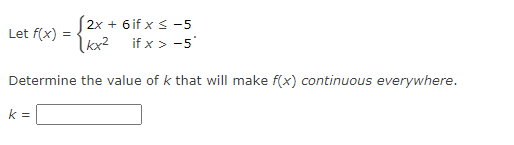
Question: 2x + 6if x s -5 Let f(X) = kx2 if x > -5 Determine the value of k that will make f(x) continuous everywhere.
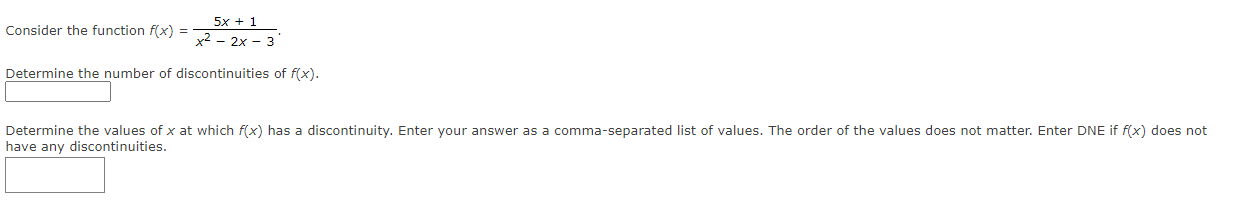
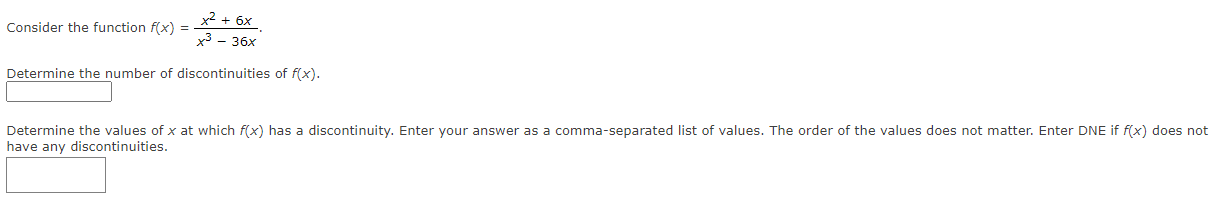
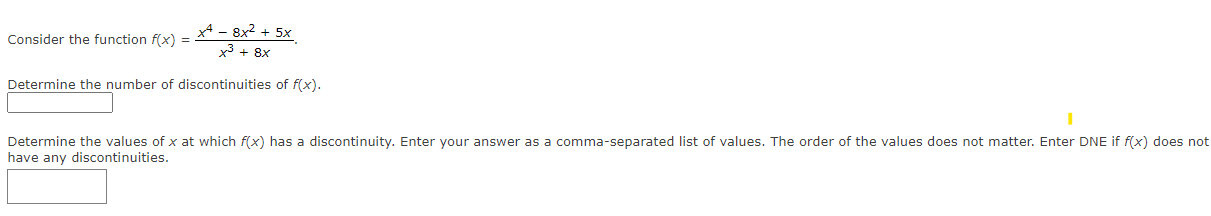


2x + 6if x s -5 Let f(X) = kx2 if x > -5 Determine the value of k that will make f(x) continuous everywhere. K :5x + 1 Consider the function f(x) = x2 - 2x - 3 Determine the number of discontinuities of f(x). Determine the values of x at which f(x) has a discontinuity. Enter your answer as a comma-separated list of values. The order of the values does not matter. Enter DNE if f(x) does not have any discontinuities.x2 + 6x Consider the function flx) = . x% = 36x Determine the number of discontinuities of f{x). Determine the values of x at which f{x) has a discontinuity. Enter your answer as a comma-separated list of values. The order of the values does not matter. Enter DNE if f{x) does not have any discontinuities. x* ax? + 5x 8 Consider the function fix) = Determine the number of discontinuities of f{x). Determine the values of x at which f{x) has a discontinuity. Enter your answer as a comma-separated list of values. The order of the values does not matter. Enter DNE if fix) does not have any discontinuities. Determine whether each statement is true or false. You have one submission for each statement. (a) All rational functions are continuous on their domain. OTrue OFalse (b) The function f(x) = *- 23 is continuous at x = 5. x - 5 OTrue OFalse (c) If f(x) is defined at x = a, then f(x) is also continuous at x = a. OTrue OFalse (d) If f(x) is continuous at x = a, then x = a is in the domain of f(x). OTrue OFalse (e) If f(x) and g(x) are continuous at x = a, then f(x)g(x) is also continuous at x = a. OTrue OFalse (f) If f(x) and g(x) are continuous at x = a, then f(x ) is also continuous at x = a. g(x) OTrue OFalseDetermine whether each statement is true or false. You have one submission for each statement. (a) For every function f(x), if lim f(x) does not exist, then lim f(x) does not exist. x- a OTrue OFalse (b) For every function f(x), if lim f(x) exists, then lim f(x) exists. x- 3 OTrue OFalse (c) For every function f(x), if lim f(x) exists, then lim f(x) also exists. x - a OTrue OFalse (d) For every function f(x), if lim f(x) and lim #(x) both exist, then lim f(x) also exists. x- a x- 2 x- a OTrue OFalse (e) For every function f(x), if lim f(x) does not exist, then lim f(x) does not exist. x- a OTrue OFalse (f) For every function f(x), if lim f(x) does not exist, then lim f(x) does not exist. x- a x- 3 OTrue OFalse
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


