a x = 6 per hour) and the average arrival rate has been = 6 per hour. As always, we use the exponential distribution as a reasonable approximation for both the interarrival and service times. After meeting with McNeese's upper- administration, the manager of the credit union is considering two possible scenarios for the service layout: Scenario 1: two M/M/1 (dedicated) queues that each serve 1/2 arrivals . Scenario 2: one M/M/2 (pooled) queue that serves all , arrivals A queuing analysis was conducted on each scenario, and the results are as follows: Scenario 1 Scenario 2 Utilization factor p=0.50 P=0.50 Mean number in the queue E(L) = 0.50 customers E[L] = 0.37 customers 1 For Scenario 1, what is the average time in line minutes) for a customer, E [W.]? (Hint: remember to use the correct arrival rate detailed in the first bullet point above.) O a. 8.7 minutes O b. 5 minutes OC 20 minutes . d. 10 minutes For Scenario 1, what is the average time (minutes) spent in the system, E [W]? (Hint: as always remember to first derive the mean number in the system E [L].) a. 5 minutes 9 b. 10 minutes c. 20 minutes O d. 8.7 minutes Clear my choice What is the probability distribution of L (the number of customers in the system) for Sce- nario 1? . f O a. Geometric(0.37) ag Ob. Geometric(0.25) O c Geometric(0.5) Od. Geometric(0.63) Clear my choice 4 od What is the probability that there is more than one customer in the system (waiting plus service), in the form P(L > 1), for Scenario 1? of a. 0.5 0.1 Calculate the average time in line (minutes) for Scenario 2. (Hint: remember to use the correct arrival rate detailed in the second bullet point above.) O a. 7.4 minutes O b. 3.7 minutes O c. 10 minutes Od 5 minutes The credit union is now considering adding a third teller (in the form of an M/M/3) with the goal of solving the following argument: arg min $158 +$11E (L) BE (2,3) Recall the term "arg min" or "argument of the minima" gives the solution s such that the function () = $158 + $11E (L) attains its minimum value. Before solving this problem, what is the utilization p for 8 = 3? (Hint: remember that and ji were given in the opening scenario.) a. 0.4 O b. 0.5 . .33 Od 0.67 Using your answer to the above question, what is the average number in the queue E[Lq) for S = 3? a. 2.03 customers Ob. 1.02 customers OC. 0.07 customers O d. 0.85 customers Using your answer to the above question, determine the total cost () = $158 + $11E (L) for 8 = 3 O a $54.35 O b. $67.33 O c. $45.77 O d. $56.22 What is the optimal number of tellers to staff, s*? (Hint: you know the total cost of 8 = 3 from the above problem; to calculate 8 = 2 you can simply use the corresponding EL,) for Scenario 2 presented in the table.) 3tallers Considering s*, what is the average number of customers in the system, E [L]? O a 1.07 customers b. 1.37 customers O c. 2.51 customers O d. 3.01 customers Clear my choice